Sand in the gallbladder is the initial stage of gallstone disease. The formation of microconcretions is a fairly common pathology. Sand consists of bile components, among which cholesterol occupies the main place. The pathology is practically asymptomatic, but it is more dangerous than it might seem at first glance. Unremoved sand eventually forms stones and provokes cholecystitis. A physician, gastroenterologist or hepatologist identifies symptoms and treats sand in the gallbladder.
How sand is formed
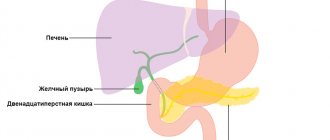
Bile secreted by the liver contains many components. They are needed to digest food in the duodenum. The liver produces up to 2 liters of bile per day. But not all of it is used at the same time. The function of storing this important biological fluid is performed by the gallbladder, releasing the required amount of bile as food arrives.
Under the influence of provoking factors, the proportional ratio of the composition of bile is disrupted and biliary sludge is formed - sediment. It consists of cholesterol crystals, pigments, calcium salts and other elements found in the structure of bile.
If the cause of the formation of bile sludge is not eliminated, over time the sediment turns into sand or microconcretions with a diameter of about 1 mm. The process of stone formation does not stop there. The stones increase in size to 1 cm or more.
Approximately 90% of the sand in the bladder is cholesterol.
Diagnostics
A thorough history taking comes to the forefront of the diagnostic search. This way, parents themselves could notice that their child had swallowed a toy, indicate the size of this object, thereby speeding up the work of doctors.
X-ray examination can help in diagnosis, which will allow you to see a foreign body on an x-ray as a contrast object.
Fibrogastroscopy helps not only to see the swallowed object, but also to remove the foreign body.
Causes and provoking factors
Predisposing factors to the formation of sand grains are primarily considered to be gender and age. According to statistics, the number of women with sand in the gallbladder is many times greater than the number of men with this disease. Age also makes itself felt. Over the years, the tone of internal organs decreases, and the risk of sand appearing after 70 years is already 30%.
The next at risk are people with an obese physique who lead an inactive lifestyle. Among the total number of patients, the proportion of obese people is 65%.
A genetic factor can play a decisive role when a person is born with an abnormal structure of an organ (kink, constriction). These deficiencies interfere with the normal flow of bile.
Hormonal disorders and other diseases also lead to the formation of sand:
- diabetes;
- liver diseases;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- gout;
- taking hormonal medications;
- pregnancy.
An important factor in the progression of the disease is nutrition. The predominance of fatty foods, sweets, carbonated drinks, and alcohol in the diet significantly provokes sand deposition. The same thing happens during long periods of fasting and following strict diets.
Sand symptoms
It is quite difficult to determine the presence of grains of sand, since in the first stages a person is not bothered by specific symptoms. Sand can form over several years. Most often it is discovered accidentally during the diagnosis of other diseases.
However, some signs of general malaise suggest the need to check the condition of the gallbladder:
- constant fatigue;
- difficulty falling asleep;
- rapid physical and mental fatigue;
- indigestion;
- nausea after eating fatty foods or alcohol.
When the stones reach large sizes and begin to move, a severe attack of pain occurs - hepatic colic. The heart rate increases, blood pressure decreases, and even loss of consciousness is possible.
Cholelithiasis. Clinical symptoms
Asymptomatic cholelithiasis can be a finding of ultrasound examination during medical examination or manifest itself as symptoms of damage to other organs and systems.
Symptomatic cholelithiasis can manifest itself as pain in the upper abdomen, attacks of biliary colic, obstructive jaundice, and biliary dyspepsia.
The pain can be dull, aching, and often an attack of biliary colic occurs, which is a pathognomonic sign of cholelithiasis.
Biliary colic is characterized by sharp, spastic pain that intensifies with inhalation and positioning on the left side, and decreases slightly on the right side. The patient is tossing about in bed due to pain, there is tachycardia (palpitations), increased sweating, nausea, slight vomiting that does not bring relief to the patient, and bloating. With biliary colic, the pain is localized in the right hypochondrium or epigastric region, radiating under the scapula on the right, or the collarbone. Pain can radiate to the chest and to the heart area, simulating pain in the heart (angina) - cholecystocardiac reflex.
