Mild, moderate or severe pain in the lower abdomen in women, the causes of which can be different, is a very common complaint received from numerous patients - both very young and elderly. In some cases, although these are unpleasant, they are normal variants that do not indicate any pathologies. But, often they are one of the symptoms of a large list of diseases. First of all, gynecological health is under suspicion, although pain can also arise for other reasons. In any case, you need the help of specialists who will identify the source of the painful condition.
Lower abdominal pain. Causes: gynecological diseases
The content of the article
Pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation
Dysmenorrhea is one of the most common pathologies that causes pain in the lower abdomen. Dysmenorrhea can be a primary cause, or secondary when diseases of the female genital organs already exist.
In severe cases of dysmenorrhea, in addition to abdominal pain, vegetative symptoms appear, such as:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- headache;
- general weakness;
- nervousness.
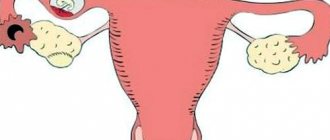
Endometriosis is a cause of pain in the lower abdomen
Endometriosis is a disease characterized by the appearance of the lining of the uterus outside the organ itself. The mucous membrane grows and undergoes the same changes as the uterine mucosa during the menstrual cycle.
Endometriosis
Monthly bleeding of endometriotic tissue very often causes pain in the lower abdomen. Abdominal pain usually begins a few days before the start of menstruation.
Other symptoms of endometriosis include:
- painful sexual intercourse;
- lack of pregnancy (infertility);
- dysmenorrhea.
How to get rid of pain?
Pain in the rectum and lower abdomen, as we already know, is associated with various causes, so treatment can only be prescribed by a doctor. However, if the patient already knows the source of the pain, then you can try to alleviate the condition yourself. The following methods may help:
- Take a hot bath for 15 minutes two to three times a day.
- Use cream or ointment to relieve hemorrhoids.
Take stool softeners or eat fiber foods to reduce pain when moving your bowels. Diet is also important in the prevention and treatment of rectal and lower abdominal pain. We explained the origin of pain in the rectum and lower abdomen, and also talked about the method of getting rid of discomfort.
Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs
Pelvic inflammatory processes can be caused by numerous pathogenic microorganisms: bacteria, viruses, protozoa or fungi.
The main symptoms of inflammation of the female genital organs include:
- stomach ache;
- slight bleeding from the uterus and vagina;
- soreness of the uterus upon independent palpation of the abdomen.
When there is inflammation of the appendages on the right side, the pain that appears must be differentiated from acute inflammation of the appendix.
When is a doctor needed?
You can use ointment or cream to relieve pain.
Pain in the rectum and lower abdomen does not necessarily indicate a serious pathological process, but some signs require medical attention. The patient should consult a doctor if the following symptoms are detected:
- Rectal pain becomes more pronounced, fever and weakness in the body appear.
- The pain spreads from the rectum to a large area of the abdomen.
- Passes more bloody clots in the stool.
- General signs of illness appear, including dizziness and pale skin.
- There is a feeling of a foreign body in the rectum or there is a suspicion of rectal prolapse.
The patient should immediately consult a doctor if he suspects hemorrhoidal thrombosis. Long-term blockage of veins can lead to serious consequences. Also, immediate medical attention is needed if you suspect heavy bleeding or colon cancer. Extensive blood loss may be accompanied by dizziness, pale skin and loss of consciousness.
How to treat rectal fistula, you will learn from the video:
Abdominal pain during pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy in which implantation of the embryo occurs outside the body of the uterus. The most common site of ectopic pregnancy is the fallopian (uterine) tube.
Risk factors for ectopic pregnancy include: in vitro fertilization, pelvic inflammatory disease and gynecological surgery.
To diagnose it, the level of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is determined, ultrasound examination and laparoscopy are performed.
The main symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy include:
- delayed menstrual bleeding;
- irregular discharge mixed with blood from the uterus;
- severe pain in the abdominal cavity.
Types of ectopic pregnancies
Common reasons
If the discomfort is caused by a pathology of the digestive tract, the most common cause is gastritis, enteritis, colitis and infection. It is important to first assume the cause depending on the symptoms that appear in order to prescribe further diagnostics.
