Fetal development
The baby continues to develop rapidly and gain weight. This week his height can reach 45 cm, and his body weight can reach 2 kg. If a woman is expecting twins, then each child will weigh less than normal.
At this time, the baby acquires its own unique facial features. The original fluff gradually disappears, and along with it the original lubricant disappears. The hair on the head continues to grow, and the more active this process is, the thicker the baby’s hair will be at birth. The child’s skin becomes pinkish, wrinkles are smoothed out, and subcutaneous fat is gained. Its content is about 8% of the total body weight. Every day the baby becomes cuter and cuter.
In the womb, a baby can suck its thumb for a long time. In this way, it improves the sucking reflex and prepares the facial muscles for the upcoming feeding process. While performing sucking movements, the baby swallows amniotic fluid. They, passing through the body, prepare its digestive organs for the upcoming work. At the same time, kidney function improves. Every day they return about 500 ml of clear urine to the amniotic fluid.
At 34 weeks, the baby assumes the body position in which he will be born. Normally, he should lie head down and buttocks up. Sometimes the child lies down radically differently. At 34 weeks, you can still try to change the baby's position. To do this, doctors perform special manipulations, the need for which is decided on an individual basis.
The bones of the child's skull remain soft and mobile. This is possible due to the fontanelles, which will gradually close when the baby is born. Nature itself provides such a structure of the newborn’s skull in order to ensure the easiest passage through the birth canal.
Other bones gradually harden, cartilage tissue thickens, and nails continue to grow. All this requires a lot of calcium, which the fetus will take from the mother's body. Therefore, a woman needs to take care of a sufficient intake of all vitamins and microelements from food.
In the third trimester of pregnancy, the baby's heart and blood vessels develop very actively. His heart rate is currently twice that of an adult. If a mother knows what position her baby is in, she can use a stethoscope to listen to his heart rhythm on her own.
The fetal nervous system continues to improve. At this time, periods of sleep and wakefulness are established, which largely depends on the mother.
Inside the abdomen, the baby is able to distinguish sounds and respond to light. In bright light, he closes his eyes.
At 34 weeks, the baby already has a functioning endocrine system that produces growth hormone. The work of the thyroid and pancreas, and the adrenal cortex is also honed.
Interestingly, the baby can already distinguish taste, since the papillae on his tongue are well formed by the 34th week.
Thanks to the developed hearing system, the baby is already able to respond to sounds. Therefore, a woman needs to listen to pleasant music, sing lullabies to her child and read fairy tales aloud. It’s good to just talk to your baby in an even and calm voice.
Medical observation
In some cases, at 35 weeks of pregnancy, the gynecologist may prescribe an ultrasound. The study will allow you to determine the weight and position of the child, as well as identify possible complications, for example, anomalies of the placenta, oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios, entanglement of the fetus with the umbilical cord, etc. The information obtained will help the specialist develop tactics for future childbirth.
This week the doctor will definitely measure your blood pressure and determine your weight and size. In addition, as usual, you will need to do a general urine and blood test.
Ultrasound
If the pregnancy is progressing normally, then the woman needs to undergo 3 scheduled ultrasound examinations. The third ultrasound is performed at 32-34 weeks, so now is the time to head to your doctor's office and get a referral.
Sometimes an ultrasound is performed at 34 weeks of pregnancy for certain indications. For example, it is necessary to ensure that the fetus does not suffer from hypoxia, or its exact position in the uterus needs to be determined.
In addition to the fact that ultrasound provides information about the condition of the child, this study allows you to assess the degree of maturity of the placenta, the volume and quality of water, the readiness of the cervix for the upcoming birth, and eliminate the risk of the child being entangled in the umbilical cord. It is dangerous if the cervix shortens to 25 mm or less during this period. In this case, the risk of premature birth increases. If a woman simultaneously experiences increased uterine tone, she requires hospitalization. Therefore, you should not refuse to undergo an ultrasound examination. The doctor interprets the ultrasound results. You should not interpret the data obtained on your own.
In addition to the fact that at 34 weeks of pregnancy a woman undergoes an ultrasound, she will also need to donate blood and urine for a general analysis.