An attack of biliary colic requires emergency care, the pain should not be tolerated, an ambulance must be called, possibly hospitalization, an assessment of the patient's condition and indications for surgical treatment or conservative management of the patient are given.
After biliary colic, which can last from ten minutes to several hours, jaundice may appear - yellowness of the sclera and skin, darkening of urine, discolored feces.
Simultaneously with or without an attack of biliary colic, biliary (bilious) dyspepsia may occur, which is manifested by a feeling of bitterness in the mouth, nausea, especially in the morning, sometimes vomiting that does not bring relief, bloating, and a tendency to constipation. These phenomena are transient and can occur independently or during an attack of pain in the right hypochondrium.
Correct and timely diagnosis allows you to clarify the disease, exclude the involvement of other digestive organs and complications and outline adequate ways to manage the patient
Why is it dangerous?
Sand in the gallstone is not the last stage of the pathological process of stone formation. Stones up to 2-3 mm in size can pass through the bile duct into the intestines without causing harm to other organs.
But over time, the stones grow in size, reaching several centimeters. When it enters the bile ducts, choledocholithiasis develops. When a situation occurs that provokes the movement of large particles, they can injure the walls of the duct or completely block it. An infection enters the gall bladder and inflammation begins - cholecystitis.
Severe attacks of hepatic colic with large stones require immediate surgical intervention.
Many women carry gallstones. Is it always necessary to remove the gallbladder in this case? Is there an alternative to surgery?
The head of the Department of Hospital Surgery of the Russian State Medical University, surgeon of the 31st City Clinical Hospital of Moscow, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Sergei Georgievich Shapovalyants, .
– Is it necessary to remove the gallbladder if only one small stone has formed in it? Is it worth sacrificing an entire organ?
– Many patients ask this question, because few people want to immediately take radical measures. They believe that small gallstones do not pose any danger and can simply be observed. And sometimes such tactics are actually used. However, we must admit that it is very, very dangerous. After all, even small stones can cause serious complications. If large formations can lead to bedsores and gall bladder ruptures, then small stones are insidious in their own way. They can migrate and penetrate the bile ducts. Wandering along them, the stones reach the level of the confluence with the duodenum and get stuck there. Due to a violation of the outflow of bile, the pigment bilirubin begins to accumulate in the blood, and obstructive jaundice occurs. In addition, a severe attack of acute pancreatitis can quickly develop. In this case, there is no time for thinking - an ambulance from a doctor is needed.
All patients should also know that if a stone appears in the gall bladder, it will never completely resolve. The presence of even the smallest stones indicates that the functioning of the gallbladder is impaired, and bile begins to precipitate. And if this trend has appeared, it will develop.
– But there is a method for dissolving stones with the help of medications. Why not try it before going to the surgeon?
– Indeed, there are drugs that can be used to try to influence some gallstones. But not to completely dissolve them - this does not happen, but only to slightly reduce their size. This can only be done with a strict combination of the size of the stone, its chemical composition, the contractile function of the gallbladder and drug tolerance.
Bile acids are used to dissolve stones. Two of them are used as drugs - chenodeoxycholic acid and ursodeoxycholic acid. These drugs are produced by many companies under different names. Some of the most famous are Henofalk and Ursofalk. With the help of these remedies you can act exclusively on cholesterol stones. If there is a lot of calcium or bilirubin in the stones, then the use of bile acids is useless. They never dissolve these substances.
Gallstones should have a diameter of no more than 2 cm. Larger formations, of course, can be tried to be reduced. However, this will take a very long time, up to several years, because on average the stones decrease by 1 mm per month.
In addition, stones can be dissolved only if the function of the gallbladder is preserved, when it continues to contract normally and remove bile. But in case of acute inflammatory diseases of the gallbladder and bile ducts, liver diseases, peptic ulcers of the stomach and intestines, doing this is contraindicated and pointless.
It is also worth mentioning that taking bile acids is very often accompanied by undesirable reactions, in particular, stool upset. But despite this, the patient must take these drugs regularly and for a long time, at least several months. All you have to do is stop treatment, and the stones grow back. So the drug method has very limited effectiveness.
