Material reviewer
Professor Kapranov S.A. — Doctor of Medical Sciences, twice Laureate of State Prizes of the Government of the Russian Federation in the field of science and technology, Laureate of the Lenin Komsomol Prize, author of more than 350 scientific works on medicine, 7 monographs, and 10 patents for inventions in medicine, with more than 30 years of personal experience 10,000 different endovascular operations
Today, hemorrhoids are considered to be one of the most unaesthetic and “shameful” diseases, which is unpleasant to talk about, let alone close people, even medical specialists. In this regard, many remain silent at an appointment with a proctologist, suffering from severe hemorrhoids or some more serious complication.
Important! Treatment of developing hemorrhoids is quick and painless if you treat the disease with conservative methods in its initial stages.
One of the most serious consequences of hemorrhoids that are not treated in a timely manner is thrombosis of the hemorrhoid (thrombophlebitis). The pain syndrome at this stage of the disease is so severe that the patient has no choice but to seek help from a proctologist. Such lateness does not bode well!
The essence of the disease
Hemorrhoidal thrombosis is a complication that occurs when hemorrhoids occur in an acute form. It is characterized by the appearance of blood clots in the cavernous vascular plexuses of the anal area. Thrombosis of an inflamed hemorrhoid does not occur by itself. This means that the patient already had a hidden or external hemorrhoid in which a blood clot had formed.
Important! The pathological condition is often caused by a chronic inflammatory process localized on an enlarged hemorrhoidal node, but extremely rarely it occurs in parallel with actively developing hemorrhoids.
Schematically, thrombosis of an inflamed hemorrhoid occurs as follows:
- On the inner or outer side of the anal sphincter there is an inflamed venous plexus, the membrane of which is damaged.
- To avoid bleeding, the venous lumen is clogged with a blood clot, which, in turn, disrupts the flow of blood.
- The location of the pathology swells, which is accompanied by the onset of an active inflammatory process.
- A feeling of sharp pain appears in the rectum or anal area. Moreover, the size of the elements of thrombosis does not in any way affect the strength of the pain syndrome.
- The patient develops a natural fear of going to the toilet, provoking the syndrome of “psychological constipation”.
- Defecation after a long period of time leads to the fact that hemorrhoidal cones are damaged, and the pain, as a result, intensifies.
Statistical data indicate that acute hemorrhoidal thrombosis occurs in almost every 3rd patient with chronic inflammation and enlarged hemorrhoidal nodes.
What are hemorrhoids and how do they manifest?
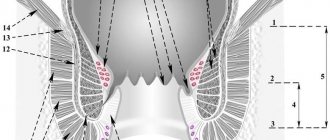
Hemorrhoids are a vascular disease that is characterized by varicose veins of the cavernous hemorrhoidal plexuses of the rectal veins. The immediate cause of this pathology is an excessive increase in blood pressure in the vessels of the rectum and weakness of the venous wall of the drainage vessels.
Reference. Favorable factors for the development of the disease are considered to be a sedentary lifestyle, heavy lifting, pregnancy and childbirth.
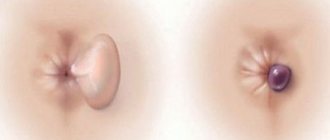
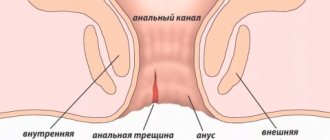
Based on location, nodes are divided into external and internal
External hemorrhoids appear around the anus under the skin, while internal hemorrhoids appear inside the anal canal. They are covered with the mucous membrane of the rectum. With a combined course of internal and external manifestations of the disease, combined hemorrhoids are diagnosed. According to clinical signs, the disease is divided into acute and chronic.
Clinically, hemorrhoids are manifested by pain that occurs mainly during defecation, itching of the anal area, periodic appearance of blood from the anus, and prolapse of internal nodes. The severity of hemorrhoid symptoms and the size of the nodes determine the stage of the process.
Stages of development of internal hemorrhoids
Causes of acute thrombosis of hemorrhoids
Based on the foregoing, we can say that the immediate problem of thrombosis is damage to the vascular walls. The following factors provoke such damage:
- Excessive straining during bowel movements, labor, or increased physical activity.
- "Non-traditional" sexual practices.
- Hypothermia of the pelvic organs. In this case, the vascular canal narrows, the blood stagnates and, as a result, the vessel wall is damaged.
Considering the relationship between thrombosis of hemorrhoids and hemorrhoids, it is worth noting the factors contributing to the development of these two pathologies:
- Sedentary lifestyle and frequent sitting. Physical inactivity is one of the root causes of congestion in the intra-abdominal part and pelvis.
- Regular and prolonged physical activity associated with work or sports activity. Due to this “heaviness,” the elasticity of the walls of the vascular canal decreases.
- Malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). Hardening of feces, caused by difficulties in removing it from the body, leads to regular damage to the mucous membrane and hemorrhoidal nodule located in its path.
- Poor nutrition and addiction to alcohol. Any foods and substances that irritate the gastrointestinal tract contribute to excessive blood flow to the organs.
