Baby in arms: Pixabay Constipation after childbirth is observed in a third of women. Most of them are faced with this, although not dangerous , but still unpleasant problem in the prenatal period. After the baby is born , it often occurs again , causing discomfort, disrupting well-being and mood. about how to normalize intestinal function and how to get rid of constipation in the article.
Attention! The material is for informational purposes only. You should not resort to the treatment methods described herein without first consulting your doctor.
Constipation after childbirth: causes
Constipation is defined as difficulty or partial bowel movement, as well as a complete absence of bowel movements for one and a half days or more. At the same time, heaviness appears in the abdomen, unpleasant pain occurs, gas formation increases, and metabolic products enter the body, which cause intoxication.
Before answering the question of how to get rid of constipation, let's consider the main reasons for this phenomenon. These include:
- incorrectly formulated diet, including insufficient amount of water consumed;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- weakened and stretched abdominal and perineal muscles due to childbirth;
- increased size of the uterus and its pressure on the intestines;
- impaired peristalsis (motor activity of the intestine, which moves feces);
- psychological problems (especially fear of suture dehiscence after caesarean section);
- congenital elongation of intestinal sections.
Even increased physical and mental stress associated with caring for a baby can cause constipation after childbirth. The forum for young mothers always contains many questions on this topic, since in practice we have to face the fact that women are in no hurry to see a doctor with this problem. But this must be done in order to accurately establish the cause and select a remedy for constipation.
What to do for constipation during pregnancy?
The article was prepared by a specialist for informational purposes only. We urge you not to self-medicate. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
Description of the disease
Constipation during pregnancy is a slow or difficult bowel movement.
In a healthy person, bowel movements normally occur from 3 times a day to 3 times a week. Retention of stool can be considered constipation if it:
- occurs less frequently than every 24 hours;
- accompanied by severe nausea when going to the toilet;
- leaves a feeling of incomplete bowel movement.
People of any age and lifestyle are susceptible to constipation. However, there are conditions that increase the risk of developing a bowel movement disorder. One of them is pregnancy. Gynecologists consider constipation as an inevitable companion of any expectant mother.
Abnormal bowel movements in pregnant women may present with the following symptoms:
- a feeling of pressure, distension in the rectum;
- rumbling, a feeling of “transfusion” along the intestines;
- increased gas formation, bloating;
- pain in the sacrum, buttocks;
- feeling of weakness, malaise, loss of appetite, unpleasant taste in the mouth, coating on the tongue, nausea, headache, nervousness.
Causes of constipation during pregnancy
Changes that occur in a woman’s body during pregnancy can lead to disruptions in the proper functioning of the intestines. These include:
- Hormone progesterone
Progesterone is the main hormone of pregnancy. One of its biological actions is to relax the smooth muscles of internal organs. This is necessary in order to reduce the tone of the uterus and prevent the threat of miscarriage. Since the intestinal wall also consists of smooth muscle fibers, under the influence of the hormone, its activity decreases.
- Pressure of the uterus on the intestines
The growing uterus pushes the intestines backward and upward. This leads to a slowdown in the passage of its contents towards the anus
- Low physical activity
The work of the intestines and the act of defecation are closely related to the condition of the abdominal and perineal muscles. Sedentary work, bed rest when there is a threat of miscarriage, stretching of the anterior abdominal wall by the growing uterus, refusal of physical activity for fear of harming the unborn baby lead to a decrease in the motility of the digestive organs.
- Errors in diet, low water intake
The best stimulator of intestinal function is dietary fiber. Their sources are vegetables, fruits, bran, and some grains (buckwheat, oats). Unfortunately, in big cities, most expectant mothers lack these products.
In order for the intestinal contents to have the desired consistency and be easily transported towards the anus, it is necessary to drink at least 1.5-2 liters of water daily. This factor plays an important role in the development of constipation in pregnant women for whom the attending physician has limited their drinking regime due to high blood pressure, kidney disease or edema.
