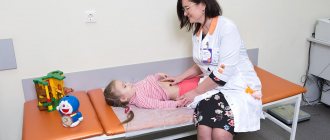
Parents often hear complaints from children about painful sensations in the abdomen. The pain can be acute, chronic or recurrent (regularly repeated). During a certain period, the organs of the digestive system in children grow and develop especially intensively, namely during the first year of life, from 5 up to 6 years and at 9-12 years of age. During this period, gastroenterological diseases often develop. Functional disorders may occur, manifested by increased gas formation, cramps in the intestines, and untimely bowel movements. Such painful manifestations are not dangerous. If the body is affected by negative factors, this can cause the progression of disorders and transformation into a chronic pathology.
Factors that provoke abdominal pain
Children may have stomach pain due to:
- Helminthic-parasitic infestation. In addition to painful manifestations in the abdominal area, nausea, loss of appetite, changes in stool, and the possible appearance of a rash are of concern.
- Gastroesophageal reflux. In a child at an early age, this disease manifests itself in the form of frequent, profuse (fountain-like) regurgitation. In babies over one year of age, it is accompanied by cough, otolaryngological diseases, damage to the enamel coating on the teeth, refusal to eat, hiccups and other signs.
- Infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Painful sensations in the abdomen are accompanied by symptoms such as belching, heaviness in the stomach, and nausea.
- Constipation.
- Carbohydrate intolerance (usually lactose).
- Problems with the biliary tract. In this case, the child complains of aching pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea, bitterness in the mouth and other manifestations.
- Intestinal infections, food intoxication.
- Intestinal pathologies of inflammatory nature.
- Gynecological diseases - adnexitis, ovarian cysts, etc. Typically, these causes appear in girls during adolescence.
- Diseases of the chest organs - pneumonia, pleurisy.
- Diseases of the urinary system of an infectious nature. Accompanied by impaired urinary function and increased body temperature.
In addition, the stomach can hurt due to chronic stress. The cause of stress lies in the following factors:
- increased school and extracurricular loads;
- increasing the flow of information received;
- violation of the food consumption schedule.
If your stomach hurts, you need to reduce the amount of food you consume, and food can only be boiled, stewed or baked. You will have to give up fast food, marinades, smoked foods, soda, fatty, fried, spicy and salty foods.
If a child has acute abdominal pain, the primary requirement is to exclude a number of diseases that are combined into the concept of “acute abdomen.” This includes acute disease of the peritoneal organs, which requires emergency care.
You should immediately seek the help of a specialist:
- for acute painful manifestations that bother the child for more than 2 hours;
- for cramping pain lasting more than 12 hours;
- when vomiting occurs, including discharge mixed with blood and bile;
- when blood is detected in the stool;
- when refusing food, and also if the baby does not allow touching the stomach;
- when pain is localized in the lower right side of the abdomen;
- if the pain appeared after injury;
- if, due to pain, the child wakes up at night and cannot fall asleep;
- for pain in the abdominal area accompanied by difficult or painful urination;
- with pronounced pallor of the skin, the appearance of cold sweat, fever, rashes, drowsiness and lethargy;
- with prolonged constipation, loose stools, lack of gas;
- for severe pain that occurs during eating or immediately after eating.
Mom, my stomach hurts! What is hidden behind a child’s abdominal pain?
From constipation to appendicitis, from intestinal colic to pyelonephritis. There are many pathologies in which this symptom occurs.
Why might a child have a stomach ache? Doctors at the Expert Clinic Tula told us about some of the reasons - pediatrician Valeria Aleksandrovna Golovko, and gastroenterologist Yulia Anatolyevna Saltymakova.
Gastroenterologist Yulia Anatolyevna Saltymakova
— Yulia Anatolyevna, there are probably no children who would never complain of abdominal pain. Tell us, what diseases can be hidden behind abdominal pain in a child?
These can be many ailments, including those not related to the digestive system. The most common causes may vary depending on age. For example, in babies in the first months of life it is intestinal colic (this diagnosis may hide other diseases). At older ages, pathology of the stomach (for example, gastritis) and biliary tract (dyskinesia) is more common.
Abdominal pain can also occur due to kidney pathology (for example, acute pyelonephritis, heart disease (carditis).
In my practice, there was a case when abdominal pain was one of the manifestations of epilepsy.
If you have abdominal pain, you should always look for its cause.
— Does any pain in the abdomen signal danger, or are there situations when there is no reason for serious concern?
An important point is the general condition of the child. If it does not suffer in any way, the pain is not severe, the child eats and plays normally, then you can contact the pediatrician as planned. It is wrong to say that there is no reason to worry - you must always deal with the cause of the pain.
— What type of abdominal pain in a child requires immediate medical attention? In what situations should you call an ambulance?
Dangerous cases are when the abdominal pain is severe; the child begins to refuse food; takes forced positions in which pain can be relieved (for example, the baby bends his knees to his stomach, lies on his side); his body temperature rises; pain occurs, for example, in the stomach and gradually descends to the right iliac region; nausea and vomiting appear; there is blood in the stool. In such cases, you must immediately call an ambulance. You cannot give your child any painkillers or antispasmodics on your own, as they can “blur” the picture of the disease.
Symptoms of appendicitis can vary. Don't try to diagnose yourself - consult a doctor!
— Can parents independently determine that their child probably has appendicitis?
Symptoms of appendicitis in children can be varied, so it will be difficult for parents to understand that we are talking about appendicitis. One of the options for the development of manifestations of this disease: pain appears in the stomach area, and over time moves to the right iliac region. But, again, signs can be very variable.