-What can you say about the method of crushing gallstones? Do they crush kidney stones?
– Analogies between the crushing of kidney and gallstones are actually often drawn. At one time, gallstones were crushed by extracorporeal lithotripsy. Moreover, this method was very popular. During a lithotripsy session, multiple shock waves were directed at the stone from outside the body. As a result of this impact, the stone was crushed into fragments. Then the small fragments independently left the body through the bile ducts and intestines. At the same time, large fragments that could not pass through the duct remained in the gallbladder. But that's not so bad. The fragments formed as a result of crushing often got stuck in the bile ducts, clogged them and disrupted the entire process of bile secretion.
There is one more important point. Before lithotripsy, stones are usually even, smooth, adapted to the shape of the gallbladder. And a person often does not feel them. As soon as you crush it, turn it into a mass of small but sharp fragments, biliary colic, jaundice appear, and the pancreas becomes inflamed. The patient's situation may deteriorate greatly. So this method can be considered simply dangerous, and many foreign and domestic clinics refuse it.
– It is clear that all conservative methods do not bring much success. But if you decide to have an operation, why is it necessary to remove an entire organ? Is it possible to remove only the stones and leave the gallbladder?
– Alas, this method is recognized today as ineffective, although it is still practiced in some places. There is an opinion that some patients, especially young ones, should not have their gallbladder removed. Still, it performs certain important functions in the body.
Proponents of this approach perform an operation during which a small incision is made in the gallbladder. Through it, gallstones are removed, then the bladder is sutured, and after two or three days the satisfied patient returns home. No stones, and the gallbladder is in place.
However, not everything is so simple. About 2-3 months after such an operation, cholelithiasis rears its head again. The same symptoms and complications that the person had before the intervention return. The relapse rate at different intervals reaches almost 100%. This is due to the fact that one of the prerequisites for the formation of stones in the gall bladder is its poor contractility. Such a bubble is called stagnant. Another reason is the congenital features of the structure of bile. When bile, with any diet, even purely vegetarian, concentrates and precipitates. In this case, removing stones alone simply makes no sense. The problem can be finally solved only by completely eliminating the gallbladder.
– Is abdominal surgery always necessary for this?
- Of course no. In large clinics and hospitals, gallbladder removal is performed by laparoscopy. The operation is performed through three or four punctures in the abdominal wall. An optical system is introduced inside. The abdominal cavity is examined and the gallbladder is removed with special instruments.
As a rule, this is where all the patient’s troubles end. After a short period of adaptation, he can forget about cholelithiasis forever. Moreover, the absence of a gallbladder will remain practically invisible to him. Indeed, in fact, its “biological loss” occurred much earlier - even at the stage of stone formation. Even then, the gallbladder ceased to function normally, and other parts of the biliary system took over the job.
– To be honest, I know of cases where after such an operation people did not feel better, but even worse... What do you say about this?
– You are right, there is such a thing as postcholecystectomy syndrome. It implies exactly the deterioration in well-being that you are talking about. Most often this happens if the operation is performed at an already advanced stage of the disease. When neighboring organs are involved in the inflammatory process. In this situation, only one thing can be said - do not take it to extremes. Perform the operation as planned, and not when “thunder strikes.”
But there is another reason for the poor condition. And this is a fairly serious problem with deep roots. The fact is that the operation of removing the gallbladder has come to be considered technically simple for doctors and quite easily tolerated for patients. For these reasons, many people go for it without much thought. Although in reality it is not always worth doing this.
The range of examinations performed on the patient is often limited to one ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. Moreover, according to its results, a person may not have stones as such, but “clumps” or “suspensions” are detected. True, the patient presents some complaints similar to the symptoms of cholelithiasis. They are taken as the basis for the decision.
The patient is quickly operated on, but the operation does not bring relief. The question arises: was the gallbladder really the cause of poor health? After all, the same symptoms can arise due to other problems, in particular due to duodenal dyskinesia. And if in such a situation the gallbladder is removed - a kind of buffer that mitigates unpleasant manifestations - then the existing problems will immediately worsen. A pain syndrome will appear and the whole complex of symptoms will emerge.