| Pathology | Causes | Signs |
| Gastritis | Inflammation of the walls of the stomach with the risk of pathology spreading to the upper intestines | Dyspeptic disorders, heartburn, sudden loss of energy, constant nausea |
| Peritonitis, appendicitis | Inflammatory process in the appendix, release of contents when the wall ruptures (peritonitis) | Fever, decreased appetite, pain in the right side, limping, hypertension |
| Intestinal obstruction | Lack of passage of feces due to adhesions, cancerous formations, penetration of a foreign body, severe spasm | Dry mouth, flatulence, tachycardia, vomiting |
| Intestinal colic | Compression of intestinal muscle tissue due to consumption of poor-quality food, excessively hot or cold food, intoxication, nervous tension | Hard stool with constipation, white plaque in the mouth |
| Poisoning | Eating low-quality food, frequent drinking of large doses of alcohol, exposure to chemical reagents, active metabolism of bacteria or viruses | Increased body temperature, diarrhea, nausea, decreased appetite |
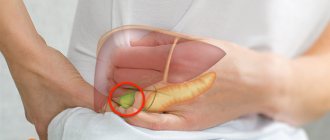
| Pancreatitis | Inflammation of the pancreas | Girdle pain similar to the penetration of a dagger, increased gas formation, impaired stool formation, nausea, vomiting with a yellow admixture (due to bile) |
| Irritable bowel syndrome | Eating poor quality food, frequent nervous tension | Flatulence, loose or hard stools, bad taste in mouth, pain under the ribs |
| Enteritis | Inflammation of the small intestine | Loose stool, colic, flatulence, white or yellow coating on the tongue |
| Helminth infection | Spread of helminths, pinworms, and other parasites into the digestive tract | Colic, flatulence, nausea, vomiting, pallor, dizziness, loss of consciousness, itching in the anus, skin rash |
Attention! Even if the signs that appear indicate a disease, it is impossible to establish a diagnosis without first conducting laboratory and instrumental diagnostics. The doctor identifies the disease and prescribes treatment only after tests. In some cases, surgery may be required, so self-medication is also prohibited.
Miscarriage
Miscarriage is the most common complication of pregnancy. This term refers to the expulsion of the fertilized egg from the uterus before 22 weeks of pregnancy. If three more miscarriages occur after the first one, this condition is called recurrent miscarriage.
The main symptoms of a miscarriage include bleeding and pain in the lower abdomen of varying severity. The most common causes are genetic, hormonal, anatomical and immunological pathologies. The risk of miscarriage is related to the age of the pregnant woman. Women who become pregnant after age 35 have a much higher risk of miscarriage.
Characteristics of rectal pain
Rectal pain can last from a minute to half an hour.
Rectal tenderness is sudden and intense, and the sensation usually lasts less than a minute. In some rare cases, painful discomfort can last up to half an hour.
Patients describe this sensation as a sharp, stabbing or cramping pain that occurs in the anus.
Such pain can wake a person even during deep sleep, depriving him of peace for a long time. The soreness may be chronic and appear daily and then disappear for several weeks or months.
The pain may be related to the levator ani muscle. This sensation will occur in the rectal cavity and will be perceived as strong pressure. The pain increases when sitting and decreases when walking. The discomfort usually lasts 15-20 minutes or longer and tends to recur.
Most forms of hemorrhoids cause only mild pain, but the occurrence of hemorrhoidal thrombosis sharply increases the pain syndrome. This occurs when the blood in the veins of the rectum becomes viscous and forms impassable clots.
Symptoms of hemorrhoidal thrombosis are excruciating throbbing or stabbing pain that begins suddenly and lasts for several days.
An anal fissure causes sharp and cutting pain immediately upon occurrence and gradually develops into a dull pain that lasts for several hours. Damage to the skin in the rectal area may cause mild bleeding and blood in the stool.
Each bowel movement irritates the damaged skin, creating a burning pain. The pain can be so intense that many patients try to prevent bowel movements to no avail.
Genital cancer – pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen
Malignant neoplasms of the genital organs are one of the most common tumors found in women. One of the most common types of cancer is endometrial cancer, and the most severe types with the poorest prognosis are ovarian tumors.
A woman is often not bothered by anything; signs of ovarian cancer are uncharacteristic, and their appearance begins in a late stage of development. Manifestations of ovarian cancer include: increased circumference, pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen. 20% of patients experience symptoms of diseases from the genital organs, gastrointestinal tract and bleeding from the vagina.
Other fairly rare causes of abdominal pain include:
- torsion of the uterine appendages;
- rupture of an ovarian cyst;
- acute degeneration of uterine fibroids.
These diseases are characterized by acute, sudden, very severe pain in the lower abdomen and require hospitalization and emergency medical care.
Pain on the right and left
In some cases, patients complain of pain in a specific location. Pain in the lower abdomen may occur in a woman on the right due to right-sided inflammatory lesions of the uterine appendages (adnexitis, salpingoophoritis), ileal spasm, tumor formations. Also in this place is the cecum, which has a vermiform appendix - the appendix. If it becomes inflamed, appendicitis develops and the patient needs emergency care.
The most common causes of pain in the left lower abdomen in women are secondary inflammation of the appendages, spasm of the sigmoid colon, tumor process, and ulcerative colitis. Sometimes the problem may be associated with disorders in the joints of the spine and their tissues, a herniated disc, or radiculitis.
