The disorders begin with an acute pain syndrome, after which the inflamed muscle is seized by a spasm. When palpating, severe discomfort is felt, the body is tense. If inflammation has manifested itself at least once in the past, then under unfavorable circumstances and exposure to aggressive environmental factors, the pathology will again make itself felt. In any stressful situation for the body (hypothermia, excessive physical activity), a feeling of spasm appears, which seriously impairs a person’s quality of life.
Where is?
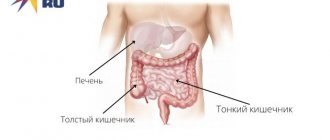
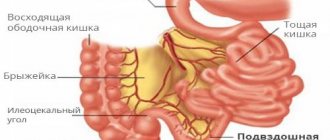
The iliac region is located inside the abdominal cavity of men and women. This part of the human body is conventionally divided into right and left sides. In each part of the ileum there are internal organs that have their own functional purpose.
In the right cavity are concentrated:
- cecum;
- appendix;
- ileum.
The cecum, which has no pathological changes and is not in a painful state, is closed in front by loop-shaped tissues of the small intestine.
If the cecum is completely filled with gases, it covers the entire cavity. The left side of the iliac fossa contains loops of the jejunum. The sigmoid colon is also located in this part of the abdominal cavity, but it runs from the 3rd sacral vertebra to the iliac crest.
If the cavity of the bladder and rectum is completely filled with biological contents, the loops of the S-shaped intestine smoothly move to the left side of the ileum.
The ileum also contains the following organs of the reproductive system of men and women:
- the ureter connecting the renal pelvis to the bladder;
- round ligament of the female reproductive organ - the uterus;
- The male reproductive organ is the vas deferens.
All of the above organs receive stable blood supply through the main blood vessels. The ileum is one of the least capacious parts of the abdominal cavity.
Structure
The iliac region is located in the lower part of the abdominal cavity, covering its sides, as well as the lower abdomen. In order to ensure high-quality diagnosis and control over the health of the internal organs of the digestive and genitourinary systems, the ileum is divided into 2 main structural segments. This part of the body has the following structure.
The iliac region consists of the left and right parts
| Name of the structural part of the iliac region | Location in the abdominal cavity |
| Left | This part of the iliac region is located inside the abdominal cavity in the space between the lower left row of ribs and the ilium. |
| Right | The right iliac fossa covers the abdominal cavity from the right side from the lower ribs to the ilium. |
If we look at the anatomical structure of this part of the peritoneum in the pictures, we get the visual impression that the left and right iliac regions are located directly above the lateral part of the pelvic bones or directly above the hip joints.
Both parts of the ileum are located opposite each other and perform a single physiological function as a reservoir for the internal organs of the digestive and genitourinary systems.
Cost of treatment for arthrosis of the sacroiliac joint at SL Clinic
Treatment of SI joint arthrosis involves inserting needles into the projections of the diseased joint and treating them in a temperature regime. The procedure is minimally invasive and outpatient i.e. you can go home the same day.
The cost of radiofrequency treatment of arthrosis of the SIJ is 68,000 rubles and depends on: - The cost of needles for radiofrequency ablation; — Clinics and class wards. The price includes: — Stay at the clinic before and after surgery; — Operation; — Cost of needles for radiofrequency ablation; — Observation and consultation during the rehabilitation period. All clinic services and costs are listed in the price list.
What organs are located in the iliac region?
The iliac region is located in the lower part of the abdominal cavity. It contains the following internal organs, which are vital for maintaining the stable functioning of all systems of the human body:
- cecum;
- appendix;
- sigmoid colon;
- ureter (this organ is localized in this part of the abdominal cavity, in both men and women);
- loop-shaped tissues of the jejunum;
- small intestine;
- ileum;
- vas deferens in men;
- round ligament of the female internal reproductive organ - the uterus.
This part of the abdominal cavity contains a nerve plexus that connects tissues and muscle fibers to the lumbar spine. Thanks to them, nervation of the above internal organs, as well as other elements of the digestive and genitourinary systems, is carried out.
Symptoms of arthrosis of the sacroiliac joint
In the early stages of development, the disease practically does not manifest itself. Signs of a degenerative process occur when cartilage tissue is destroyed. This may be accompanied by:
- discomfort in the lumbosacral spine and buttocks, aggravated by physical work, bending, turning, prolonged sitting or walking;
- increased muscle tone in the sacral area;
- limitation of motor activity and range of motion, feeling of stiffness;
- the appearance of a characteristic crunch when bending or turning the body;
- gait disturbance;
- increased urge to urinate;
- decreased libido.
