Appendicitis is a very common disease, affecting one in ten people. It would seem that everyone knows the symptoms of appendicitis since childhood, but for some reason the disease is sometimes difficult to diagnose even for experienced surgeons. Today we’ll figure out what signs and how you can identify appendicitis. And we will find out what will happen if you delay the diagnosis of the disease and why you should go for an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity if you have abdominal pain.
What is the appendix and appendicitis and why is the disease difficult to diagnose?
The content of the article
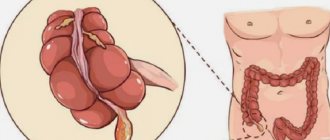
The appendix, the vermiform appendage of the cecum, is an organ of variable size and location. You can roughly determine where the appendix is by drawing 2 imaginary lines:
- horizontally, from the navel to the right;
- vertically, from the right breast nipple down.
The lower right corner formed by the crosshairs of these lines is the right iliac region - the most likely location of the appendix. Due to the long mesentery, the appendix is easily displaced, therefore, where exactly the appendix is located is determined by ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
Inflammation of the appendix is called appendicitis. The disease is characterized by the variety and complexity of symptoms. Abdominal pain associated with appendicitis is typically similar to symptoms of other abdominal and pelvic conditions, including diverticulitis, ovarian mass, ectopic pregnancy, and even kidney stones.
Every year, about 300 thousand operations to remove the appendix turn out to be erroneous due to a false diagnosis.
It is especially difficult to diagnose appendicitis in the initial stages, when the pain is not strictly localized and the symptoms are too vague, and in chronic forms - only ultrasound helps here. You can independently guess that appendicitis has begun only when the pain has already reached its peak and the operation may go beyond a simple one.
Diagnosis of appendicitis
- First of all, a consultation with a surgeon is required in the first hour of hospitalization. Special diagnostic scales are used (AAS, Alvarado, RIPASA).
- If you have appendicitis in women, you need to consult a gynecologist.
- For dysuria, consult a urologist.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
- CT scan of the abdominal cavity (pregnant women with appendicitis undergo ultrasound or MRI instead of CT).
- Diagnostic laparoscopy is a minimally invasive intervention in which the abdominal cavity is examined through a small incision with a laparoscope. Having detected signs of appendicitis, they proceed to laparoscopic appendectomy.
Is appendicitis dangerous?
Having identified appendicitis, the patient is referred for surgery - more than a million such interventions are performed in the Russian Federation every year. Since this organ is not vital, if the appendix is removed in a timely manner, health quickly returns to normal.
If the disease has gone too far and the inflammation has developed into peritonitis - purulent inflammation of the peritoneum, you can lose not only neighboring organs, but also your life along with the appendix. According to statistics, approximately 5 thousand patients die annually from complications of appendicitis.
Types of pathology
Acute appendicitis develops rapidly and manifests itself with pronounced symptoms. With inaction, the pain intensifies and inflammation can lead to serious complications.
By its nature, acute appendicitis can be complicated or uncomplicated. Uncomplicated pathology, in turn, has 2 forms: catarrhal (only the mucous membrane is inflamed), destructive (deeper layers are affected).
Chronic is a fairly rare form. In most cases, it develops as a result of acute appendicitis in the absence of treatment. Has the same symptoms, but they manifest themselves very sluggishly. There are periods of exacerbation and remission, like any chronic disease.
Chronic appendicitis is also divided into subtypes:
- Residual - a consequence of acute appendicitis that ended in self-healing. It manifests itself as a dull aching pain in the right iliac region.
- Recurrent – has a paroxysmal nature: exacerbations occur from time to time, followed by remission.
- Primary chronic – develops independently, without preceding acute appendicitis.
Signs and symptoms of appendicitis in adults
Attacks of appendicitis usually appear between the ages of 10 and 30, but the disease can occur at any age. The pathology is rare only in children under 2 years of age.
The 10 most common signs and symptoms of appendicitis:
- abdominal pain;
- tightening of the abdominal wall;
- nausea and vomiting;
- loss of appetite;
- fever;
- diarrhea;
- constipation;
- abdominal distension;
- leukocytosis (increased number of white blood cells in the blood).
Not all of the signs and symptoms listed above are necessarily present in patients with acute appendicitis. In fact, some of them, such as diarrhea, constipation or bloating, occur in less than half the cases.
Treatment of appendicitis
In the vast majority of cases, acute appendicitis requires surgery.
Only with appendiceal infiltrate and sometimes during pregnancy do they begin with conservative therapy, that is, intravenous antibiotics (amoxiclav or cefotaxime with metronidazole, tigecycline, ertapenem) for 2 days. Before the operation, medication preparation is carried out (water and electrolyte disturbances are eliminated, antibiotic therapy is administered, intoxication and pain are relieved, and thrombosis is prevented).
