A ruptured appendix due to acute or chronic appendicitis is the result of failure to provide emergency medical care within 1-2 days. In acute cases, it may take only 10-12 hours before rupture.
Rupture of the appendix is a serious complication of appendicitis, leading to the spread of purulent-infectious exudate beyond the vermiform appendix of the cecum, diffuse peritonitis. If your appendix bursts, you should immediately consult a doctor.
What is a ruptured appendix
Rupture of the appendix in acute appendicitis is one of the most severe surgical complications , when a purulent-infectious infiltrate penetrates beyond the cecum, fills the peritoneal cavity and contributes to the development of diffuse peritonitis. In fact, the wall of the appendix is perforated, and the contents flow out. Doctors often call the stage of appendix rupture peritonitis.
The high risk of mortality from appendicitis is due precisely to the development of inflammation of the subcutaneous fatty tissue of the peritoneum and abdominal organs, when even surgical intervention does not guarantee complete recovery. The consequences of a ruptured appendix and generalized peritonitis are always serious and require long-term rehabilitation and compliance with all medical recommendations.
Signs and stages of a ruptured appendix
If the operation is not performed in a timely manner, inflammation of the appendicular process develops into more dangerous forms. The vermiform appendix bursts, which leads to infection and death.
Symptoms of peritonitis
- Sharp throbbing pain in the abdominal cavity;
- Flatulence and bloating;
- Abdominal wall tension;
- Feverish state against a background of high temperature, chills;
- Severe fatigue;
- Tachycardia, difficulty breathing, shortness of breath;
- Loss of appetite;
- Problems with urination;
- Constipation, vomiting.
Vomiting gradually includes an admixture of blood and becomes yellow in color. Pain in the abdominal cavity intensifies during movement and palpation. Frequent urge to urinate.
Peritonitis also manifests itself against the background of pancreatitis, inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs, acute gynecological diseases, postpartum complications, and permanent intestinal obstruction.
Stages of peritonitis
When the appendix ruptures, peritonitis begins. The disease has four stages:
- Irritation (ruptured appendix). The patient feels a sharp stabbing pain in the lower abdominal cavity, nausea, and bloating appears. Body temperature rises, vomiting may occur. On palpation, a feeling of warmth spreading throughout the abdomen appears. The abdominal organs are working normally, but infection is already beginning.
- Subsidence of painful sensations. The patient experiences relief, the pain recedes due to paralysis of the nerve endings. Nausea does not bother me, vomiting stops. Sweating, increased heart rate and pulse appear. Complete intestinal obstruction begins.
- Intensive development. The manifestation of symptoms increases many times over, leading to significant deterioration of the patient’s condition. Symptoms of body intoxication reappear (nausea, vomiting, bloating, fever up to 40 degrees). The abdominal organs (stomach, spleen, liver, bladder, etc.) suffer. Increased gas formation.
- Critical condition. A ruptured appendicular process leads to loss of consciousness if the patient is not at rest. Cutting paroxysmal pain in the peritoneum, intense constant vomiting. There are malfunctions in the functioning of the heart muscle, the functions of the respiratory system are inhibited, and renal failure appears.
If help is untimely, the patient dies. The slightest symptom of peritonitis is grounds for emergency hospitalization.
Symptoms of a burst appendix
What symptoms occur when appendicitis bursts? The main symptom of acute appendicitis is acute pain in the lower abdomen on the right . It grows and can be localized near the navel or radiate across the entire surface of the peritoneum, into the dorsum and right hypochondrium.
The localization and wandering of the pain impulse depend on the topography of the appendix . From the onset of pain to signs of intoxication (vomiting, nausea, hyperthermia) can take from one to several hours. Other symptoms against the background of acute unbearable pain recede into the background or are not recorded when the patient is questioned about concomitant complaints.
Rupture with appendicitis is characterized by a sharp attack of pain with its further subsidence . Reducing pain and calming is an unfavorable prognostic sign, which indicates necrosis, gangrenous changes in the structure of connective tissue, and paralysis of nerve endings.
Note! You can also determine the moment of rupture by a feeling of warmth in the lower abdomen, as if a warm liquid is spreading inside. A day after the rupture, peritonitis develops, acute pain returns, and intoxication intensifies.
Stages of rupture
If the appendix bursts, the pathological process will go through several key stages. What are the stages of development of a ruptured appendix called? They are closely related to the peculiarities of the formation of diffuse peritonitis:
- Stage I - reactive . The patient complains of acute spasmodic pain in the lower abdomen, near the navel. Children often lose consciousness from painful shock. Vomiting, nausea, decreased temperature, pallor and sweating of the skin are observed.
- Stage II - toxic . The duration of the period varies from several hours to two days. Intoxication becomes severe, weakness sets in, blood pressure and pulse decrease, vomiting is constant, and dehydration develops. In children, the toxic stage without assistance often ends in death.
