Types of pain due to constipation
In a stomach . Complaints that constipation causes pain in the abdomen (in the left side, right or in the navel area) are made by most people suffering from stool retention. This symptom is not associated with eating or the urge to defecate and can occur at any time. It is caused by excessive stretching of the intestinal walls by feces and gases, which are formed as a result of the decomposition of food in the intestinal lumen and the activity of bacteria.
The pain can be dull and bursting or shooting-like, depending on which part of the intestine is stretched or compressed.
In the lower back . The accumulation of feces, which occurs during constipation, increases intra-abdominal pressure and leads to displacement of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space. As a result, abdominal pain can be complemented by unpleasant or downright painful sensations in the lower back and back, which begin to be subject to increased stress.
Headache . This is one of the symptoms that is least often associated with constipation, but it is one that best characterizes its effect on overall health. The prolonged presence of feces in the intestinal lumen leads to the fact that they begin to decompose and release toxins, which, being absorbed into the bloodstream, spread throughout the body. The combination of constipation and headache may indicate the development of intoxication.
Up to contents
Pain during defecation
To eliminate the painful sensations that accompany the act of defecation, it is necessary to determine their nature as accurately as possible. There can be many reasons
.
Thus, painful bowel movements in females are caused by an ovarian cyst
, and in men, discomfort in the anus after defecation is often caused by
inflammation of the prostate
. However, more often pain during defecation, regardless of the patient’s gender, indicates acute hemorrhoids, anal fissure, paraproctitis, proctitis or rectal cancer.
1. For acute form
Hemorrhoids are symptomatic of the prolapse of hemorrhoids from the anus or their strangulation. Since hemorrhoids are equipped with a large number of receptors, the disease is signaled by severe pain during bowel movements, when running or walking, while sitting or lying down, and sometimes also at rest.
The following accompanying symptoms are possible:
- burning and itching in the anus,
- blood from the anus during bowel movements,
- sensation of a foreign body in the anus.
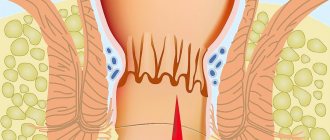
2. Anal fissure
- This is damage to the mucous membrane of the rectum in the area of the anal sphincter. Such damage is accompanied by severe pain that is difficult to ignore; it is localized in the anal canal area and appears after defecation.
In addition to pain, the presence of anal fissures can be signaled by:
- bloody issues,
- itching in the anus,
- spasm of the anal sphincter.
3. Paraproctitis
- This is a purulent inflammation of the tissues that surround the rectum. It is necessary to distinguish between acute and chronic paraproctitis. Depending on the location of the abscess, paraproctitis is divided into subcutaneous, intrasphincteric, ischiorectal (ischiorectal) and pelviorectal.
Symptoms of acute subcutaneous paraproctitis:
- acute pain in the anus, which increases during defecation, with movement and straining,
- swelling of the perineal area,
- redness and swelling of the skin,
- purulent compaction in the anus,
- elevated body temperature, chills.
With ischiorectal paraproctitis, the pain is dull and is felt deeper than with subcutaneous inflammation.
4. Proctitis
- inflammation of the rectal mucosa. Acute proctitis can take different forms.
Frequent symptoms:
- severe pain in the rectal area, aggravated by defecation and radiating to the perineum,
- unusually frequent urge to defecate,
- burning in the anus, sensation of the presence of a foreign body,
- stool disorder,
- bloody discharge from the rectum,
- increased body temperature, weakness.
5. Pain during bowel movements may also indicate the presence of a cancerous tumor.
. Symptoms of colorectal cancer include blood in the stool, pain in the lower abdomen, genitals and thighs.
The choice of treatment method for anal fissures and other pathological conditions is carried out by the doctor differentially based on the results of the examination and depends on the nature of the disease and its clinical manifestations. In any case, discomfort in the anus after defecation cannot be ignored
specialist proctologist.
Is constipation dangerous?
Pain is a perfect mechanism that warns a person about any health problems. From this point of view, pain due to constipation clearly and accurately indicates that the problem has gone beyond the “sphere of influence” of the body - it cannot cope with it on its own and needs help. But pain not only warns or signals - it can also significantly worsen a person’s general condition and even cause the development of the so-called pathological circle. In this case, pain during or after defecation is imprinted on the person’s psyche, and sooner or later he begins to put off visiting the toilet so as not to encounter unpleasant sensations again. This leads to already manageable stool retention. Fecal masses become even more dehydrated and compacted, stretching the intestinal walls even more, and the process of defecation becomes more painful. This fact is again noted at a conscious or subconscious level, and with the next urge, the person once again tries to postpone visiting the toilet in fear of pain. The pathological circle closes.
Up to contents
Tenesmus (false urge to defecate)
False urges to defecate can be painful, they exhaust the patient, causing him to experience severe discomfort. The main reason for their appearance is excessive stimulation of the nerve areas in the rectum, which can be caused by an inflammatory process, for example, colitis, or the appearance of a neoplasm: hemorrhoids, polyps, etc.