– What to do in such a situation?
– No matter how sad it is to open a new medical history. In general, in order to avoid such a development of events, before the operation you need to undergo a thorough examination of not only the gallbladder, but also all nearby organs. It is necessary to carefully evaluate the condition of the bile ducts, pancreas, duodenum, right kidney, and stomach. Not all medical institutions are equipped with the necessary equipment for this. Therefore, it is better to contact large clinics and centers.
If stones are suspected, endoscopic ultrasonography of the bile ducts is now successfully used. After all, if there are stones there too, then you first need to eliminate them, and only then take on the gallbladder. To avoid those same complications.
Computed tomography will help examine the liver and pancreas. A biochemical blood test will tell you many of the necessary details. Of course, not everyone needs these studies. But if there are any doubts, they cannot be ignored.
So take better care of yourself. Take drastic measures thoughtfully and trust your doctor.
Keep in mind! Prerequisites for the occurrence of gallstone disease are:
1. Overweight;
2. Sedentary lifestyle;
3. Pregnancy.
Make an appointment with our specialists
You can make an appointment for a fee
see a doctor by calling
the consultation and diagnostic center
, or by filling out the form provided.
Terms of provision of paid services can be found here
Make an appointment under the compulsory medical insurance policy
and
directions
you can call
+7
.
Sign up for a paid appointment
What tests need to be taken
A gastroenterologist deals with issues of gallbladder diseases. To begin with, he himself examines the mucous membranes and palpates the stomach. Next, he prescribes additional examinations.
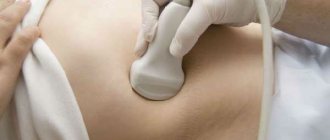
Diagnosis is carried out using ultrasound. The presence of crystallized impurities becomes obvious during the study. Computed tomography and MRI provide an even clearer picture of the condition of the gallbladder and the sediment it contains.
In addition, it may be necessary to determine the level of cholesterol in the blood, since it is the main component of bile sand. To assess liver function, you need to take a biochemical blood test.
Risk factors
Factors that may increase the risk of gallstones include:
- Female
- Age 40 and older
- Overweight or obesity
- Passive lifestyle
- Pregnancy
- High Fat Diet
- High Cholesterol Diet
- Low fiber diet
- Family history of gallstones
- Diabetes
- Having certain blood disorders, such as sickle cell disease or leukemia
- Very fast weight loss
- Taking medications that contain estrogen, such as oral contraceptives or hormone therapy.
- Liver disease
How to get rid of sand
It is important not only to detect sand in the bladder, but also to know how to treat the disease. Based on the examination results and the patient’s condition, the doctor assesses the severity of the disease and prescribes appropriate treatment. The complex of measures to combat sand in the gallbladder includes treatment with medications, physical procedures and, of course, a diet.
Drugs
To get rid of sand in the gallbladder, a specialist will prescribe appropriate medications. The most commonly prescribed drugs for sand are:
- choleretic (Ursohol, Odeston), but in no case should they be taken if stones are present;
- dissolving sand and stones (Ursosan, Ursofalk);
- hepatoprotectors (Hofitol, Rafacholine C);
- painkillers (Analgin, Baralgin);
- antispasmodics (No-shpa, Drotaverine, Spazgan).
The last two categories of drugs can be administered intramuscularly during an attack to accelerate the therapeutic effect.
During treatment, the use of oral contraceptives is prohibited.
Procedures
In some cases, the doctor selects options for removing sand from the gallbladder mechanically. For this, a laser or shock wave method is used, each of which involves crushing large stones.
In severe cases, these methods are not used due to possible negative consequences. Then the gallbladder has to be removed.
Diet
To remove sand from the gallbladder, you first need to limit the consumption of foods containing cholesterol. After all, it is the main component of sand. To do this, you will need to give up fatty meats and fish, animal fats, spicy seasonings, alcohol, and fast food products.
You need to adhere to dietary recommendations for at least six months (table No. 5):
- eat little but often;
- chew food thoroughly;
- increase the consumption of pure still water to 1.5-2 liters per day;
- When cooking, use only vegetable oils;
- increase the amount of plant fiber in the diet.