Sources
- Beatty C., Fothergill S. The Long Shadow of Job Loss: Britain's Older Industrial Towns in the 21st Century. // Front Sociol - 2020 - Vol5 - NNULL - p.54; PMID:33869461
- Hamm RF., Levine LD., Nelson MN., Beidas R. Implementation of a calculator to predict cesarean delivery during labor induction: a qualitative evaluation of the clinician perspective. // Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM - 2022 - Vol3 - N3 - p.100321; PMID:33493705
- LeFevre N.M., Krumm E., Cobb W.J. Labor Dystocia in NULLIPAROUS WOMEN. // Am Fam Physician - 2022 - Vol103 - N2 - p.90-96; PMID:33448772
- Unertl KM., Walsh CG., Clayton EW. Combatting human trafficking in the United States: how can medical informatics help? // J Am Med Inform Assoc - 2022 - Vol28 - N2 - p.384-388; PMID:33120418
- Kuzma EK., Pardee M., Morgan A. Implementing Patient-Centered Trauma-Informed Care for the Perinatal Nurse. // J Perinat Neonatal Nurs - 2022 - Vol34 - N4 - p.E23-E31; PMID:33079811
- Nadjafizadeh M., Caron FM. . // Gynecol Obstet Fertil Senol - 2020 - Vol48 - N12 - p.944-952; PMID:33011378
- Punnett L., Nobrega S., Zhang Y., Rice S., Gore R., Kurowski A. Safety and Health through Integrated, Facilitated Teams (SHIFT): stepped-wedge protocol for prospective, mixed-methods evaluation of the Healthy Workplace Participatory Program. // BMC Public Health - 2020 - Vol20 - N1 - p.1463; PMID:32993607
- Szu LT., Chou PY., Lin PH., Chen C., Lin WL., Chen KH. Comparison of maternal and fetal outcomes between delayed and immediate pushing in the second stage of vaginal delivery: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. // Arch Gynecol Obstet - 2022 - Vol303 - N2 - p.481-499; PMID:32990782
- Türkmen H., Yalniz Dilcen H., Akin B. The Effect of Labor Comfort on Traumatic Childbirth Perception, Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder, and Breastfeeding. // Breastfeed Med - 2022 - Vol15 - N12 - p.779-788; PMID:32896164
How does the woman feel?
Since the baby already weighs about 2 kg, he is becoming increasingly cramped in his mother’s belly. This leads to the fact that the woman feels every movement of the baby very well. At the same time, the movements are no longer as frequent as they were before, but their strength increases.
The child shows increased activity at those moments when the mother lies down to rest. Normally, the number of movements per day should be about 10. When a woman is at rest, the child can move up to 4 times per hour.
It is imperative to monitor the nature of the movements. After all, they can be the first to suspect possible trouble, for example, provided that there are no movements for a long time. Sometimes a child begins to move more actively if something frightens him, for example, loud noises or bright lights. Therefore, whenever possible, such situations should be avoided. After all, sudden movements of the fetus will cause it to roll over and take an incorrect position in the uterus.
As for the immediate feelings of the woman herself, they can be ambivalent. On the one hand, the expectant mother feels clumsy, because her belly is already quite large, but on the other hand, she is enjoying the last weeks of pregnancy.
If we talk about possible discomfort, women at this stage often complain of heartburn, constipation, and shortness of breath. The thing is that the stomach puts pressure on the stomach, the intestines, and the diaphragm. This is where all the above inconveniences arise. However, there is only a little patience left, very soon the stomach will drop and the unpleasant symptoms will pass.
Many women at 34 weeks of pregnancy have dreams related to childbirth. To level out your emotional background as much as possible, you need to attend various courses for pregnant women and read as much literature as possible about the natural process of childbirth. At the same time, you can start preparing your home for the arrival of a small new resident. Prenatal care is a very pleasant activity that you can devote almost all your free time to.
Causes of "acute abdomen"
When carrying a child, the growing uterus displaces neighboring organs, which provokes a deterioration in their functioning and causes the appearance of atypical symptoms of many pathologies. In addition, the symptoms of diseases characterized by an “acute abdomen” are similar to physiological pain during pregnancy.
A woman's smooth muscle tone is reduced, her hormonal levels are changed, the vessels of the uterus and pelvis are dilated, and there is a decrease in the body's reactivity. These factors can lead to diagnostic errors and delays in providing surgical care, which is potentially life-threatening for both the woman and the child.