- Impact of stress
The work of the intestines, like the whole body, is regulated by the nervous system. If there is a malfunction in its functioning, the digestive organs begin to contract chaotically. So-called spastic constipation occurs. Clinically, this is manifested by severe abdominal pain, colic, and the stool takes on the characteristic appearance of “sheep droppings.” Very often during pregnancy there is excessive excitability of the nervous system, which can lead to disturbances in bowel movements.
- Some medications: calcium and iron
Pregnant women taking iron or calcium supplements often experience constipation. This effect is most noticeable when using single drugs and is almost not observed when using multivitamin complexes. Injectable forms of iron do not affect intestinal motility.
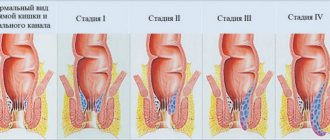
- Diseases of the anal area (fissure, hemorrhoids)
Compression of the veins of the abdominal cavity by the growing uterus, a sedentary image leads to stagnation in the pelvis. This contributes to the expansion of the venous plexuses around the anus and the occurrence of hemorrhoids. One of its symptoms is pain during bowel movements. It can be so strong that women subconsciously put off going to the toilet in order not to experience unpleasant sensations.
What are the dangers of constipation during pregnancy?
Constipation has two types of effects on the expectant mother’s body:
- Local impact
Impaired motility leads to stagnation of contents in the intestinal lumen. Digestive gruel, rich in nutrients, is an ideal environment for the development of microorganisms that normally populate the human digestive tract. This can lead to inflammation of the upper parts of the large intestine - appendix, sigmoid colon. Constant injury to the rectal wall and anal tissues by hard feces can cause the development of proctitis, anal fissures, and inflammation of hemorrhoids.
- Overall Impact
Under the influence of microflora, stagnant intestinal contents undergo decay processes. This releases toxic substances - indole, skatole, ammonia, hydrogen sulfide, methanol. Absorbed into the blood, they cause chronic poisoning of the entire body. This is manifested by weakness, loss of appetite, headaches, nervousness, and bad mood. Pregnant women under the influence of toxic products may experience disturbances in uteroplacental blood flow, delayed fetal development, early aging of the placenta, and premature birth.
Many pregnant women wonder: is it possible to push with constipation during pregnancy? There is no clear answer to this. It all depends on the duration of the bowel movement disorder, the duration and course of pregnancy.
If constipation is short-term, then straining is not dangerous in the 1st and 2nd trimesters. However, towards the end of pregnancy, the need to have bowel movements for a long time can stimulate labor.
With chronic constipation, constant straining leads to overstretching of the muscles and ligaments that support the abdominal organs. This can negatively affect the effectiveness of the pushing period and lead to prolapse of the vagina, uterus and bladder after childbirth.
Any straining is contraindicated for pregnant women with:
- threat of miscarriage;
- late toxicosis, accompanied by high blood pressure;
- eye diseases, including severe myopia;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Constipation during pregnancy: what to do?
It must be remembered that only a doctor can diagnose constipation. Even if the symptoms of the disease completely coincide, the final decision on prescribing a particular treatment should be made only by a specialist.
The following methods can be used to normalize intestinal function:
- diet;
- physical activity;
- medications.
- Diet for constipation during pregnancy
All products, according to their effect on intestinal motility, can be divided into:
- enhancing peristalsis;
- weakening peristalsis.
In order to normalize stool, it is necessary to increase the consumption of products from the first group and try to avoid products from the second.
Have a positive effect on intestinal motility:
- vegetable fiber, which is found in carrots, beets, zucchini, pumpkin, wholemeal bread, buckwheat, oatmeal, and pearl barley;
- products high in organic acids (apples, prunes, figs, dried apricots, dates);
- lactic acid products (unsweetened natural yogurt, kefir, low-fat fermented baked milk).
See the article - what you can and cannot eat if you have constipation
Slow down digestion:
- fatty red meats;
- sweets;
- pastry products;
- White bread;
- rice and semolina porridge;
- smoked meats;
- chocolate;
- drinks containing caffeine - strong tea and coffee;
- canned food;
- semi-finished products and fast food (fast food);
- pasta;
- potato.