Of the heat treatment methods, only boiling, baking and steaming are allowed. The last meal should be several hours before going to bed.
Food served on the table should be at a temperature as close as possible to body temperature.
Traditional medicine
You can quickly remove sand at home using proven folk remedies. But before using them, it is recommended to consult a doctor, since if there are large stones, they may begin to move, which will lead to blockage of the duct.
A decoction of chicory in combination with other medicinal herbs not only helps dissolve and remove gallstones, but will also support the liver in its daily work. To prepare the drink you need to take:
- 60 g chicory roots;
- 50 g yarrow herb;
- 30 g lingonberry leaves;
- 20 g chamomile flowers;
- 15 g licorice root.
Pour all ingredients into 500 ml of water, bring to a boil, keep on fire for 8-10 minutes, turn off. When the broth has cooled, it needs to be strained. Take 100 ml of decoction for a month 30 minutes before meals (three times a day).
You can remove sand from the gallbladder using corn silk. 3 tbsp. l. raw materials are poured with 1 glass of boiling water. Leave in a water bath for 15 minutes, turn off and leave for another 45 minutes, then filter. The resulting decoction is brought to a volume of 200 ml with boiled water. You need to take half a glass every 3-4 hours. The duration of treatment is recommended by the doctor.
Cholelithiasis. Initial stage - biliary sludge
Biliary sludge - what is it and what does it look like?
The term “biliary sludge” appeared in the 70s of the last century and came from English-language literature. Biliary - from the Latin word biliaris, which means bile, and sludge (English Sludge) - “suspension, dirt, mud, turbidity, silt, sand, ice porridge”, since there is no clear translation, the term sludge is used.
Currently, biliary sludge is understood as any heterogeneity of bile in the gallbladder and ducts, which is detected by ultrasound examination (ultrasound). Detection of biliary sludge is the initial stage of cholelithiasis, its prestone stage.
The first attempts to isolate the pre-stone stage of cholelithiasis were first made in the 70s of the last century, when scientists identified the initial stage of cholelithiasis, understanding by it biochemical changes in the quality of bile with subsequent physico-chemical disturbances in its structure, leading to the formation of cholesterol crystals and the formation of biliary sludge.
Progress in the study and diagnosis of the initial stages of cholelithiasis occurred when ultrasonographic examination (ultrasound) came into widespread practice, which made it possible to create a classification of cholelithiasis and identify types of biliary sludge. Currently, biliary sludge includes any heterogeneity of bile detected by ultrasound.
Main variants of biliary sludge
Echonic bile with clots
Bile with the presence of single or multiple areas of increased echogenicity, having clear or blurred contours, displaced, without an acoustic shadow (loose clots), often located along the posterior wall of the gallbladder.
Suspension of hyperechoic particles
Point, single or multiple, displaced hyperechoic formations that do not produce an acoustic shadow, detected when the body position changes.
Putty-like bile
Echo-heterogeneous bile with the presence of areas approaching the echogenicity of the liver parenchyma, displaced or fixed to the wall of the gallbladder, visible as a clear contour that does not give an acoustic shadow.
In clinical practice, in more than 70% of cases, biliary sludge variant 2 is encountered - a suspension of hyperechoic particles; the detection frequency of the other two sludge variants is 10-12%.
The sensitivity of ultrasound in diagnosing biliary sludge is 55-65%, and the specificity is more than 90%.
Among patients with complaints characteristic of damage to the biliary tract and gallbladder, biliary sludge is detected in 24-55% of cases.
Prognosis and prevention
Even complete freedom from sand in the gall bladder cannot be a reason to breathe a sigh of relief and return to your previous way of life. On the contrary, knowing the inclinations and weaknesses of your body, you need to be on guard so that the disease does not recur. Correct dietary preferences, active physical activity, and regular walks in the fresh air play a huge role in prevention.
Sand in the cavity of the gallbladder is not the worst diagnosis. If you start acting quickly and correctly, the disease will not progress. Then you can forget about gallstone problems for a long time.