- Tumor formations localized in the rectum. Such elements also provoke blood flow and, as a result, stagnation in the blood vessels. Inflammatory processes put pressure on hemorrhoidal formations and deform the nodes.
- Changes in the body associated with pregnancy. Changeable hormonal levels and uterine growth cause constipation and hemorrhoids.
Thus, very often the course of hemorrhoids contributes to the development of thrombosis localized in the enlarged hemorrhoidal node. Accordingly, when treating thrombosis, the primary task is to get rid of the enlargement of venous cones.
What to do if a hemorrhoid ruptures?
If a hemorrhoid bursts and bleeding appears, you should consult a proctologist. If you cannot get medical advice, you should immediately try to help yourself. To do this, you can use the following recommendations:
- Take a cold sitz bath. Cold promotes vasospasm and stops bleeding. Water must be boiled to prevent infection. The duration of the procedure should not exceed 5 minutes. You can repeat up to 4 times a day. It is also possible to apply an ice compress to the anal area for 10 minutes.
- If an external hemorrhoid has burst, you should generously moisten sterile cotton wool or a bandage in hydrogen peroxide and apply it to the bleeding formation. For internal hemorrhoids, use an enema with peroxide diluted in half with boiled water.
- Insert an ice suppository into the anal canal. Such suppositories can be made at home from decoctions of nettle, chamomile, St. John's wort, yarrow, propolis, and calendula.
- Take a local sitz bath with a decoction of calamus root, buckthorn bark, calendula, horse chestnut, and chamomile. These plants will help stop bleeding. During the period of bleeding, the temperature of the bath water should not be high. But after the bleeding stops, it is possible to use warm baths with the same medicinal plants to quickly resolve blood clots.
- Oral administration of decoctions of medicinal plants with a vasoconstrictor effect: horse chestnut, ginkgo biloba.
- For prolonged bleeding, it is recommended to administer a suppository with adrenaline, which has a spastic effect on blood vessels and a slight analgesic effect.
- Take a pain reliever if the pain is severe. For this purpose, drugs based on Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Nimesulide are used. However, any pain must be treated and not tolerated, as it increases muscle spasm of the perineum, which impairs blood circulation in the hemorrhoids.
- Local application of ointments after stopping bleeding (Troxevasin, Heparin, Levomekol), which help tone the veins, promotes the resorption of blood clots.
It is advisable to take any medications for hemorrhoids after consultation with a doctor.
General recommendations suggest the exclusion of any physical activity, as it can increase bleeding and resume it after successful stopping. It is recommended to lie on your stomach or back. Even a sitting position should not be taken unless absolutely necessary.
Types and degrees of development of the disease
Based on where the blood clot formed, proctologists distinguish between internal and external thrombosis, as well as a mixed type, in which the pathology affects the node on both sides. Thrombosis of the external hemorrhoid is most common, so most of the information will concern this type of pathology.
There are three main degrees of thrombosis of hemorrhoids, which correspond to the successive stages of its development.
- Blood clots begin to form. Because of this, pain appears, but not accompanied by an inflammatory process.
- Inflammation appears, accompanied by the growth of cones and increased pain. There may be an increase in temperature, swelling and redness of the skin at the site of localization of thrombosis of hemorrhoids.
- At the final stage of thrombosis of hemorrhoids, the area surrounding the site and the groin area are affected. There is a risk of severe complications.
The main characteristics of each stage of hemorrhoidal thrombosis are summarized in the table.
| Sign | 1st stage | 2nd stage | 3rd stage |
| The dimension that a node has | Small | Average | Large |
| Elasticity of the bud | Highly elastic | Tight elastic | Very dense |
| Color | Slight redness | Dark red or bluish tone | Black necrotic areas or areas with a white coating |
| Degree of pain | Moderate, aggravated by physical contact | Pronounced | Tormenting |
| Localization | Outside the rectum | Inside or outside the anal area | Domestic or mixed |
| Swelling | Unexpressed | Edema and hyperemia surrounding the node | Pronounced with hyperemia of the entire anal part |
| Sphincter spasms | No | Present | Expressed process |
| Bleeding | No | Mostly no | Expressed |
Clinical picture
Knowing its expressed symptoms will allow you to recognize the disease in a timely manner in order to begin treatment. Most often, thrombosis corresponds to the following manifestations:
- itching in the anus;
- burning sensation that accompanies bowel movement and persists after;
- ichor and mucus coming out of the anus;
- pain in dense nodes (this density is especially felt when external hemorrhoids are detected);
- acute pain during physical activity affecting the anal canal and nearby areas (standing up/squatting, sudden movements, going to the toilet);
- the node falls out, which is accompanied by swelling of the venous plexus.
For mixed, external or internal hemorrhoids in the last stage, each symptom intensifies. Heavy bleeding and unbearable pain are reasons for prompt hospitalization, since in this condition there is a risk to the patient’s life.