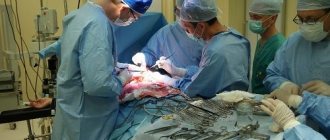
If symptoms of an “acute abdomen” appear, then urgent surgery is needed; a delay increases the risk of complications. Acute appendicitis is most often diagnosed, followed by cholecystitis, followed by intestinal obstruction and pancreatitis.
In rare cases, rupture of the liver and spleen, perforation of the ulcer, and rupture of the splenic artery may occur. “Acute abdomen” is caused by torsion and rupture of cysts and tumors, ovarian cancer, and uterine fibroids. To make a correct diagnosis, the doctor must carefully collect anamnesis and know exactly the duration of pregnancy.
A patient with an “acute abdomen” should be examined not only by a surgeon, but also by an obstetrician-gynecologist so that obstetric or gynecological pathology can be excluded. In this case, the number of palpating the abdomen should be minimal so as not to cause uterine tone.
The 2nd trimester of pregnancy is the safest for the operation, so if the intervention is not an emergency, it can be scheduled for the postpartum period
The main symptom of an “acute abdomen” during pregnancy is pain. Based on its epicenter, one can guess in which organ the pathological process is developing. Generalized pain is mainly caused by inflammation of the abdominal cavity due to bleeding, exudate, and the presence of intestinal contents.
Pain that occurs in the lower abdomen in the center can be provoked by an increase in the tone of the uterus. The pain on the lower side is most often due to rupture or torsion of an ovarian tumor. Pain in the mid-abdomen is likely caused by an intestinal disorder.
If there is pain in the upper abdominal cavity, the doctor will suspect a malfunction of the liver, spleen, stomach, small intestine, gallbladder, or pancreas. Abdominal pain, vomiting and nausea are often triggered during pregnancy by diseases of the upper gastrointestinal tract or toxicosis.
In acute surgical conditions, pregnant women develop diarrhea. The need for intervention is indicated by irritation of the peritoneum, as well as loss of consciousness. These symptoms appear when the integrity of organs is violated and bleeding occurs. Hyperthermia up to febrile levels indicates the presence of infection in the body.
Appendicitis
Most often, pregnant women undergo surgery for inflammation of the appendix. As a rule, women go to the clinic only 12 hours after the first symptoms of inflammation appear, which is explained by the following reasons:
Symptoms of appendicitis in pregnant women
- loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting are perceived as natural processes that occur during pregnancy;
- the vermiform appendix gradually rises upward as the uterus enlarges, so the pain has an uncharacteristic localization;
- at the early stage of the disease, the temperature and pulse are normal, in a quarter of patients the temperature does not rise at all;
- Blood tests do not accurately determine appendicitis, since an increased level of white blood cells is normal during pregnancy.
Due to delays in treatment and difficulties in making a diagnosis, treatment is carried out late, so pregnant patients are 2-3 times more likely to develop destructive forms of appendicitis, when purulent secretion already leaks from the lumen.
A woman after the 24th week of pregnancy may not experience typical symptoms of the disease
The pain is felt in the right side below or in the center, but it is attributed to a sprain or urinary tract disease. The longer the pregnancy, the less muscle tension and signs of peritoneal irritation appear (in the 3rd trimester, the symptom is present in only a third of patients).
The cecum rises high, so the greater omentum is not able to limit infection, therefore, the risk of developing peritonitis increases. Almost all patients have a pulse of more than 100 beats per minute, despite the fact that the temperature rises in only half.
After the operation, the patient is prescribed bed rest, antispasmodic drugs, vitamin E. If appendicitis is complicated, then magnesium sulfate is given to prevent uterine contractions. An inflamed appendix often causes labor to begin.
While the uterus has not contracted, it limits the spread of infection, but after childbirth, pus enters the abdominal space and signs of an “acute abdomen” appear a couple of hours after delivery.
Cholecystitis
3.5% of pregnant women have stones in the gallbladder. If the organ becomes inflamed due to the release of a stone, surgical intervention may also be required. The development of cholecystitis is influenced by the following factors:
- use of oral contraceptives before pregnancy;
- lithogenic properties of bile increase (a tendency to form stones appears due to changes in its composition);
- deterioration of motility of the bile ducts, stagnation of secretions;
- after the 20th week of pregnancy, the bladder enlarges, but the ability to remove secretions decreases.
