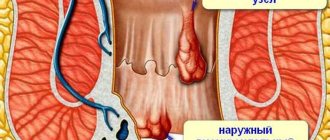
Among all the problems that expectant mothers face, one of the most unpleasant is external hemorrhoids. This is a proctological disease in which the so-called hemorrhoidal vessels, localized under the skin in the anus, become inflamed and dilated. They cause noticeable discomfort during defecation and can itch and bleed.
Treatment of hemorrhoids during pregnancy cannot be delayed, because the disease tends to progress. Advanced hemorrhoids can lead to serious complications, including thrombosis and hemorrhoidal anemia, which develops against the background of bleeding from the anus.
The danger of hemorrhoids during pregnancy
The mechanism of development of hemorrhoids with bleeding during pregnancy is associated with physiological changes occurring in the female body. The development of the disease occurs in the third trimester of pregnancy after 26 weeks.
In recent weeks, the uterus increases in size, putting pressure on the pelvic organs and hemorrhoidal plexuses. Due to increased pressure in the pelvis, constipation begins at 37-38 weeks, and hemorrhoids gradually develop.
The course of the disease is influenced by the age of the pregnant woman and the number of births. If a young woman carries a pregnancy, this happens for the first time, the risk of developing hemorrhoids is minimal - cracks do not form. A woman giving birth over 30-33 years of age is at greater risk of developing hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoids at 38 weeks of pregnancy cause bleeding and complicate the course of the upcoming birth.
The danger of hemorrhoids during pregnancy:
- The disease does not affect the course of pregnancy or fetal development. Labor does not depend on the condition of hemorrhoids. If hemorrhoids bleed during pregnancy, the risk of complications increases.
- A progressive pathological condition is accompanied by severe pain and burning in the perineal area.
- Against the background of increasing pain, the woman develops difficulties when visiting the toilet.
- The emerging complaints negatively affect the condition of the pregnant woman - fatigue and irritability increase. This state of health at 35-36 weeks negatively affects the development of the fetus, including developmental delay due to hypoxia.
- Against the background of constant bleeding from hemorrhoids, the woman develops iron deficiency anemia. It poses a threat to life and health due to increasing hypoxia of tissues of the pregnant woman and the fetus. If the node comes out and does not bleed too intensely, it is not noticed immediately, leading to the development of chronic anemia.
- Due to the addition of a secondary bacterial infection at week 39, the development of proctitis and pararectal fistulas is possible.
- The inflammatory process in hemorrhoidal veins leads to the formation of blood clots. The detachment of a blood clot, its release into the vascular bed, poses a threat to the life of a pregnant woman. Thrombosis of the hemorrhoid during pregnancy requires immediate medical intervention.
- Failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene for hemorrhoids may result in infection entering the urinary system.
- Attempting contractions during childbirth provoke the development of massive bleeding from the affected hemorrhoidal veins.
Consequences of bleeding
The danger of hemorrhoids lies in its consequences for the health and development of the fetus. At the initial stage, a woman may notice small blood stains on a napkin or underwear. As a rule, discharge appears after bowel movements. As the disease progresses, the internal cones fall out and do not refill.
Possible complications of bleeding:
- Blood clot formation. The release of blood clots into the blood vessels threatens the life of a pregnant woman.
- Development of anemia. Even minor discharge leads to a decrease in iron in the body. With severe blood loss, the fetus develops oxygen starvation (hypoxia), which has a negative impact on development and growth.
- Decreased immunity. Against the background of regular bleeding, the body's defense reactions decrease.
- Attachment of a bacterial infection. Pathogenic microflora that is present in feces can lead to the development of proctitis and pararectal fistulas. The inflammatory process in the intestines is dangerous due to the penetration of infection into the uterus.
If the nodes constantly bleed during pregnancy, after childbirth the situation only gets worse. Internal hemorrhoids can come out and become inflamed, so the disease should be treated when the first symptoms are detected (itching, burning, weeping in the perineum).
Hemorrhoids bleed during pregnancy
Hemorrhoids during pregnancy 39-40 weeks provoke severe bleeding during childbirth. It's difficult to stop. A sign of bleeding development is acute pain in the anus, detection of fresh blood on linen or a napkin.
If a pregnant woman shows signs of bleeding from a hemorrhoid, a napkin with wrapped ice cubes is applied to the damaged area. Contact a proctologist immediately. The doctor will decide how to treat bleeding from the hemorrhoid.
If signs of bleeding are detected at 30–31 weeks, you should not use ointments and suppositories with heparin (Hepatrombin). The drugs prevent blood clots and lead to increased bleeding.
Principles of treatment for hemorrhoids in pregnant women
When treating hemorrhoids during pregnancy from 35 weeks and above, follow the rules:
- Drink more fluids throughout the day. When there is a lack of fluid in the body, changes in metabolism occur and constipation develops. The condition of hemorrhoids worsens.
- As prescribed by the attending physician, vasoconstrictor and anti-inflammatory drugs are taken at 34–38 weeks. The doctor tries to choose drugs that do not penetrate the hematoplacental barrier and do not harm the fetus. Strengthen the vascular wall, eliminate pain and bleeding.
- The drugs are prescribed in local forms - suppositories, gels. Prescribed by the attending physician. Do not treat the disease yourself, using the advice of friends or materials from the Internet.