One common remedy for treating constipation is eating bran or wholemeal bread. In pregnant women, this method of stimulating digestion is unacceptable. Due to the physiological characteristics of the expectant mother’s body, coarse plant fiber, lingering for a long time in the intestinal lumen, releases a large amount of gases during digestion. This leads to bloating, pain, and negatively affects the well-being of the pregnant woman.
Instead, products containing more delicate plant fibers are recommended: figs, dried apricots, prunes, oatmeal.
For the same reason, you should avoid eating foods that promote gas formation, such as cabbage, legumes, peeled apples, grape juice, radishes, garlic, and turnips.
Pregnant women who have no contraindications regarding the volume of fluid taken should drink 1.5-2 liters of clean drinking water per day.
There are also many special products that can help normalize bowel movements, see the article - what helps with constipation?
- Physical activity
Expectant mothers should remember that pregnancy is not a disease, but a normal physiological state. Therefore, if it proceeds without complications, then there is no need to give up physical activity. You can attend gymnastics or yoga courses for expectant mothers, or do special programs at home, or you can simply walk for at least 1 hour a day. It is best if the walks take place away from roads and crowds.
- Medications
All laxatives can be divided into four groups:
- drugs that increase the volume of stool. Facilitate bowel movements due to the “lubrication” effect. In the form of suppositories (glycerin suppositories) they can be used during pregnancy only in extreme cases when other methods and drugs do not help. For drugs intended for oral use (vaseline oil), pregnancy is a contraindication.
- drugs that slow down the absorption of water from the intestine and cause an increase in the volume of intestinal contents. Drugs of this group are not absorbed in the intestine, are not digested, and do not act on the wall of the colon. Approved for use in pregnant and lactating women. These include: Duphalac, Forlax.
- drugs that enhance motility. Their action is based on stimulating the nerve endings of the intestinal wall. Contraindicated during pregnancy at all stages. These include: guttalax, dulcolax, senna-based preparations (senalex), joster fruits, buckthorn bark.
- drugs that soften stool. Laxatives of this group do not irritate the rectal mucosa, are not absorbed and are not addictive. Allowed during pregnancy at any stage and during breastfeeding. These include: plantain seeds, phytomucil.
Constipation after childbirth
Constipation often complicates the postpartum period. Intestinal motility disorders in the first weeks and months after the birth of a child can be caused by:
- hormonal levels that have not come into balance, when biological substances circulating in the blood have an inhibitory effect on intestinal activity;
- stretched walls of the anterior abdominal wall and perineal muscles, which cannot create effective intra-abdominal pressure;
- sudden mixing of the intestines after the birth of the fetus and reduction in the size of the uterus;
- disruption of bowel function after cesarean section;
- psychological reasons, when women are afraid of defecation due to pain with sutures after episiotomy, suturing of perineal tears, aggravated hemorrhoids;
- lifestyle changes associated with caring for a newborn: lack of sleep, chronic fatigue, poor diet.
What to do? It all depends on the factor that underlies constipation.
If intestinal sluggishness is caused by overstretched abdominal and perineal muscles, then a diet and special sets of exercises for women who have given birth will help.
With sutures after ruptures, episiotomy and caesarean section, softening the consistency of the stool comes to the fore. This can be achieved through diet or travel seed preparations.
In order to restore bowel function on the first day after a cesarean section, early physical activity is necessary: turning in bed, sleeping on the stomach starting from the 2nd day after surgery. Self-massage of the anterior abdominal wall has a good effect. To do this, massage the peri-umbilical area with the right hand in a clockwise circular motion. Carry out 20 massaging movements every 2-3 hours.
Women who are breastfeeding should be careful about consuming foods that have a laxative effect. Many of them can cause increased gas formation in a child. Approved for use during lactation:
- dried apricots;
- prunes;
- boiled beets;
- oatmeal and buckwheat porridge.
However, all children are individual, so it is necessary to monitor the general reaction of the newborn to the introduction of any new product into the mother’s diet.