The pain can initially usually be described as pulling, aching. They tend to radiate to the groin, legs, perineum, and buttocks.
The inflammatory process quickly worsens, which is accompanied by redness, increased sensitivity and swelling of the soft tissues in the projection of the diseased joint, impaired circulation in the affected area and a decrease in the amount of nutrients supplied. As a result, osteophytes are formed. As arthrosis progresses, the symptoms intensify, and in advanced cases the person almost completely loses the ability to move independently.
Stages of the disease
The intensity of signs of arthrosis of the sacroiliac joint depends on the stage of its development. There are 4 stages:
- At first, the disease practically does not manifest itself. After physical work, long walking or sitting, minor short-term discomfort may occur in the sacrum and buttocks, which quickly disappears after rest. At the same time, the functions of the joints are completely preserved, so the person does not notice the limitation of mobility. Attacks of acute pain that interfere with standing are rare.
- The pain intensifies and occurs more frequently, and can only be relieved by taking painkillers. This is triggered by the appearance of irreversible changes in the state of the cartilage tissue of the joint.
- Due to severe deformation of the cartilage, osteophytes are formed along the entire surface of the joint, and the bone surfaces are exposed. In some cases, separation of the sacrum is observed. This is accompanied by severe pain, completely incapacitating the person.
- Degenerative-dystrophic processes lead to complete stiffness and constant severe pain.
What diseases are localized within this area?
The right and left iliac regions can be subject to inflammatory and infectious diseases that are caused by mechanical damage to tissue, an autoimmune reaction of the body, or due to bacterial infection of tissues of internal organs. The following types of diseases can be localized within this area of the body.
| Type of disease | Characteristics of clinical manifestations and their localization |
| Appendicitis | This disease is also found under the medical term - inflammation of the vermiform appendix. The disease is characterized by acute symptoms with the occurrence of cutting pain in the right iliac region. A person with this diagnosis cannot independently stand in an upright position, as severe pain forces him to bend over or lie on his back. During palpation of the cavity, the pain intensifies. An increase in body temperature and the occurrence of fever are also recorded. Lack of timely surgical treatment can lead to the formation of a purulent abscess, rupture of the appendix and peritonitis. |
| Volvulus of the sigmoid colon | This is a pathological condition of the digestive system, which is localized in the ileal region. Occurs as a result of increased pressure inside the abdominal cavity. It can develop after strangulation of an inguinal hernia, prolonged fasting, prolonged constipation, or lifting heavy objects. Volvulus of the sigmoid colon is accompanied by sharp or cutting pain in the lower abdomen. The change in the position of the organ as a result of torsion can reach 90 degrees. In medical practice, there are clinical cases when, as a result of too active intestinal peristalsis, the sigmoid colon undergoes 2 to 3 twists. A patient who has had a sigmoid colon volvulus in the ileal region requires emergency surgical intervention. Otherwise, acute inflammation of the mucous membrane of the organ occurs, the blood supply to its tissues is disrupted, vascular thrombosis develops and the process of necrosis begins. |
| Helminthiasis | Infection of the intestines and other parts of the digestive system by parasites can also cause a painful condition of the organs located in the ileum. In the lower abdomen, pathological symptoms are felt in the form of cutting pain, increased gas formation and bloating, and the presence of atypical lumps. In addition to these signs of helminthiasis, which are localized in the intestines of the ileum, there is a feeling of nausea, loss of appetite, physical weakness and fatigue. |
| Acute prostatitis | A complication of this urological disease, which is diagnosed exclusively in men, can cause inflammatory damage to the vas deferens. This pathology develops when a bacterial infection localized in the tissues of the prostate gland spreads to other parts of the male reproductive system. The vas deferens is located in the ileum, and its damage causes acute pain, which intensifies during intense walking, squatting, heavy physical labor, and prolonged sitting. |
| Intestinal dysbiosis | This is a disease that is associated with an imbalance of beneficial and pathogenic microflora living in the intestines. The disease is characterized by cutting or aching pain in the intestines located in the ileum on the left and right sides. A person suffers from increased gas formation, lack of appetite, and nausea. Constipation or diarrhea cannot be ruled out. The disease develops as a result of prolonged antibacterial therapy, poor-quality or unbalanced nutrition, and alcohol abuse. |
| Endometritis | This disease is a gynecological pathology, the symptoms of which appear after inflammation of the inner epithelial layer lining the cavity of the female reproductive organ. The disease can be acute or chronic. Pain in the iliac fossa is also cutting or aching in nature. |