Signs of the disease:
- lack of appetite;
- vomiting, nausea;
- low-grade fever;
- pain is noted in the upper right side.
The pain may spread to the upper or lower left abdomen. As a rule, pain occurs after eating and lasts for minutes or hours. The gallbladder cannot be felt in a pregnant woman.
The diagnosis is confirmed by laboratory blood tests and ultrasound
First, drug treatment is recommended, but if the symptoms are severe and pancreatitis has developed, then surgery is indicated. Conservative therapy consists of removing the functional load from the organ (hunger, intravenous nutrition), taking antibacterial, antispasmodic and painkillers. The prognosis for timely assistance is favorable.
Acute pancreatitis
With pancreatitis, the pancreas contains activated digestive enzymes. Pathology develops due to cholelithiasis, exposure to medications (estrogens, tetracyclines, diuretics), hereditary predisposition, abnormalities of the pancreas and small intestine, infection, abdominal trauma, vascular disease, and alcoholism.
In the second half of pregnancy, the development of pancreatitis is provoked by:
- stagnation of bile and impaired motility of the gallbladder due to the action of the hormone progesterone;
- due to activation of the pancreas during this period, there is an increase in the secretion of enzymes (lipase, amylase, acid proteases);
- increase in blood lipids;
- increase in intra-abdominal pressure;
- contraction of the uterus and spasm of the sphincter of the bile ducts occur simultaneously;
- deterioration of mineral metabolism.
The disease has the following clinical picture:
- abdominal pain (can be girdling, acute, or increases gradually);
- nausea, vomiting;
- low-grade fever;
- tachycardia;
- abdominal muscle tension;
- blood pressure changes depending on body position (standing, lying down).
If a pregnant woman consults a doctor within 2-3 days after the onset of symptoms, then the amylase level in the serum exceeds the norm several times (after this time the indicator returns to normal).
Methods for diagnosing pancreatitis such as probing, angiography, and retrograde pancreatography cannot be used in pregnant women, so some difficulties arise in making a diagnosis
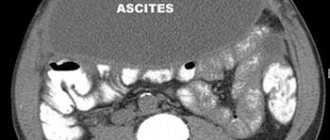
An ultrasound can detect fluid in the abdomen, peripankeratic hematoma, abscess, pseudocysts, but with a gestation period of more than 30 weeks, the uterus closes the gland and it is possible to visualize only its body. The disease is dangerous for the child, since pancreatic enzymes are able to penetrate the placental barrier, as well as due to hypocalcemia and electrolyte imbalance.
Conservative treatment involves refusing to eat, infusion therapy, removing gastric contents through a tube, taking painkillers, antispasmodics, and medications that inhibit enzyme activity. This treatment helps 90% of patients, improvement or worsening of the disease occurs within 3-5 days.
Surgery is necessary for abscess, rupture of pseudocyst, secondary pancreatitis.
Intestinal obstruction
Surgery is required if a pregnant woman develops intestinal obstruction. Impaired movement of feces and gases may occur during pregnancy due to:
- compression of intestinal adhesions by the enlarged uterus (in 55% of cases of obstruction, 45% of which occur in the third trimester);
- torsion of intestinal loops (in 25% of cases);
- hernias (in 10% of cases);
- benign or malignant tumor.
If there are adhesions, then there are three periods when there is a risk of developing pathology: raising the uterus from the small pelvis (first trimester), lowering the baby’s head into the small pelvis (third trimester), a sharp decrease in the uterus after the birth of a child with a jump in intra-abdominal pressure.
Women who have had appendectomy or other abdominal surgery are predisposed to adhesions.
With intestinal obstruction, diffuse abdominal pain occurs; it can be constant or periodic (the interval between attacks is 4-5 minutes if the pathology is in the small intestine and 10-15 if it is in the large intestine). There is retention of stool and gases, and vomiting begins in 80% of cases.
At the initial stage of the disease, the abdominal muscles are not tense. As the disease progresses, fever, a decrease in the amount of urine excreted by the kidneys, and a state of shock appear. Therefore, if a pregnant woman has clinical symptoms of obstruction and has a history of surgical interventions, then an x-ray examination is necessary.