Author of the article:
Volkov Dmitry Sergeevich |
Ph.D. surgeon, phlebologist Education: Moscow State Medical and Dental University (1996). In 2003, he received a diploma from the educational and scientific medical center for the administration of the President of the Russian Federation. Our authors
Constipation after childbirth: types
How to cure constipation? First of all, you need to establish its type. In the article “Pathogenesis, clinical picture, treatment and prevention of constipation in obstetric practice” O.I. Mikhailova, T.V. Kirsanov and V.L. Tyutyunnik is described by the following main varieties:
Atonic constipation
This type is associated with a decrease in intestinal muscle tone, which disrupts peristalsis. Such muscle weakness often results from cesarean section and is a common reaction to surgical interventions. Errors in diet can also cause its development.
With atonic constipation, a feeling of intestinal fullness is created, the formation of gases increases, the stomach hurts, pulls and aches. Nausea occurs and appetite disappears. Lethargy, apathy and depressed mood are a logical consequence of constipation. During defecation, a lot of formed stool appears first, followed by a liquid part. There may be mucus and blood in the stool.
Spastic constipation
Kolesov D.V., Mash R.D., Belyaev I.N.: Biology.
Human. 8th grade. 3rd ed. — M.: Bustard, 2016 Spastic constipation is a consequence of increased intestinal tone. Simply put, the muscles seem to clamp down and tightly hold the feces inside. The main reason for its occurrence is psychological.
Constipation of this type is accompanied by spasmodic paroxysmal pain in the abdomen on the left. There is also bloating, nausea, loss of appetite, the woman becomes irritable and lethargic. The urge to defecate occurs frequently, but it is not productive. Dense round small portions of feces are also called “sheep feces”.
Congenital lengthening of the intestine
According to the clinical picture, this type resembles spastic constipation. However, its cause is the long passage of feces as a consequence of the congenital characteristics of the woman’s body. When this occurs, the intestinal walls absorb water, leaving the stool dry and hard, making it difficult to pass. Nutritional adjustments and anti-constipation products help solve this problem.
Characteristics
Constipation during lactation manifests itself as a whole complex of symptoms:
- cramping pain;
- bloating and rumbling in the stomach;
- stool becomes lumpy and dense;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- belching;
- feeling of incomplete emptying;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- nervousness, apathy;
- sleep problems;
- decreased performance;
- frequent headaches.
Constipation causes cramping pain in the abdomen
Experts distinguish two main forms of constipation – spastic and atonic. In the first case, difficulties in peristalsis are caused by increased intestinal tone. Feces are passed in small portions in the form of hard compressed stool. Most often, spastic constipation is caused by psychological reasons.
Manifests itself in the form of paroxysmal pain in the left side of the abdomen, flatulence, nausea, lack of appetite, nervousness, fatigue. First of all, women with spastic constipation are advised to establish a daily routine. New mothers need sleep and rest. It is also worth adjusting your diet, drinking more water and not eating prohibited foods.
With atony, the tone of the muscle wall of the intestine, on the contrary, is weakened. The cause of sluggish peristalsis can be a cesarean section, dietary errors, or taking certain medications. Atonic constipation can lead to tears in the rectum and anus, as well as the appearance of bloody stool.
Women with atony are bothered by nagging and aching pain in the abdomen, a feeling of intestinal fullness, nausea, and flatulence. Fighting with home measures alone will not be enough; the condition requires qualified help from a specialist.
How to treat constipation after childbirth
What to do for constipation and how to improve bowel function? Given the prevalence of the problem, many of my colleagues are paying close attention to this issue. In addition, most laxatives are contraindicated for young mothers, so they have to look for other ways to solve the problem.