- The diet of a pregnant woman is adjusted. First courses and plant foods are included.
- Eat small, frequent meals throughout the day. Chew pieces of food thoroughly.
- To prevent constipation, eat prunes and dried apricots. Mild laxatives may be taken as prescribed by a doctor. They are taken with caution so as not to provoke the development of uterine hypertonicity and the threat of premature termination of pregnancy. At 40 weeks, after childbirth, the doctor prescribes Duphalac to soften stools and eliminate constipation.
Rectal suppositories for hemorrhoids are placed during the emptying of the intestines at night - before going to bed. Used for prolapse of nodes and inflammation. If a bleeding node is detected, hemostatic agents are prescribed.
How to recognize the disease: common symptoms
In 60% of pregnant women, hemorrhoids occur in external form. Lumps can be felt under the skin around the anus. When defecating, a woman feels a burning sensation, itching, and moderate pain.
During pregnancy, hemorrhoids bleed with varying intensity:
- scanty spotting discharge - observed on linen, toilet paper with external appearance of nodes, in the initial stage of internal inflammation, provoked by poor diet, carrying heavy bags;
- abundant stool on the surface or flowing out in a stream without defecation—more often observed in acute thrombosis of the node, internal hemorrhoids, or advanced chronic process.
Blood clots on the surface of the stool indicate internal bleeding and delayed excretion, difficult intestinal patency. Against this background there are:
- constant pain in the anus radiating to the tailbone;
- weeping anal skin with redness and small boils;
- unpleasant smell from laundry.
Usually the color of blood is scarlet or dark cherry.
The appearance of anemia in a woman complements the symptoms of hemorrhoids:
- complaints of palpitations, shortness of breath, weakness, dizziness;
- tendency to low blood pressure;
- pale skin;
- hair loss
The initial manifestations of the early stage occur only after defecation. They are not permanent and go away quickly with proper behavior and treatment by the expectant mother.
In those women who refuse to promptly consult a doctor and treat the disease, hemorrhoidal bleeding becomes chronic and permanent or leads to complications.
What drugs are used
Reliable and safe topical medications are used to treat hemorrhoids in pregnant women.
Relief
The suppositories and ointment are based on shark liver oil. The drugs are reliable, without side effects that pose a threat to the fetus or mother. Shark liver oil is a natural component that stimulates tissue regeneration processes. Other components included in the suppositories have an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect.
Candles with sea buckthorn
Sea buckthorn candles are made from natural products. The plant is characterized by anti-inflammatory and wound-healing properties. Sea buckthorn oil does not harm the fetus and is harmless to a pregnant woman.
Heparin ointment
The drug is used when the patient shows no signs of bleeding. Heparin ointment is used to prevent thrombosis of hemorrhoidal veins, relieve pain, and inflammation.
List of approved drugs
Drug therapy includes anti-inflammatory and hemostatic agents. Since external nodes bleed more often, prescriptions necessarily include ointment preparations and suppositories. Cooled vasoconstrictor solutions are used locally.
Taking pills is regulated by the need to stop bleeding from internal nodes. Products that are as safe as possible for the fetus are selected.
In complex therapy:
- Troxevasin, Proctosan, Methyluracil, and heparin ointments are recommended (to prevent thrombosis);
- Rectal suppositories include Proctosan, Relief, Nigepan.
Ointments are prescribed in courses of 7–10 days at night. They are spread on a sterile napkin and applied to the inflamed site.
Rectal suppositories are inserted into the anus and pushed into the depths with a finger. It is advisable to carry out the procedure after each bowel movement and at night after washing with a herbal decoction. Lie on your side for 30–40 minutes until the drug is absorbed.
Treatment using folk remedies
Traditional recipes for the treatment of hemorrhoids in pregnant women are used in combination with traditional treatment, with the permission of the attending physician. Home remedies are relatively safe and help speed up recovery.
Well-known traditional medicines are decoctions of chamomile flowers, oak bark, and calendula flowers. They are characterized by a pronounced antimicrobial and astringent effect. Thanks to baths and lotions, wounds and cracks in the perineal area heal quickly. If there is discharge with blood or suppuration, it is prohibited to use baths.
Home treatment for hemorrhoids in pregnant women is used using honey. The product has a pronounced anti-inflammatory and wound healing effect. Honey for the treatment of hemorrhoids is used in the form of lotions and homemade candles. You can use honey internally and make microenemas. Inflammation goes down, thrombosis of the hemorrhoid is prevented. The negative side of honey is its increased degree of allergenicity. Pregnant women are advised to use the product with caution.
Traditional medicine has long used raw potatoes to treat hemorrhoids. Grate the peeled and washed potatoes and apply to the external hemorrhoids. Use a compress to quickly relieve pain and swelling.
Prevention of hemorrhoids in pregnant women
To prevent the development of hemorrhoids and prevent bleeding, establish proper nutrition. Avoid salty, spicy foods, marinades, and smoked foods. Products provoke an increase in pressure in the abdominal cavity. Increase the amount of plant foods in your diet.
To prevent the development of hemorrhoids, give daily moderate physical activity. Walking in the fresh air will benefit the pregnant woman and the fetus. It is useful to do simple gymnastic exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles.
To reduce pressure in the abdominal cavity, doctors recommend daily stay in the knee-elbow position. Improves blood flow in the pelvis, prevents the development of hemorrhoids.