Removal of appendicitis - appendectomy - is performed as an abdominal or laparoscopic operation.
The risk of blood clots increases with:
- heavy weight;
- over 50 years of age;
- oncological diseases;
- history of heart attack and stroke;
- varicose veins;
- SLE and erythremia;
- postpartum period;
- injuries;
- taking hormonal contraceptives.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia or conduction anesthesia.
In case of a complicated course, antibiotics are also prescribed in the postoperative period; in case of catarrhal appendicitis, this is not required. On the first day, only liquid pureed food is given. The patient is discharged from the hospital on the 3-4th day, and the sutures are removed on the 5-8th day.
Features of pain syndrome with appendicitis in adults
- The most typical symptom, present in almost 100% of cases of appendicitis, is abdominal pain. But abdominal pain can be caused by dozens of different diseases. The appendix itself is a poorly innervated organ, so the first signs of appendicitis are difficult to recognize even by the body itself. Despite the fact that the organ is located in the lower right quadrant of the abdominal cavity, pain with appendicitis in the first 6-8 hours is usually felt around the navel. The patient cannot accurately determine the place that hurts. When asked what and where is bothering him, he moves his hand around his navel.
- During the first 24 hours, as inflammation spreads to the intestinal loops and peritoneum (the membrane surrounding the gastrointestinal tract), the brain receives precise signals about problems in the lower right side of the abdomen.
- Over time, the pain completely migrates to the right lower quadrant of the abdominal cavity, manifesting itself in a specific point. This symptom of appendicitis is diagnosed in 60% of cases.
- When the peritoneum is affected, the pain of appendicitis intensifies, and palpation of the abdomen becomes very painful. The pain also tends to get worse when the patient coughs, tries to walk, or makes any sudden movements.
On physical examination, there is a typical sign of acute appendicitis pain called decompression or Bloomberg's sign. This signal is examined by pressing the hand on the lower right side of the abdomen. When there is appendicitis, rapid removal of the arms causes severe pain at the site, much greater than the pain caused by compression.
How is diagnostics carried out?
The appendix can be examined at any local clinic or private medical center. The cost of diagnostics is affordable for every average person.
Preparation
No special preparatory measures are required before performing an ultrasound scan of the appendix. Despite this, due to possible difficulties in visualizing the organ against the background of excess gas formation, it is recommended to stop eating foods that increase it 2 days before: cabbage, peas, legumes, dairy products. On the contrary, it is recommended to include grain porridge, meat, lean fish, and low-fat cheese in your diet.
In addition, some doctors recommend taking special medications that can help get rid of flatulence. This can be activated carbon or Espumisan.
Other forms of appendicitis pain: appendicitis on the right, back and groin
Where exactly the pain is concentrated during an attack of appendicitis cannot be described by small children, elderly people, immunocompromised patients who do not develop violent inflammatory processes, etc. Abdominal pain is often difficult to recognize due to severe headaches and other signs of inflammation.
Atypical pain is observed in the following cases:
- In approximately 15% of people, the appendix is located posteriorly, and as a result, instead of the typical pain in the right lower quadrant, the patient may complain of back pain, right upper quadrant pain, or pain around the right flank.
- If the appendages are low, the pain may be in the groin, anus or pubic area. Urination may cause pain to worsen.
- If the organ is longer than usual and extends to the left side of the abdominal cavity, the stomach may hurt on the left side.
- Chronic appendicitis is manifested by attacks of pain that pass without reaching a peak.
Since in chronic appendicitis other organs are also involved in the process, it is very difficult to determine the exact location of the pain.
Causes of appendicitis
The exact reasons for the development of the inflammatory process are still unclear. But there are several common options:
- Disturbance in the balance of microflora - bacteria that are safe in a normal environment become toxic and cause inflammation.
- Vasospasm causes deterioration in tissue nutrition. Some areas die and become a source of infection.
- Stagnation in the intestines - feces, foreign bodies, neoplasms or parasites can close the lumen of the appendix. At the site of closure, mucus accumulates, where the microbiome begins to multiply. Narrowing and compression of the appendix disrupts blood circulation and lymph flow, which leads to rapid progression of inflammation and necrosis of appendix tissue.
A predisposing factor will be frequent constipation, which forms fecal stones.
Can nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, diarrhea and constipation be considered signs of appendicitis?
Nausea, vomiting and loss of appetite are three symptoms that usually occur soon after the onset of abdominal pain. This ailment occurs in 90% of cases of appendicitis. Diarrhea or constipation, especially severe ones, are much less common.
All these symptoms also occur with any disease if it is associated with the abdominal organs, so it is impossible to diagnose appendicitis using them. However, when these signs are associated with abdominal pain that worsens and migrates to the lower right quadrant within 24 hours, a diagnosis of appendicitis becomes highly likely.
The classic triad of appendicitis symptoms is abdominal pain, vomiting and loss of appetite.