| Abscess of the iliopsoas muscle | This is a dangerous disease of the musculoskeletal system, which is characterized by an acute inflammatory process and the formation of a purulent abscess. The disease affects the muscle fibers of the iliopsoas muscle, which are destroyed as a result of an infectious-inflammatory process. The disease develops as a result of mechanical trauma to tissue due to blows, falls, lifting heavy objects, and the consequences of surgical intervention on the organs of the iliac fossa. The main symptoms of this disease are acute pain, an increase in local and general body temperature, a change in the color of the skin in the area where the purulent abscess is localized (it becomes red, purple or even bluish). |
| Inflammation of the appendages | Diseases associated with the development of acute or chronic inflammation in the uterine appendages can also cause pain in the iliac region. The pathology may be associated with inflammation of the ovaries, the formation of benign or cancerous tumors in their tissues. |
| Oncology of the ilium | This is bone tissue that is located in close proximity to the iliac space. Its defeat by a malignant neoplasm causes a large number of unpleasant symptoms associated with impaired motor activity of the lumbar spine, hip joint and lower limb. One of the first signs of the disease is prolonged and persistent pain in the iliac fossa, which cannot be eliminated by taking potent analgesics. |
| Inguinal or femoral hernia | The appearance of an inguinal or femoral hernia disrupts the functioning of internal organs and tissues located in the iliac region. A characteristic sign of the disease is the formation of a round lump that rises above the general level of the skin surface of the abdomen. This is a hernial sac that is soft to the touch. The main danger of this disease is the high risk of strangulation of the hernia, which will lead to the development of necrosis of the tissues from which it was formed. The disease is treated by surgical removal of the hernial formation. |
| Urolithiasis disease | Symptoms of this disease manifest themselves in the form of burning or aching pain if foreign stones or sand enter the cavity of the ureter from the kidney. The pain syndrome appears periodically or bothers the person constantly. The pathological condition of the organs of the excretory system can cover the right, left side of the iliac fossa, or both sides at once, if the patient suffers from bilateral kidney damage from stones. The disease is treated with medication or surgery. |
Men diagnosed with inflammation of the seminal vesicles may also experience a feeling of discomfort and nagging pain, which is localized in the iliac fossa. In medical practice, there are cases when the painful condition of this part of the body was associated with pathological changes in the tissues of the ilium.
Reasons for development
The sacroiliac joint is a paired joint that is the junction of the spinal column and the pelvis. In the sacral region, the vertebrae are firmly fused to each other, forming an almost monolithic bone. Both of its lateral surfaces are covered with hyaline cartilage. The ilium is tightly adjacent to them.
The joint or articulation thus formed is strengthened by numerous rigid, practically immovable ligaments. It has a slit-like shape, and the articular cavity itself is filled with synovial fluid and acts as a shock absorber during movement.
The sacroiliac joint is practically motionless, but at the same time provides stability when standing, is responsible for stabilizing the body position when performing certain movements, when sitting, and distributes the load on the pelvis and legs when walking. Therefore, the slightest disturbances in its functioning affect the condition of the spinal column and can provoke the development of a wide variety of complications.
Over the years, the sacroiliac joint gradually changes and becomes prone to degenerative and dystrophic changes. The following can provoke the development of arthrosis:
- various types of injuries to the lower back and tailbone;
- multiple pregnancies and births, especially when carrying a large fetus;
- abnormalities of bone tissue development;
- infectious diseases affecting bone tissue;
- obesity;
- metabolic disorders that provoke calcium deficiency in the body;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- autoimmune disorders, in particular ankylosing spondylitis;
- excessive physical activity.
A genetic predisposition to it significantly increases the risk of pathology. Most people diagnosed with this condition are over 55 years of age. Although recently there has been a tendency towards rejuvenation of diseases of the musculoskeletal system, therefore today it is no longer uncommon to find arthrosis of the sacroiliac joint in people from 25 to 35 years old. Most often, the pathology is diagnosed in women, due to the peculiarities of the anatomy.
What does pain in the iliac region mean?
The iliac region is located on the sides of the lower abdomen. The occurrence of discomfort, a feeling of acute or aching pain on the left or right side may indicate the development of an inflammatory or other pathological condition of the internal organs.
Left
The occurrence of pain on the left side of the iliac region may be associated with inflammation of the mucous membrane of the sigmoid colon, volvulus, intestinal obstruction, constipation or dysbacteriosis. The pain syndrome is characterized by frequent cramping attacks, which intensify as the inflammatory process worsens.