How to treat constipation? Please note three important points:
Products with laxative effect
Correction of nutrition is the first and very effective remedy for constipation. We are not talking about a strict diet at all. It is important that the diet contains:
- porridge. Oatmeal in the morning, pearl barley or buckwheat as a side dish in the afternoon and evening - and peristalsis will quickly improve;
- vegetable oils (sunflower, olive and others). They are added to ready-made dishes or drunk a teaspoon before meals;
- vegetables and fruits. Apples, apricots, peaches, carrots, beets, and cabbage contain fiber, which is necessary for normal digestion, as well as beneficial vitamins;
- fermented milk products (low-fat kefir and yoghurts);
- black bread;
- dried fruits and compotes based on them.
In addition, it is recommended to drink a glass of water in the morning on an empty stomach, and ensure that you drink enough fluid throughout the day. This simple measure stimulates the intestines well.
Finally, it is worth remembering which foods cause constipation and eliminating them from the menu. What should you not eat if you are constipated? The main list is as follows: rice and semolina porridge, white bread, dark chocolate, strong black tea, nuts, hard cheeses, legumes, blueberries, pears, currants.
Enema for constipation
What to do if you have severe constipation at home? An emergency simple method is enemas:
- ordinary cleansers. This is done using up to 2 liters of boiled water at room temperature (approximately 25–27 °C). The urge to defecate appears very quickly;
- saline. They not only help cleanse the intestines, but also improve its functioning. Dissolve 1 tsp in 100 ml of water. table salt. Half of the resulting solution is injected into the intestinal cavity. The effect is observed after 20 minutes;
- oil Prepared by diluting 3 tbsp. l. sunflower oil in 100 ml of water. The procedure is done before bedtime in order to get the desired effect in the morning.
You cannot use enemas all the time. I had to deal with the consequences of washing out microflora and even more problems with the intestines as a result of constant cleansing with enemas. Therefore, if you have chronic constipation, you should definitely consult a specialist.
Folk remedies for constipation
Kolesov D.V., Mash R.D., Belyaev I.N.: Biology.
Human. 8th grade. 3rd ed. — M.: Bustard, 2016 Most standard laxatives are contraindicated during breastfeeding. The fact is that the active substances will enter the baby’s body with mother’s milk and also affect him. These medications also have a serious drawback: with constant use they are addictive. Therefore, in general, in clinical practice this group of drugs is treated with caution.
The only thing the doctor will recommend in such a situation is suppositories for constipation. The simplest option is a glycerin-based drug. The natural composition does not harm mother and baby and is effective. Such suppositories are contraindicated for hemorrhoids and anal fissures. In this case, sea buckthorn suppositories are used for constipation.
Along with correcting nutrition at home, you can also use the following folk recipes for spastic constipation:
- grate raw potatoes on a coarse grater, squeeze out the juice, dilute with water in a 1:1 ratio, take a quarter glass twice a day half an hour before meals;
- 2 tbsp. l. Boil figs in a glass of milk or water. After cooling, take 1 tbsp. l. three times a day;
- prepare a mixture of equal parts of anise fruit, nettle herb, valerian rhizome, strawberry and peppermint leaves, and chamomile flowers. Pour 1 tbsp boiling water over a glass. l. the resulting collection and leave for 2 hours, after which it is filtered. Take half a glass twice a day after meals.
Atonic constipation is treated using the following folk remedies:
- mix equal parts of anise fruit, cumin and fennel. Take 2 tsp per glass of boiling water. mixture, leave for 20 minutes, filter, drink 50 ml three times a day before meals;
- a mixture of equal quantities of oregano and nettle herbs, rowan and fennel fruits, blackberry leaves is brewed with 1 glass of boiling water, left for 2 hours, filtered, taken 50 ml before meals three times a day;
- pour 1 tbsp into a glass of water. l. gooseberries, boil for 10 minutes, filter. Take 50 ml 4 times a day, you can add sugar, dried apples, cherries.
Recommendations for nursing mothers
A comprehensive approach to the treatment of constipation in women who are breastfeeding is necessary. First of all, you should analyze your diet and lifestyle.1
- Physical exercise will not harm anyone, especially after childbirth, when every woman wants to quickly return to her previous shape. On the other hand, it is important not to overdo it: the degree of activity should be chosen based on how you feel and the doctor’s testimony;
- It is necessary to include in the daily menu fresh or thermally processed vegetables (pumpkin, beets, carrots, zucchini, etc.) and approximately 300 g of berries and fruits (apples, currants, gooseberries, etc.). It is not recommended to eat tropical fruits.