Moreover, the X-ray at the beginning is not informative, but since the pathology develops quickly, a repeat image taken after 5-6 hours already indicates intestinal dysfunction. Before diagnosis, symptomatic therapy is carried out: intestinal stimulation, gastric lavage, siphon enema, medications. Once the disease is identified, surgery is performed.
If in the third trimester it is impossible to perform an operation on the intestine due to the uterus, then a caesarean section is performed.
Ulcer
Stomach ulcers occur extremely rarely in pregnant women. Less than a hundred cases of pathological complications have been described in the literature (most occur after the 28th week of gestation). When carrying a child, a woman's gastric motility and secretion of gastric juice decrease, but the production of mucin increases.
There is an assumption that such protection of the mucous membrane is due to the action of estrogen. An exacerbation of a peptic ulcer (dyspeptic disorders, abdominal pain) can be regarded by a woman as typical signs of pregnancy. When an ulcer perforates, pain occurs, signs of peritonitis are noted, and shock develops.
In such a clinic, surgical treatment is required. The disease is diagnosed using gastroscopy. In the third trimester, a cesarean section is performed to reduce the harmful effects on the fetus of hypoxemia and maternal hypotension.
Causes of pain at 34 weeks of pregnancy
Most women at this stage experience pain in the lower back, back, and abdomen. This is considered normal, as they occur due to increased pressure from the uterus on the nerve endings. In addition, the center of gravity shifts, because the woman’s weight has increased significantly, which leads to an increase in the load on the entire body as a whole, and on the musculoskeletal system in particular.
Pain in the abdomen and lumbar region is a consequence of softening of the ligaments and joints. This happens under the influence of hormones that prepare the body for childbirth. Moreover, aching and nagging pain can occur in the pelvis and sacrum, in the pubic area.
It is worth mentioning that the pain should not be too intense. If they increase, they may be a signal of the onset of premature labor. Therefore, if at 34 weeks severe and prolonged pain appears that was not there before, you must seek medical help. Early onset of labor may be indicated by abdominal prolapse, release of mucous plug, rupture of water, and regular contractions.
Contractions can be not only real, but also training. Doctors often call them "Brexton" or Braxton-Higgs contractions. They may be painful, but such uterine contractions always remain irregular. Contractions begin from the upper part of the uterus, gradually descend lower and disappear. If training contractions go away on their own, then the real ones will intensify.
Pain may also occur in the legs, because the load on them has increased significantly. A woman during this period is prohibited from wearing high heels; the most optimal height is considered to be 1-2 cm. The more comfortable the shoes, the less the load on the lower limbs. To reduce pain and relieve stress on your legs, you can ask your husband to give you a massage.
It's time to go to the maternity hospital!
So, when is it time to go to the hospital?
- Over the course of an hour, you feel about 10 contractions with a break of 5-7 minutes.
- The duration of each contraction is 30-60 seconds.
- Your amniotic fluid has broken - especially if it happened at one moment - the water gushed out in a torrent.
Serious symptoms that require you to go to the maternity hospital urgently:
- Unexpected bleeding (more than normal menstruation)
- Sudden pain in the uterine area - not at all the same in nature as pain during contractions
- Constant dizziness.
For every woman in labor, labor begins and progresses differently. Some are like a textbook, when contractions develop gradually, the intervals between them gradually decrease, others do it rapidly, their contractions are immediately painful, and the intervals between them are short. For others, the first period, on the contrary, is prolonged. Be guided by your condition and constantly keep your doctor up to date.
Inessa Smyk
What should the weight be?
Compared to the initial weight (before conception), a woman by this time can gain about 11-12 kg. Beginning at 34 weeks, weight gain often slows down. At the same time, it must be monitored especially carefully. If there is a significant deviation from the norm, it is necessary to follow a rational diet, which should be based on reducing the consumption of foods rich in easily digestible fats and carbohydrates.
Sometimes weight gain occurs due to edema. Normally, there may be slight swelling in the arms and legs, as well as in the face, feet and ankles. If swelling persists for a day or more, and also appears in the area of the abdominal wall and in the area of the legs, then you must inform your doctor about this. It is possible that a pregnant woman develops dropsy.
What's happening to the stomach?
By this time the belly is already quite large. It rises on average 33 cm above the womb. Therefore, a woman needs to choose appropriate clothes.