On right
Pain on the right side of the iliac region most often indicates inflammation of the appendix, which is also known as appendicitis.
In men, similar symptoms may be associated with inflammation of the seminal vesicles and hyperplasia of prostate tissue. In women, acute or aching pain in the right side of the iliac region occurs due to pathologies of the uterine appendages.
When should you worry?
Even if the pain is mild, or its cause is known, it is better not to delay a visit to the doctor. There are cases when an urgent call to the ambulance is required. These include:
- excruciating painful sensations that do not go away for more than three hours and are not relieved by analgesic drugs;
- serious mechanical damage to tissues and organs;
- pain throughout the entire peritoneal area when pressed;
- the occurrence of vomiting, severe diarrhea, dizziness;
- unexpected temperature rise;
- loss of coordination of movements, clouding of consciousness, fainting;
- paleness or other change in skin tone;
- tachycardia;
- decrease in pressure.
All these signs indicate the need for urgent medical attention, and in some cases, even surgery. If such symptoms are combined with pain above the inguinal fold or hypochondrium, you should call an ambulance. Peritonitis and other inflammatory processes, as well as ectopic pregnancy without urgent treatment can lead to death.
Fracture of the ilium
The ilium is the largest part of the 3 paired bones that form the pelvis. With its help, the bone tissue of the pelvis is connected to the spine. An ilium fracture is a high-energy pelvic injury that can occur as a result of an accident, a fall from a great height, a gunshot wound, or a mine explosion.
This pathology is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- acute pain in the lumbar spine, which intensifies when pressing on the pubic bone;
- formation of a subcutaneous hematoma in the scrotum in men and perineum in women;
- urinary incontinence or involuntary urination if bone tissue has been displaced with damage to the excretory organs;
- vaginal bleeding in women;
- violation of the position of the prostate gland and the inability to palpate it in men;
- presence of blood inside the urethra;
- persistent pain in the lower abdomen on the left or right;
- anal bleeding;
- weak or complete absence of sensitivity in the perineum, pubis, anus, inner thigh or entire lower limb (this symptom is characteristic of ilium fractures with damage to the nerve plexus of the lumbar spine).
Diagnosis of an iliac bone fracture involves the use of radiography and CT scan of the pelvis. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the traumatologist or surgeon takes measures for external or internal fixation of the bone tissue that has undergone a fracture.
During the treatment period, the patient is bedridden and requires constant care. The duration of therapy ranges from 1 to 6 months. depending on the severity of the fracture and the possible presence of complications.
How will diet help?
For any manifestations of abdominal pain in men, doctors recommend following a diet during the period of examination and treatment. The basis of the diet is liquid broths and pureed soups. It is recommended to add white bread crackers and rice without salt and spices. Such food has an enveloping effect, which protects the intestinal mucosa from the effects of medications and is easily digestible.
If the cause of the pain is identified and eliminated, you can return to your normal diet, excluding fried spicy foods. Nutritionists recommend starting the day with porridge if you have stomach pain. The ideal option would be liquid oatmeal, but if you do not like such food, you can replace it with buckwheat or rice. During illness, it is recommended to exclude fresh vegetables from the diet. They are replaced with stewed or baked vegetables. As a dessert, you can have baked apples with cottage cheese and honey.
Ilial bone cancer: causes and signs
The first symptoms of a malignant tumor of the ilium are the following sensations experienced by a sick person:
- feeling of aching pain in the perineum or lumbar region;
- body temperature in the area where the affected bone is located is 1-2 degrees higher;
- the skin surface on the inner side of the thigh, scrotum, perineum becomes swollen and red;
- the sensitivity of the skin on the back of the thigh is impaired;
- While walking, you feel a sharp pain in your thigh or lower abdomen.
The main reasons for the development of oncology are hereditary predisposition, daily contact with carcinogenic and toxic substances, bad habits, a sedentary lifestyle, previous pelvic injuries, chronic inflammation of bone tissue.
Urinary system problems
The urinary system not so rarely provokes in patients aching or throbbing pain in the groin area on the left side. In this case, the patient’s condition can remain stable for a long time until the acute stage occurs.
Of the pathologies of the urinary system, urolithiasis most often causes discomfort. In most cases it occurs without serious symptoms. But the slightest movement of the stone leads to sharp pain. It may immediately appear in the lumbar region, but with the movement of the accumulations it will move to the left side of the abdomen and groin.