- It is recommended to exclude from the diet: coffee, strong tea, pomegranate juice, winter pears and quince, as they contain tannin (has astringent properties); rice, jelly, cocoa, which reduce colon peristalsis; radishes, onions, radishes and garlic, as they irritate the intestines, as well as cabbage, beans, peas and black bread, which provoke increased gas formation. White bread, pasta and baked goods contribute to constipation, so it is also better to limit their consumption.
- It is worth limiting, or even completely eliminating, the consumption of fish and meat broths, smoked meats, pickles, garlic, and onions from the menu.
- Limit consumption of whole cow's milk. Introduce fermented milk products, cereals and wholemeal bread, lean meat, vegetable oils, and soups into your diet.
- You should drink more water and juices (about a glass of juice with pulp per day, preferably intended for baby food); chicory is recommended instead of coffee.
- You need to avoid worries and walk more in the fresh air.
Causes of constipation in the postpartum period
There are several reasons that determine the manifestation of constipation after childbirth. First of all, changes in intestinal function can be affected by a very sharp change in hormonal levels that occurs after childbirth. When a baby is born, a woman’s abdominal muscles and perineal muscles are stretched and greatly weakened.
In the first days after birth, the uterus, which is still quite enlarged, continues to put pressure on the intestines. The uterus will return to normal size only after 6-8 weeks. At the same time, the intestines are also “in motion”: they gradually shift to their normal position after they have moved during the process of bearing a child. During the postpartum period, a woman’s intestinal motility is very often disrupted, and feces move more slowly.
Women who have had a difficult birth or cesarean section have newly placed stitches on their bodies. Because of their pain, as well as the fear that the stitches will come apart after surgery or episiotomy, the young mother cannot strain enough to get a bowel movement. Hemorrhoids can be considered an equally problematic phenomenon; the pain that occurs with them often becomes an obstacle to the establishment of normal bowel movements after childbirth.
Constipation after childbirth often occurs as a consequence of an incorrect approach to nutrition for a nursing mother. An equally important factor should be considered the constant psychological stress that is associated with new troubles and worries. In addition, congenital intestinal abnormalities can be the cause of postpartum constipation.
Types and stages of constipation
Constipation is a consequence of a disturbance in the process of formation and subsequent movement of feces through the intestines. With the development of constipation, digestive waste stagnates in the intestines or rectum. It is customary to distinguish several types of constipation according to etiopathogenetic characteristics. Alimentary constipation occurs when a person violates the dietary regime, has an inadequate diet, or consumes too little fluid. With dyskinetic constipation, the motility of the colon is impaired, and such constipation can be hypotonic , hypertonic , or spastic . If a patient has organic constipation, then it is caused by various defects and tumors of the spinal cord, as well as the presence of scars and other formations in the anus and anorectal area.
Conditioned reflex constipation occurs when the urge to defecate is constantly suppressed, in stressful situations, and also in the presence of neuropsychogenic causes. This type of constipation sometimes develops in patients with rectal fissures and paraproctitis . Constipation of the intoxication type occurs in the case of intoxication with poisons or medications.
Clinically speaking, there are three stages of constipation. In the compensated stage, the act of defecation occurs after 2-3 days, and the patient feels that the intestines have not completely emptied. Approximately half of patients suffer from flatulence and abdominal pain. At the subcompensated stage, stool is delayed for a period of 3 to 5 days. In this case, defecation occurs only after taking laxatives or an enema. In most cases, flatulence occurs, abdominal pain bothers you, and a person feels pain when defecating.
The decompensated stage of constipation is characterized by the absence of stool for 10 days or more. The act of defecation occurs only after hypertonic or siphon enemas. The patient develops signs of fecal intoxication, and during palpation, “fecal stones” are found in the abdomen.