Prostate diseases
Pain in the lower abdomen in men can occur as a result of prostate disease. Prostate diseases that cause pain in the lower abdomen include:
- inflammation of the prostate gland;
- prostate hypertrophy;
- prostate cancer.
Stages of prostate cancer
Inflammation (prostatitis) in the absence of treatment becomes chronic, possible development of abscess and fistulas of the prostate gland, cystitis and pyelonephritis, infertility due to the formation of autoimmune antibodies.
Pathologies of the reproductive system
There are many causes of pain associated with gynecological problems. Among the most common:
- Endometritis. It is characterized by inflammation of the endometrium, which can occur acutely or chronically. Often accompanied by menstrual irregularities, spotting, uterine bleeding, and nagging pain.
- Adnexitis. Inflammation of the uterine appendages is one of the most common diseases in gynecological practice. In addition to painful sensations (can be in one side or spread to the entire lower abdomen), patients are faced with signs of intoxication and fever. The disease is caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi.
- Endometriosis. In this disease, the cells of the uterus grow and end up outside the uterus. Accompanied by pain during urination, defecation, sexual intercourse and simply with sudden movements, heavy bleeding during menstruation. Regardless of the cycle, brownish discharge is observed.
- Uterine fibroids, which are usually characterized by dull pain in the pelvic area. Cysts and other benign, as well as malignant formations can cause discomfort of varying intensity and spasms.
- Spikes. They may be the result of inflammation in the genital organs, varicose veins and other diseases. Complications during pregnancy. This may include spontaneous abortion, placental abruption and other pathologies. In such cases, the pain is sudden and sharp, accompanied by bleeding from the genitals.
Separately, it is worth focusing on sexually transmitted infections - mycoplasmosis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, trichomoniasis and other diseases. They affect the reproductive organs, causing pain, profuse vaginal discharge of a pathogenic nature, burning, itching and are fraught with complications if left untreated.
Diagnostics
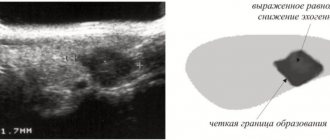
You should contact a therapist. He will refer you to more specialized specialists. Basically, patients are received and examined by a gastroenterologist. If women are suspected of having diseases of the reproductive system, they are examined by a gynecologist. The doctor interviews the patient, palpates the abdomen, and orders blood, urine, and stool tests. A study of the microflora of the urogenital tract is being carried out. Treatment cannot be prescribed without instrumental examination of internal organs. Most often used:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity (often with duplex scanning of blood vessels);
- plain radiograph;
- endoscopy;
- gastroscopy;
- colonoscopy;
- CT scan of the abdominal aorta.
Ultrasound is a mandatory test for heaviness in the lower abdomen. Photo: freepik.com
How is a hard lower abdomen treated?
A tense stomach is treated depending on what caused the development of this symptom. If life is threatened, for example, with appendicitis, adhesions or peritonitis, an urgent operation is required, during which the source of inflammation is removed or stitched. During recovery, antibiotics and other medications are prescribed.
Surgery may also be indicated for endometriosis and polycystic disease. But more often they first try to cope with the disease conservatively with the help of hormonal and anti-inflammatory treatment. The operation is performed only if such therapy does not help.
For other diseases, the methods and duration of treatment are determined by the doctor based on the clinical picture, examination results, the severity of the disease, the presence of complications and some other factors.
You should not self-medicate and use medications that relieve symptoms, as this can lead to the development of complications.
In some cases, for example, during pregnancy or painful ovulation, specific therapy is not required. However, the doctor may prescribe symptomatic treatment that relieves pain and relaxes the muscles of the uterus.
Cherepenko Lyudmila Vikentievna
doctor - therapist • doctor - cardiologist
Heaviness in the lower abdomen is a symptom that is observed in a variety of diseases. You should not self-medicate. The sooner you consult a doctor and start treatment, the better the prognosis. You can get our doctors’ opinion right now.
Online consultation
Treatment
Since heaviness in the lower abdomen can be caused by various diseases, there is no clear treatment program. It depends on the diagnosed disease and the cause of its occurrence.
Infectious inflammations are treated with antibiotics. If the cause is spasms, antispasmodics are prescribed. Intestinal diseases in most cases require complex therapy. It includes taking enzymes and drugs that help protect and restore the mucous membrane. To restore the intestinal microflora, probiotics and synbiotics are needed. Corticosteroid hormones and cytostatics¹ can be used. The patient is recommended to normalize his diet, go on a certain diet, organize fasting days, and walk a lot.
Surgical treatment is performed in complex clinical cases when conservative therapy is not effective. This mainly concerns the removal of tumors and vascular pathologies of the abdominal cavity.