To treat urolithiasis, painkillers are used, and diuretics may be prescribed. Potassium bicarbonate solutions and citrate mixtures are used to crush accumulated fractions. Medications such as Progesterone, Glucagon and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are necessarily prescribed. If conservative treatment is not possible, operations may be prescribed, during which the surgeon removes the stones.
Cystitis and urethritis
Urethritis is one of the most common diseases of the urinary system in men. This is due to the peculiarity of the male urethra, which has contact not only with urine, but also with the fluid that forms in the prostate gland. Therefore, various infections can enter the urinary canal in several ways: from the prostate, bladder or kidneys. For the development of cystitis in men, the body must be overcome by several factors. Such factors may be:
- chronic or acute stress;
- hypothermia;
- stagnation of fluid in the bladder;
- weak immunity.
There are unlikely to be any questions about bed rest. As for drug treatment, the patient needs to take a number of medications:
- almost always these will be antibiotics from the group of fluoroquinolones or cephalosporins;
- when chronic cystitis is suspected in men, physiotherapy is prescribed;
- NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) are prescribed as pain relievers;
- vitamins increase resistance to infections.
When compiling a diet, be sure to take into account the urine pH environment, since acidic urine predisposes to the precipitation of urates, neutral urine promotes the formation of oxalate crystals, and alkaline urine promotes the formation of phosphate salts.
Trephine biopsy of the iliac bone
Trepanobiopsy of the iliac bone is a type of diagnostic examination, the conduct of which involves the selection of bone marrow particles, as well as tissues.
The main purpose of the procedure is their histological examination, aimed at determining the health of the bone tissue structure. Doctors receive comprehensive information about the quality of the cellular composition of the bone marrow, the percentage of adipose and hematopoietic tissue, the condition of blood vessels and stroma.
Histological analysis makes it possible to determine the presence of a benign or cancerous neoplasm if signs of a tumor process are found in the structure of the ilium. Biological material is collected using a needle puncture. The patient is under general anesthesia, and the diagnostic procedure itself is a simple surgical operation.
Diagnostics
It is impossible to establish the cause of pain only on the basis of the existing clinical picture, since more than 15 different diseases are accompanied by symptoms typical for arthrosis of the sacroiliac joint. In particular, ankylosing spondylosis, L5-S1 hernias, spinal canal stenosis, scleroderma and other diseases manifest themselves in a similar way.
To diagnose the disease, the following are prescribed:
- CBC - used to detect signs of an inflammatory process (with arthrosis, the number of leukocytes in the blood and ESR are usually not much higher than normal);
- biochemical blood test - necessary to assess the functioning of internal organs;
- X-ray or CT - each method allows you to detect narrowing of the joint space, signs of destruction of cartilage tissue and osteophytes;
- MRI is the most informative diagnostic procedure, with which you can detect even minimal deviations from the norm in the condition of ligaments, muscles and joints;
- Osteoporosis screening – prescribed to identify bone weakness.
At SL Clinic you can get advice from a specialist who has been treating this problem for many years. Therefore, when undergoing treatment with us, you will definitely not miss the progression and development of the disease when you contact immediately after the first symptoms appear.
Treatment
Treatment of diseases of the iliac region is symptomatic. In the case of the development of dysbacteriosis, colitis with infectious inflammation of the mucous membrane of the sigmoid colon, antibacterial agents are used, the active components of which are effective against microorganisms of specific strains. The type of antibiotic is selected based on the results of laboratory diagnostics.
Appendicitis, volvulus of the sigmoid colon, malignant and cancerous neoplasms, blockage of the ureter with stones, acute inflammation of the prostate gland with impaired urine outflow require surgical intervention.
Most operations performed on the organs of the iliac region are not complicated. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, the prognosis for a full recovery is positive.
The iliac region is a depression in the lower abdomen that is divided into the right and left sides. Its cavity contains the cecum, sigmoid colon, ureter, uterine appendages in women, vermiform appendix, and vas deferens in men.
The depression is located between the ilium and the lower ribs. Diseases of this part of the body are associated with dysfunctions of the digestive and genitourinary systems. Treatment of pathologies is symptomatic. Includes the use of anti-inflammatory, antibacterial agents, as well as surgical intervention.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Disease prevention
Since arthrosis is an age-related disease, it is impossible to guarantee its absence, especially if there is a hereditary predisposition. But it is possible to reduce the risk of its development. For this purpose it is recommended:
- regular moderate physical activity;
- avoid prolonged sitting or standing;
- promptly treat any infectious disease;
- avoid stress and nervous tension;
- do not lift too heavy objects;
- maintain normal weight.