Critical risks for the disease without treatment
There is a certain chance of hemorrhoidal thrombosis going away on its own if, when the blood walls are destroyed, the blood clots leave the hidden or external node. However, such luck is unlikely - often qualified treatment for thrombosis of hemorrhoids is required. Without timely treatment of thrombosis, the risk of developing the following critical complications is high:
- necrosis in the node - the death of inflamed areas with the formation of ulcers in their place;
- perarectal abscess - suppuration in the subcutaneous part of the anal area.
When treating thrombosis of hemorrhoidal nodes, it is possible to avoid death, which can result from blood poisoning.
When is surgical correction necessary?
In some cases, conservative therapy does not give the desired results in treating a burst hemorrhoid. Therefore, if bleeding continues during the day and your health progressively worsens, you should consult a proctologist. It is possible that the thrombus from the node was not completely evacuated with the released blood through the perforated vein. In this case, surgical revision may be necessary.
In addition, other hemorrhoids may be in a state of thrombosis and threatening rupture. In this case, the doctor can significantly alleviate the patient’s condition by making an incision over the node, followed by its revision and suturing.
Surgical treatment is the only way to radically cure hemorrhoids
Surgical treatment is also most often inevitable when signs of purulent inflammation appear in the node.
Diagnosis of the disease
The severity of symptoms simplifies the process of making a diagnosis for thrombosis of internal or external nodal elements. Experts use three main research methods:
- visual – you can observe the presence of formations and determine the degree of pathology, taking into account the color of the node;
- finger - palpation allows you to determine the structure of the lump, but can be performed with anesthesia if palpation increases acute pain;
- instrumental is the most effective (a rectal speculum is used), but also requires anesthesia in case of severe pain.
Often, patients' assumptions about the presence of typical hemorrhoids lead to the detection of thrombosis of hemorrhoidal nodes during examination.
Diagnosis of pathology
The most correct action if the hemorrhoidal node has burst is a visit to the proctologist. This needs to be done as quickly as possible. Indeed, in some cases it is impossible to do without qualified surgical intervention. In addition, if blood comes from the anus, then rupture of the hemorrhoid is not the only cause of this symptom.
If you have rectal bleeding, you should not hesitate to visit a doctor, because other more dangerous diseases can be hidden under the mask of hemorrhoids
Proctological examination includes:
- collection of complaints and medical history;
- inspection and palpation of the perianal area;
- digital rectal examination;
- anoscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- fibrocolonoscopy.
Some of the instrumental examinations may not be carried out if more accessible and simpler methods allow an accurate diagnosis. In any case, the scope of the diagnostic program is determined only by the proctologist.
Features of conservative treatment
The type of treatment determined for the patient by the physician depends on the degree of development of thrombosis. Therapeutic stages are relevant for thrombosis of stages 1 and 2, as well as during pregnancy. During the treatment the following tasks are solved:
- relieving severe inflammation;
- elimination of swelling and pain;
- relieving tension from the anal sphincter;
- dissolution of blood clots and prevention of thrombus formation.
Conservative treatment involves the use of medications or ointments that dissolve the blood clot localized in the node. The choice in favor of one or another means takes into account the location where the nodes are located. The course can also be supplemented with various painkillers that block the pain syndrome that occurs during thrombosis. Naturally, during pregnancy the range of drugs available for treatment is significantly reduced.
Surgical intervention
Thrombosis in the most acute forms requires immediate surgical elimination. There are the following types of surgical effects on nodes:
- Thrombectomy. The thrombosed lump is opened to remove the blood clot. There is a risk of recurrence, since the cut is perceived by the body as a reason for the formation of new clots.
- Hemorrhoidectomy. The node is removed along with the clot. This form of surgery is more effective and there is no risk of relapse.
Attention! Surgical intervention is relevant not only for acute forms of pathology, but also in cases where medications and active ingredients of ointments are incompatible with the patient’s body.
Only a specialized specialist who has carefully examined the patient and determined the main characteristics of painful formations can determine the most appropriate method of dealing with nodes, or the optimal treatment course for eliminating hemorrhoids.
Is preparation for surgery necessary?
Often, surgical treatment is performed on an outpatient basis using local anesthesia. Therefore, hospitalization and further treatment in a hospital may not even be required. Depending on the clinical situation, the operation can also be performed in an operating room. Then you will need to fulfill a list of requirements before hospitalization, including additional examinations and tests. Special bowel preparation before surgery is not needed in this situation.
surgical treatment of thrombosis
Forecasting and preventive measures
It is worth repeating that there are certain chances of cure if the disease is only in the 1st stage. However, contacting a medical specialist is necessary in any case, even if the main symptoms disappear after some time. The prognosis for cure will also be favorable if all the previously mentioned symptoms were noticed in a timely manner. It is unacceptable to start the disease by transferring it to the 3rd critical stage of development.
Preventive measures to avoid acute thrombosis:
- proper nutrition (avoiding spicy and salty foods);
- stabilization of the gastrointestinal tract (it is extremely important to prevent the formation of constipation and physical complications during bowel movements);
- avoiding hypothermia;
- increasing physical activity (mobility) as a permanent way of life.
It is extremely important to follow all the recommendations in order to restore your usual way of life and not feel discomfort when being in society.