Since the center of gravity shifts, the expectant mother needs to be extremely careful, even in such familiar moments as getting out of bed.
To prevent the appearance of stretch marks, you need to properly care for your abdominal skin. To do this, it is regularly lubricated with nourishing creams.
As for the prolapse of the abdomen, this happens at a later date (about 2-3 weeks before the onset of labor), and sometimes just before childbirth. However, if your stomach has dropped now, you shouldn’t panic, but it’s still better to see a doctor.
What kind of discharge can there be?
Normally, the volume of discharge at 34 weeks of pregnancy should be moderate. Their color is light milky. Sometimes the discharge may have a slight sour smell. If they contain a small amount of mucus, then this is also normal. It indicates the gradual softening and opening of the cervix.
A curdled discharge indicates a fungal infection. Discharge with pus, yellow or green in color, is unhealthy. You should definitely consult a doctor if you find flakes or foam in them, as well as if they provoke itching and burning. It is important to get rid of sexually transmitted infections before the onset of labor so as not to infect the baby.
Discharge with blood is also a deviation from the norm. When they appear, you need to call an ambulance, as they often indicate placental abruption. This is dangerous due to the development of fetal hypoxia. If a woman is regularly seen by a doctor, then by this time such a pregnancy pathology as placental abruption is always excluded. And if the need to visit a doctor is ignored, then the appearance of blood may well indicate this formidable disorder.
Liquid, transparent, yellowish discharge may appear due to the rupture of amniotic fluid. They can come off in large masses or in small portions. In both cases, you need to call a medical team.
Childbirth is approaching
Mucus plug
Under the influence of hormonal changes, the mucus plug may come off. It looks like a lump of mucus ranging from one teaspoon to two tablespoons in volume - transparent or with small streaks of blood, ichor, or even brown color (all this is absolutely normal). The plug can come off at different times - from 1-2 weeks before birth or directly on the “X” day. For some women, the plug comes out in one go, while for others, the discharge continues for several days.
Contractions
As we remember, training contractions begin as early as 30 weeks of pregnancy, and gradually they become more frequent. How can we determine how training (otherwise called false) contractions differ from real, labor contractions?
There are several clear indicators for this:
- Regularity. False contractions are irregular, true ones gradually become stronger, longer and more frequent. However, sometimes in the evenings there are periods of regular contractions (for two or four hours), which then go away on their own. It is better to write down the time and duration of contractions in a special notebook - it will help you cope with anxiety, and will be useful to the doctor to assess your condition.
- Duration. False contractions last 15-20 seconds, true contractions gradually become longer. If you managed to fall asleep peacefully between contractions, then they were false.
- Take a warm shower or bath. False contractions will disappear, true contractions will continue.
- During false contractions there is no mucous discharge from the vagina, while true ones are often accompanied by discharge mixed with blood.
- Famous American pediatricians William and Martha Serza offer this method. If you are in doubt whether you have started labor or not, monitor the nature of your contractions for an hour. If you have six or more gradually intensifying contractions lasting at least 30 seconds over the course of an hour, you are most likely going into real labor. Labor pains last on average 10-12 hours during the first birth and 6-8 hours during repeated births.
Leakage of amniotic fluid
Normally, amniotic fluid drains at the end of the first stage of labor, when the dilation of the cervix reaches 7 cm or more. But sometimes this happens earlier, sometimes even before the contractions begin. What is important to pay attention to if your water breaks?
- Color. Normally, the water should be light and transparent, white flakes are also acceptable - this is a cheese-like lubricant. Dark, greenish-brown waters are an alarming sign indicating fetal hypoxia.
- Smell. Ordinary amniotic fluid has no odor. An unpleasant odor may indicate that the baby is passing meconium - original feces.
- Amount of water They are usually about 1-1.5 liters. 500-700 ml is insufficient volume, often happens during post-term pregnancy. However, do not rush to diagnose yourself. Sometimes only the so-called anterior waters recede at first, while the amniotic sac itself may still remain intact. In this case, the amount of amniotic fluid may be very small - about 200-300 ml.
Either way, if your water breaks, labor should begin within 24 hours, so don't wait too long to get ready. After the water breaks, the nature of the contractions changes, they become stronger and more painful.