- Stage III - terminal . At a later stage, there is transient relief when symptoms subside. The stage is characterized by tissue necrosis and necrosis of nerve endings. The patient may lose consciousness or fall into a coma from severe intoxication.
We recommend: Reasons for the formation of polyps in the intestines, their symptoms and treatment
At the third stage of rupture and advanced peritonitis, it is quite difficult to save the patient even with the full scope of medical intervention. Survival is also determined by the body's protective resources.
Can it burst without pain?
Acute appendicitis is always accompanied by pain that constantly increases . It is the pain syndrome that contributes to timely consultation with a doctor. The rupture itself may not be accompanied by pain; this moment can be missed due to severe background pain due to acute appendicitis.
Usually a doctor is consulted at the first stage of acute appendicitis , since it is impossible to endure and endure the pain for 24 hours. Sometimes patients harm themselves when they begin to relieve spasms and pain with painkillers.
Symptoms of appendicitis
The first signs of appendicitis are pain in the abdominal cavity. The pain is initially localized in the center, around the navel or in the upper abdomen. Within an hour, the pain radiates to the right iliac region (lower peritoneum).
In some cases, the entire abdominal cavity, lumbar region hurts, and there may be stabbing pain in the area of the liver and kidneys. The atypical anatomical structure of the body suggests the location of the appendix on the left side. In this case, it will be more difficult to understand that it is appendicitis. Tenderness in the left iliac region may indicate a number of other diseases, especially if the patient is a woman.
Parallel symptoms will help you recognize the disease:
- Temperature increase.
- Nausea, possible vomiting.
- Intestinal disorder.
- Weakness, fatigue.
- Interruptions in the functioning of the heart muscle (tachycardia).
Gradually the pain increases. If the operation is not performed on time, the consequences will be insidious. The cessation of painful sensations occurs when appendicitis bursts. Inflammation of the appendicular process develops into peritonitis (inflammation of the abdominal cavity).
Provoking factors
Main reasons for the breakup:
- long-term use of antispasmodic and painkillers;
- atypical location of the rudimentary process, its bend;
- injuries of the peritoneum and pelvic organs;
- concomitant inflammatory diseases of the intestinal tract.
Considering that rupture occurs as a result of long-term inflammation of the appendix , one of the factors is the lack of timely medical care for appendicitis.
Prevention
To prevent peritonitis from developing, timely removal of the inflamed appendicular process is necessary. The operation should take place within the first three days after symptoms of acute appendicitis are detected.
Urgent consultation with a doctor
If the slightest signs of disease occur, you should contact a specialized institution. Sometimes the diagnosis is difficult to determine. In this case, hardware examinations (ultrasound, radiography, laparoscopy) are prescribed. The author's diagnosis is also used (43 symptoms of appendicitis).
According to statistical studies, 65% of people with appendicitis are women of reproductive age. Diagnosis of such patients is extremely difficult. The symptoms of inflammation of the appendix are similar to the symptoms of most exclusively female diseases (gynecological). Pregnant women are a special risk group; diagnosis is complicated by fetal development and uterine enlargement; delay will lead to serious consequences (premature birth, placental abruption, threat of miscarriage).
Nutrition rules
To delay the onset of appendicitis, you must follow some rules:
- Balanced, healthy eating.
- Eliminate unhealthy and “useless” foods (fast food, fried, spicy, fatty).
- Chew pieces of food thoroughly.
- Do not swallow seeds, pits, thick peels, or chewing gum.
- Eat more fruits and berries (apples, pears, raspberries).
- Consume foods with fiber (cucumbers, cabbage, carrots, corn, beets, tomatoes, bran, flaxseed or oil).
- Undergo preventive examinations with a gastroenterologist (1-2 times a year).
- Eliminate alcohol and cigarettes from consumption.
- Cleanse the intestinal tract (use enemas, micro, water, 1-2 times a month, depending on the state of intestinal motility).
Each individual sign may indicate the development of inflammatory processes. You urgently need to consult a doctor. Even if the diagnosis is not confirmed, you should not rush to leave the medical facility. Inflammation reaches its climax 12-24 hours after the start of the infection process. Health is not something to joke about.
Diagnostics
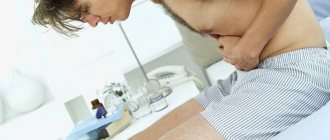
Diagnosis is based on a physical examination of the patient, an objective assessment of the condition , palpation of the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs. When palpating, there is pronounced pain in the area of pressure and stroking; when bending the right leg, it intensifies, and when lying on the left side, the pain becomes pressing.
Ultrasound of the peritoneum and pelvic organs and radiography are indicated as differential diagnostics. If the appendage of the cecum is atypically located and atypical symptoms develop, magnetic resonance imaging may be performed. Blood and urine tests are required.