Leukocytosis
Leukocytosis is a laboratory sign indicating an increase in the number of white blood cells in the blood. White blood cells are one of the most important protective cells in our immune system. When an infection enters the body or an extensive inflammatory process begins, there is an increase in the production of white blood cells.
More than 80% of patients with acute appendicitis have leukocytosis on blood tests. The more intense the leukocytosis, the more intense the inflammatory process.
Signs and symptoms of appendicitis in babies, children and teenagers
Appendicitis is rare in children under the age of five, and it is especially rare when it is diagnosed before the age of 1 year, but pathology cannot be completely excluded. The low incidence of appendicitis in this age group is likely due to the conical shape of the appendix, as opposed to the tubular organ in adults and older children.
With appendicitis, children are worried about: fever, vomiting, diffuse abdominal pain and abdominal stiffness are the predominant symptoms. Additional signs: irritability, wheezing, difficulty walking and complaints of pain in the right thigh.
Features of inflammation of the appendix in childhood:
- migration of pain to the right lower quadrant of the abdominal cavity occurs in less than 50% of cases;
- diarrhea and fever (37.8 - 38 degrees) are much more common than in adults.
The frequency of signs and symptoms of appendicitis in this age group is as follows:
- abdominal pain - 94%;
- fever - 90%;
- vomiting - 83%;
- loss of appetite - 74%;
- abdominal wall tension - 72%;
- diarrhea - 46%.
The clinical picture of appendicitis in adolescents is basically the same as in adults. In children under 12 years of age, the most common signs of appendicitis are abdominal pain and vomiting. The characteristic transfer of pain to the lower right quadrant may be absent.
The frequency of signs and symptoms of appendicitis in this age group is as follows:
- pain in the right lower quadrant of the abdominal cavity - 82%;
- nausea - 79%;
- loss of appetite - 75%;
- vomiting - 66%;
- fever - 47%;
- diarrhea - 16%.
What the study shows
Classic symptoms of appendicitis occur in only 50% of cases. In other people, a different picture is observed, which is inherent in many other pathologies, including those that do not occur in the appendix. To make a diagnosis and identify the cause of pain, an ultrasound is prescribed.
Ultrasound is characterized by painlessness and allows you to detect the following changes in the appendix:
- tubular structure in normal condition;
- a tubular structure in an inflamed state;
- perforated tubular structure;
- signs of an abscess;
- signs of peritonitis;
- signs of gangrenous changes;
- signs of sepsis.
By performing an ultrasound of the appendix in a timely manner, it is possible to identify acute conditions of the organ and immediately take urgent measures to treat the underlying pathology and prevent complications.
Why do you need to immediately perform an ultrasound for any abdominal pain?
Diagnosis and removal of appendicitis are two simple and inexpensive procedures that are performed in almost every clinic. And at the same time, the number of patients who died from appendicitis is surprisingly high. The main reason for this situation is the carelessness of patients who are too lazy to undergo an ultrasound.
- Due to untimely diagnosis associated with late presentation of patients, the inflammation takes on a catastrophic character - the inflamed caecum festeres and bursts, the contents of the abscess enter the abdominal cavity, causing purulent peritonitis.
- Atypical symptoms and pain are attributed to other causes - mild food poisoning, colds, etc. The patient begins to self-medicate, temporarily dampening the process. Chronic appendicitis is a constant source of infection in the body. Sooner or later he will make himself known.
- The appendix shares lymph and blood circulation with other organs, so the infection spreads to them. Advanced general inflammation is already difficult to detect on ultrasound; various types of surgical intervention are required, for example, diagnostic laparoscopy.
That's why, if you notice any discomfort in the abdominal area, you need to sign up for an abdominal ultrasound. Seeing that inflammation of the appendix begins, the doctor will print out the results and immediately send you to surgery. If the diagnosis is not confirmed, other pathologies will be identified, which, quite possibly, also need to be treated immediately.
Recovery after appendectomy
With uncomplicated appendicitis, recovery occurs quickly; complications require longer hospitalization and a longer period of postoperative rehabilitation.
Factors contributing to early recovery: early diagnosis and timely surgery, absence of concomitant diseases, young age, absence of complications.
Risk factors: late hospitalization, obesity, elderly and senile age, peritonitis, sepsis, multiple concomitant diseases.
Within a month after removal of appendicitis you should:
- limit physical activity, especially stress on the abdominal muscles;
- follow a diet that excludes vegetables, fruits, essential oils, smoked meats, animal fats, fried, spicy foods, foods rich in purines and cholesterol (red meat, lard, jelly, strong broths, packaged soups, smoked meats, fatty fish, legumes, canned food) , raspberries, figs, grapes, eggs, cottage cheese, butter, margarine, fatty dairy products.
With the modern level of development of medicine, appendicitis is treatable, but much depends on timely access to a doctor and correct behavior after surgery.