Sex
As for intimate life, it is allowed, provided that there are no medical restrictions. In this case, sex should be performed as carefully as possible so as not to disturb the child. To do this, you need to avoid sudden movements and avoid poses that place pressure on your stomach.
If a woman has any doubts about the possibility of having sexual intercourse, she should definitely consult a doctor. If pain or other unusual sensations occur during intimacy, you should stop it immediately.
If a woman does not have a regular sexual partner, then she should understand that now the child is especially susceptible to various infections. Therefore, any sexual contacts must be protected.
Childbirth at 34 weeks of pregnancy
Labor should not normally begin at 34 weeks of pregnancy, but sometimes this happens. It is worth noting that the statistics in this regard are very encouraging: the mortality rate among children born at 34 weeks of gestation is exactly the same as among full-term infants. Moreover, a 34-week baby is not considered premature; it is only recognized as being born prematurely.
Premature birth can be triggered by factors such as too vigorous sex, Rh conflict, infectious diseases, and a woman’s age under 18 or over 40 years old.
The child will be able to breathe on his own, which is very important. However, you should be prepared for the fact that you will have to spend a little more time in the neonatal center. There, doctors will provide proper care for the child. After discharge from the hospital, the baby will be no different from all other children.
Other dangers that can await a woman at 34 weeks of pregnancy:
- Low water.
The normal amniotic fluid index is 72-278 mm. If this indicator is below the maximum permissible limit, then the woman is diagnosed with oligohydramnios. It can be pronounced and moderate.
- Polyhydramnios.
Excessive amniotic fluid is no less dangerous than oligohydramnios and requires hospitalization.
- The umbilical cord is wrapped around the baby's neck.
This can be detected during the third planned ultrasound.
The risk of complications increases if the pregnant woman has chronic diseases of the endocrine system, or has previously experienced miscarriages or premature births.
What should a pregnant woman pay attention to?
- A woman should avoid stress. This needs to be understood not only by her, but also by her relatives.
- It is necessary to carefully monitor fetal movements. There should be about 10 of them per day.
- You need to eat right. The common phrase “you need to eat for two” is valid only in relation to the quality of food, and not in relation to its calorie content. This will help you avoid gaining excess weight and make labor easier.
- You should definitely check yourself for swelling. If, when pressing with your fingers on a woman’s shin, a hole remains, then there is swelling. You should consult a doctor if they appear suddenly and persist for a long time.
- A woman at this stage should not experience heavy physical exertion. Even housekeeping needs to be done with caution. This will prevent you from getting injured. However, physical activity cannot be completely limited. It is useful to do special gymnastics for pregnant women, which will help maintain muscle tone.
- It’s great if you have the opportunity to take daily walks in the fresh air.
- It is useful to study various information regarding how childbirth takes place and how to properly handle the newborn.
Recommendations for the expectant mother
- Monitor changes in your condition , and also discuss alarming symptoms with the gynecologist managing your pregnancy. You need to record changes in your weight and measure your blood pressure to rule out the development of preeclampsia. We remind you: gestosis is characterized by increased pressure, the development of edema and the presence of protein in the urine. Therefore, if your weight increases too quickly, also check for swelling by finger pressing on the shin above the bone (if the dimple persists for some time, this speaks in favor of swelling).
- Eat right. Firstly, it will benefit your figure, and secondly, it will have a positive impact on the formation of your baby’s eating habits. By reducing the amount of salt in your diet, you will reduce the likelihood of developing edema, and adding fiber will prevent constipation. And, of course, your menu should be varied and nutritious so that all the necessary nutrients enter your body and your baby. It is better to eat small portions and more often. And remember: you need to eat not for two, but for two.
- Rest more, worry less . The baby feels your condition subtly, so it is especially important to avoid all kinds of conflicts and stressful situations. And proper rest will help you recover from the load, which by 34 weeks has already increased quite significantly.
- Take a walk in the fresh air. This is good for your figure and also saturates the body with oxygen. In addition, it is believed that after a good walk you sleep better. If you have trouble sleeping, an evening walk may be one solution.
- If you have not yet had time to pack your things for the maternity hospital, do this so as not to run around in a panic at the last moment. Now you can calmly assess what you will need and certainly won’t forget anything. You can also think about choosing a maternity hospital in order to feel comfortable in the institution where you will be during childbirth and after - with the baby.