You can focus on the overall well-being of the baby. Those. if the pain does not go away, he loses interest in his surroundings, refuses to eat, this is always a reason to immediately consult a doctor (pediatrician and pediatric surgeon).
You can make an appointment with a pediatric surgeon here
Please note: the service is not available in all cities
“We’ll leave surgical pathology to the surgeons.” Let's look at situations when a child has a stomach ache for other reasons. What examination should children undergo if they are bothered by abdominal pain?
The most necessary are an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, a clinical blood test, and a general urine test. Also, for abdominal pain, a coprogram is performed (one of the stool examinations).
You can read about preparing for an abdominal ultrasound here
Pediatrician Golovko Valeria Aleksandrovna
— Valeria Aleksandrovna, how can parents help their child if he has abdominal pain? Is it possible to make a decision on your own and give your baby some medicine?
To know how to help your baby, you need to know the cause of the pain. Parents' options in this regard are quite limited, but something can be done. You need to ask the child when was the last time he went to the toilet, or, if the child is small, monitor the frequency of his bowel movements.
If it is indeed confirmed that he has not had a bowel movement for a long time, you can try to resolve the issue at home. If unsuccessful, consult a doctor.
If the problem is not the absence of stool, you need to ask the child to show where it hurts, ask how severe the pain is, whether it is constant or intermittent, in order to report these points to the doctor.
At the time of pain, do not feed the child, give clean drinking water.
There is no need to prescribe any medications yourself, since in most cases it is not known why the stomach hurts. Therefore, this is the prerogative of the doctor.
Remember: heat on the abdominal area during pain in the abdomen can aggravate the child’s condition!
— Since ancient times, young mothers, in case of abdominal pain in a child, were taught to apply a heating pad or warm cloth to the baby’s abdominal cavity. When is this acceptable?
Only in the case of infant intestinal colic. Those. you need to be completely sure that the pain is precisely because of them. Alternatively, place your baby's stomach on your stomach.
In other cases, thermal procedures can be harmful (for example, during an inflammatory process, perforation of a stomach or duodenal ulcer).
— Is there the only correct algorithm for parents’ behavior if their child complains of abdominal pain?
Until a certain stage. You should try to find out the cause of the pain, specifying its location, nature (acute or not), intensity, and presence of stool. Otherwise, the steps will be different, since there are many causes of abdominal pain.
Other materials on topics:
What to do if your child has a stomach ache?
What is dysbiosis in children and how to treat it?
Is there a stomach flu? Rotavirus in children: prevent and neutralize
The consultation was held by:
Preventive actions
To prevent the appearance of abdominal pain in a child, you initially need to normalize the diet and eating routine. To improve the digestive process, children's menus must include fermented milk products. In addition, you need to worry about the child’s body receiving all the necessary vitamins and minerals. Moreover, food for a child must be of high quality. You should avoid consuming sweet juice, soda and flour in excessive quantities.
To maintain the health of the digestive tract, it is important to monitor the child’s diet and compliance with hygiene measures. The diet must be balanced taking into account the child’s age.
A favorable family environment helps reduce the likelihood of abdominal pain. It is necessary to protect the baby as much as possible from stressful situations and nervous shocks. This is dangerous for children of any age and can cause disruption of body functions.
If a child regularly experiences abdominal pain, it is necessary to consult a pediatrician and gastroenterologist to determine the cause and select treatment.
If you identify the problem in a timely manner and begin therapy, you can often completely cure the baby, as well as improve the quality of life. In addition, this helps reduce the frequency of exacerbations and, as a result, the cost of medications. You shouldn’t let the disease get worse; it’s better to seek specialized help in time.
False alarm?
My stomach hurts! This is the most common childhood complaint. And mothers get used to “fighting” pain with the usual means: antispasmodics, analgesics, enzyme preparations. But often, under the usual abdominal pain, serious diseases are hidden that require emergency surgical care.
One of the most dangerous situations is acute appendicitis: inflammation of the appendix of the cecum. It most often develops in children between 8 and 14 years of age, but the disease can occur at any age. Appendicitis in children is often disguised as an attack of cholecystitis or gastritis, urinary tract infections, and even ARVI or pneumonia.
Article on the topic
Acute appendicitis: history of the disease and first symptoms Sometimes on the 5th–7th day after a sore throat or cold, the child begins to complain that his stomach hurts. This, of course, does not mean that he has appendicitis - the child’s body is designed in such a way that the stomach can hurt for a variety of reasons. For example, loose stools appear - and there are no other dangerous signs. The child is being treated for an intestinal infection, but he has something completely different.
What should parents be wary of? Specialists are well aware of these situations.
● The child has a sharp, cramping or aching pain. This is how appendicitis always begins.
● The child complains: his stomach hurts, pointing to his navel. Sometimes the pain spreads to the entire abdomen, gradually moving to its lower right part (iliac region).
● Pain radiates to the arm, leg.
● The child becomes irritable.
● Often he takes a forced position: he lies on his right side, pressing his legs to his stomach.
● Does not allow you to touch your tummy.
● The disease progresses, nausea and vomiting occur.
● The temperature may remain normal, but sometimes rises to 37.5.
● Loose stools appear.
Important
The situation requires emergency medical attention if the child:
● severe abdominal pain,
● tension of the anterior abdominal wall,
● nausea and vomiting,
● excessive excitement,
● elevated temperature.
If a child has severe, acute abdominal pain, you should not:
● give him painkillers, laxatives and any other medications - this will complicate the diagnosis;
● putting a heating pad on the stomach, giving an enema - the inflammation will intensify, which can lead to the development of peritonitis (purulent inflammation);
● give the child water and food until he is examined by a doctor: if surgery and anesthesia are necessary, the presence of food and liquid in the intestines will lead to vomiting.