Causes
False urge to have a bowel movement is a symptom of many intestinal pathologies. The most common ones are:
- haemorrhoids
- proctitis
- sigmoiditis
- fissures in the rectum
- accumulation of stool in the colon
- fistulas
- polyps
- adenomas
- adenocarcinomas
- stenosis, etc.
Another common cause of false urges is irritable bowel syndrome. This pathology affects the central and autonomic nervous systems and disrupts the intestinal microflora. As a result, patients may feel a false urge to defecate.
Clinical picture and symptoms
False urges are caused by spasms of the smooth muscles of the intestine. These spasms in turn cause contractions of the abs, pelvic muscles and perineum. Contraction of these muscles without relaxation of the sphincters leads to difficulty in bowel movements. Feces either do not come out or are thrown out in small portions. Mucus, blood, or pus may be released.
With tenesmus, patients note the following symptoms:
- cramping pain in the lower abdomen
- strong desire to have a bowel movement
- ineffective trips to the toilet (no or very little stool)
- there is blood, pus, or mucus in the stool
- itching in the anus
- possible prolapse of the intestinal mucosa from the anus
Diagnostics
If you feel false urges, contact a proctologist. Based on the collected medical history and digital examination data, the doctor may prescribe the following studies:
- sigmoidoscopy
- colonoscopy
- irrigoscopy
- coprogram
- bacterial culture of stool
- general blood test, etc.
Treatment
Treatment of false urges is aimed at eliminating the disease that caused them. Depending on the pathology and degree of development, drug or surgical treatment may be used. Infectious pathologies are treated with antibacterial therapy. To treat anal fissures, hemorrhoids and fistulas in the initial stage, ointments, suppositories and drugs that improve blood circulation are used. In more severe and chronic forms, these pathologies are eliminated surgically. To relieve pain during tenesmus, the patient is prescribed myotropic antispasmodics. Also, the complex of therapeutic measures includes therapeutic baths and microenemas.
We recommend that you do not be ashamed of your problem and, at the first discomfort, contact a proctologist.
How to relieve constipation pain
Since the cause of pain is constipation, by eliminating it, you can get rid of the unpleasant or painful sensations that accompany it. In the process of treating bowel disorders, you should follow several simple rules that will help both in the fight against constipation and in relieving pain:
- exclude from your diet foods that stimulate the formation of gases in the intestines (legumes, brown bread, whole milk, fresh cabbage, carbonated drinks, etc.);
- remove from the menu or minimize foods that have a fixing effect (chocolate, rice, potatoes, blueberries, hard-boiled eggs);
- follow the principles of fractional nutrition: eat at least 5-6 times a day in small portions. This will ensure an even flow of food into the gastrointestinal tract and reduce pain caused by stretching of the intestinal walls;
- Make it a habit to take daily walks or do 5-10 minutes of exercise in a ventilated room. Even such mild physical activity will improve intestinal motor function and relieve pain caused by cramps.
Up to contents
Why does pain occur in the anus?
Most often, pain in the rectum is a symptom of the following diseases:
- hemorrhoids
- anal fissure
- thrombosis of hemorrhoids
- paraproctitis
- rectal tumors
Most often, pain is accompanied by bleeding during bowel movements. This is typical for hemorrhoids, as well as anal fissure. Pain from hemorrhoids is associated with the formation of enlarged hemorrhoids and a decrease in the outflow of venous blood from them. With an anal fissure, the integrity of the rectal mucosa is disrupted and tears form. With hemorrhoids, the pain is of medium intensity, and blood is often released in drops at the end of a bowel movement. An anal fissure is characterized by pain of high intensity - cutting, shooting, and bleeding can be significant. With an anal fissure, the groin and lower back may hurt, and urination may be reflexively impaired. Patients in such cases avoid bowel movements, which causes even greater constipation, which is a characteristic manifestation of both hemorrhoids and anal fissure.
Pain in the anus can occur when complications of hemorrhoids develop:
- paraproctitis
- inflammation of the subcutaneous fatty tissue of the rectum, - thrombosis
- the formation of blood clots in hemorrhoids.
When these complications occur, not only the nature of the pain in the anus changes - the constant feeling of itching and burning is replaced by intense, pulsating, shooting sensations. Other symptoms also appear: in the case of thrombosis, this is an increase in hemorrhoids and their acquisition of a “bluish” color; in paraproctitis
– increased body temperature, redness and swelling in the area of the external sphincter of the rectum.
Prolonged pain in the anus is characteristic of cancer. Tumor tissue grows sequentially through all layers of the rectum: this leads to constant irritation of nerve endings and pain of varying intensity. In this case, the pain syndrome is not associated with the act of defecation, and is constant, exhausting in nature, and is also difficult to treat with traditional methods.
Pain in the anus is a symptom that requires consultation with an appropriate specialist. This symptom is nonspecific and is characteristic of many diseases not only of the rectum, but also of nearby organs. Only a specialist will be able to conduct a full examination, recommend the necessary diagnostic measures, make the correct diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Procto-Glivenol® is a modern, combined drug for the treatment of hemorrhoids
Procto-Glyvenol® reduces the incidence of bleeding from hemorrhoids thanks to tribenoside, does not contain hormones and antibiotics, is available in the form of suppositories or cream, which allows each patient to choose the most comfortable treatment.
More information about the drug