In children
Symptoms and methods for diagnosing an acute surgical condition do not differ significantly . The psychological factor is of great importance. Children of early preschool and school age tend to hide symptoms due to fear of medical procedures.
Trouble is determined by moodiness, elevated body temperature, refusal to eat, and uncontrollable vomiting.
Important! Most complications are associated with appendicitis in children, since they are not able to objectively assess the degree of pain, its localization, and variations in pain during diagnostic procedures.
Treatment of peritonitis
If the development of peritonitis is diagnosed in the early stages, then successful treatment is possible. Otherwise, the disease cannot be dealt with and the patient will die.
Diagnostics
To make the correct diagnosis, the doctor, after a preliminary examination, prescribes:
- General, biochemical blood test;
- General urine analysis;
- Ultrasound examination, CT scan, x-ray of the peritoneum;
- Abdominal puncture.
Special palpation is also performed (after pressing on the abdominal cavity, the doctor sharply withdraws his hand, at which point the patient experiences increased pain).
Medical assistance consists of removing purulent filling in the abdominal cavity during surgery. Postoperative therapy includes antibiotic and detoxification drugs with enhanced action. The recovery process is quite long; round-the-clock observation in a hospital is necessary.
If there is a small accumulation of emissions from the appendix in the peritoneum, drug treatment in a medical facility is possible. If the infiltrate breaks through, urgent surgical intervention follows.
It should be remembered that diffuse peritonitis cannot be treated with medication, using folk recipes. Delay in contacting a specialized institution will lead to the death of the patient! Particular attention should be paid to children. If a child has complaints of abdominal pain, it is necessary to call an ambulance.
Treatment
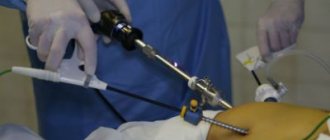
Surgery is the only adequate treatment for ruptured appendix as a complication of acute appendicitis. The operation is urgent. Before it, an urgent ultrasound of the abdominal organs and a rapid blood test are prescribed, and the severity of the patient’s condition must be taken into account.
We recommend: Incubation period of rotavirus in children and adults
The consequences of a rupture are eliminated only by dissecting the peritoneum to inspect most internal organs for their antiseptics. Laparoscopy is rarely used due to the risk of leaving some of the spread exudate.
After cleansing the peritoneum of pus, it is recommended to install drainage structures to ensure unimpeded exit of the pathological mass. Solid suturing is performed only after determining complete dryness of the wound canal.
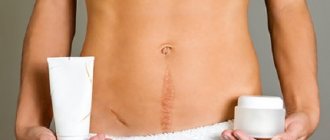
Postoperative period
Immediately after the operation, the patient is placed in a ward or intensive care unit until his condition stabilizes. Throughout the hospital period, the patient is monitored by medical personnel, antibiotic therapy (7-10 days) is prescribed to prevent relapse, and symptomatic treatment.
The duration of rehabilitation is determined by the initial condition of the patient upon admission to the surgical hospital, the addition of other complications, and the volume of surgical intervention. On average, hospital stay for a ruptured appendix ranges from 10 to 21 days.
Diet
On the first day after surgery, fasting and drinking plenty of fluids are recommended. If the patient is in a medically induced coma in the intensive care unit, nutrition is provided parenterally or through an esophageal tube.
In the next 24 hours, broths, slimy porridges, vegetable broths, and drinks are recommended . As the patient recovers, they are gradually transferred to their usual diet. The main indicator of recovery in terms of digestion is painless spontaneous bowel movements a few days after surgery.
Note! The purpose of food restrictions is to reduce the digestive load and internal aggressive factors.
Recommendations and restrictions
From the second day after surgery, physical activity, performing exercises in bed with limited walking , and following all medical recommendations are indicated. The sutures are removed on days 7-10, and discharge from the hospital is made on days 10-14 if there are no complications and the patient’s condition is stable.
Restrictions at the late recovery stage are imposed on:
- visiting a bathhouse, sauna;
- tanning procedures in a solarium;
- drinking alcoholic beverages;
- physical exercise.
We recommend: Is immunity to rotavirus developed after illness?
The course of antibiotic therapy is stopped when leukocytes, the main sign of the inflammatory process, are no longer detected in blood and urine tests.
Note! Failure to comply with medical recommendations leads to disruption of the normal healing of the suture component, adhesions, inguinal-scrotal hernia in boys and men, and other consequences.
Complications and consequences
What happens if appendicitis bursts? A ruptured appendix is in itself a serious complication of acute appendicitis, but if timely assistance is not provided, the following may develop :
- abscess;
- diffuse peritonitis;
- appendicular infiltrate;
- pylephlebitis.
If the patient sees a doctor late, he dies from blood poisoning as a result of extensive sepsis . Advanced peritonitis almost always ends in death. If appendicitis ruptures during pregnancy, the woman needs emergency delivery by cesarean section.