Fetal movement
The child is in a state of readiness. All parts of the face and body are finally formed, all internal organs are ready to work outside the mother’s belly. The average fetal height at 40 weeks is 51.2 cm, and body weight reaches 3.5 kg. The baby already has subcutaneous fat, has acquired chubby cheeks and smooth skin. He strives for the first meeting with his mother and the wide world.
Although the child no longer has enough space for active movements, the woman will constantly feel his movements. At the same time, even the slightest attempt of the child to change the position of the body is clearly felt, because the uterus is very stretched.
The baby is in a position that facilitates passage through the birth canal as easily as possible. His head is pressed to the pelvis, his legs are bent, his arms are folded on his chest. This is the well-known “fetal position”.
There is enough surfactant in the lungs to ensure normal breathing of the baby immediately after birth. From this moment on, the alveoli will begin to enrich the blood with oxygen. The heart and blood vessels are also fully formed; as soon as the child takes the first breath of air, they will be included in the general blood flow system.
The baby's intestines are sterile, containing only meconium, which is passed in the first days after birth.
At week 40, a woman must pay attention to the nature of the baby’s movements and their frequency. By these signs one can judge the well-being of the unborn child. It is worth consulting a doctor if there is no movement for a long time, or, on the contrary, the fetus becomes overly active.
The normal number of movements per day is about 10. If the baby begins to move more actively, this may indicate oxygen starvation. But the absence of movements is an equally dangerous sign. Therefore, you should not delay going to the doctor.
How does the baby feel during childbirth?
Simply, the birth plan could be described as follows: the Baby’s body, ready for independent life, gives the command to the mother’s body to create conditions for reaching the surface, that is, birth. In response to this command, the mother’s body strives to: expand the birth canal to the required diameter and make it softer, move the Baby’s head and body to the end of the birth tunnel with increasingly rhythmic contractions of the uterine muscles, and expel amniotic fluid. Then everything is even simpler: as soon as the head appears, in the next moment the rest of the body is born. Once - and now the Kid announces in his voice: this is what I am! I breathe myself, I see and hear!
Have you ever made your way to the exit of an extremely crowded bus or subway car? You are being squeezed from all sides, an unknown force is pushing you towards the exit with uneven pushes, sometimes you are suffocating, you are visited by the fear that the doors will close before you can get out, and great relief when, finally, you find yourself outside this terrible crush. Your baby experiences approximately the same thing when he is born, and this experience is natural for him - it has been tested by other human beings billions of times.
How does the expectant mother feel?
As a rule, every woman at such a late stage of pregnancy is in constant anticipation that contractions will begin soon. There is no need to worry about your pregnancy taking too long. Most likely, an error was made in the obstetric calculations. Therefore, there is no reason to panic.
You shouldn’t constantly sit in your apartment, keeping a bag of things for the maternity hospital on hand. You need to continue to lead your usual lifestyle, but do not forget that childbirth is getting closer every day and even every hour, and contractions can begin at any moment.
Good to know
How do you know if labor is about to begin?
Standard procedures during childbirth
How to stop being afraid of childbirth
Large fruit. Features of pregnancy and childbirth
Planned birth. Planned delivery and caesarean section - indications and preparation
Speeding. What are the dangers of rapid birth?
What should a husband do if his wife gives birth urgently?
How to survive contractions: devices for active labor
Causes of labor pain
All texts for pages about mother and baby were kindly provided by RAMA Publishing - these are chapters from the book by Svetlana Klaas “Your Favorite Little Man from Conception to Birth”, reviewer Irina Nikolaevna Kononova, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology of the Ural State Medical Academy (Ekaterinburg).
Precursors of labor at 40 weeks of pregnancy
There are some signs that indicate that labor will begin soon. Every pregnant woman should know them and be able to recognize them.
Firstly, before the upcoming birth, the stomach drops, and with it the uterus and the baby. The baby presses his head against the pelvic floor, and the pressure on the diaphragm decreases. Thanks to this, the woman feels easier breathing. Also, annoying heartburn and belching disappear. However, the prolapsed uterus begins to put more pressure on the bladder, which leads to more frequent urination.
Secondly, impending birth may be indicated by disturbances in the functioning of the digestive organs, which appear approximately 1-2 days before the onset of contractions. Diarrhea occurs, and nausea and vomiting may occur.
Thirdly, many women indicate that they are experiencing an unprecedented surge of strength. The pregnant woman directs almost all of this energy to arranging her home, trying to prepare the new little family member as much as possible for his arrival.
Fourthly, a decrease in appetite may indicate an imminent birth. Sometimes the desire to eat food is completely absent. At the same time, the weight is lost or fixed at one level. The maximum loss can be 2 kg.
You definitely need to pay attention to 3 main points by which you can accurately understand that labor will begin very soon:
- Removal of the mucus plug.
It looks like a dense lump of mucus, it may contain inclusions of bloody streaks. This plug covered the cervix throughout the entire time, protecting the child from viruses and other infections. After its departure, the birth canal becomes free.
- Rush of amniotic fluid.
It is impossible not to notice this, since streams of transparent, slightly yellowish liquid will flow down your legs. Sometimes by 40 weeks the baby’s intestines are cleared of meconium (original feces). In this case, the amniotic fluid becomes greenish in color.
- Frequent and painful contractions indicate that labor will begin soon.
However, it is worth remembering that contractions can often be false. To distinguish them from the real ones, you just need to get up and walk around the room. If the contractions stopped, then they were false. If contractions continue and their frequency increases, then they are real. This means it's time to go to the maternity hospital.
How to prepare for childbirth?
To tune in to a successful birth means to transfer all your experiences from the area of “I-experiences” to the area of “we-experiences”. Namely:
- understand what is happening to your baby at each specific moment of childbirth, think first of all about him, help him mentally (if you know prayers, pray for the Baby);
- maintain contact with him, talk, talk about your feelings, calm him down, encourage him until the moment when he is placed on your chest;
- concentrate mentally on the situation when childbirth is already behind you and you can enjoy contemplating your baby in a calm atmosphere. This image needs to be rotated in your head constantly, more and more associating it with positive emotions (the less time remains before the birth of the Baby, the more actively you should imagine this image);
- firmly believe that you will have a healthy Baby with two arms and legs, eyes and ears, one mouth and nose, hearing, seeing, with five fingers on each limb. Did you smile? But many mothers are afraid that the Baby will not live up to their expectations in appearance! Remember how happy the parents were from Ray Bradbury's story when they first saw their... baby pyramid. Your fear that you won’t like the baby will lead to the Baby’s counter-fear of not liking you. And it is quite possible that all his life he (smart, talented, handsome), without realizing the reasons, will be afraid that others will not like him, and will spend his energy fighting for their recognition. No matter how your Baby appears outwardly, you must assure him that you need him as he is, long before birth. And this is one of his most important expectations.
Stomach ache
Abdominal pain of a pulling nature is normal at such late stages of pregnancy. It can also radiate to the lower back, which is explained by the position of the child in the stomach: the baby has dropped lower and puts pressure on the pelvic bones. A woman experiences severe stress, which mainly falls on the stomach and lower back.
The pain usually intensifies after the stomach drops. Although it may remain in the same position and not go down until the birth. This is the norm, and there is definitely no need to worry about this.
In addition to the fact that a woman feels pain in her stomach and lower back, she may also have pain in her legs, back muscles and spinal column as a whole. This is quite natural, because the body is preparing for the birth of a child: bones and joints soften, muscles and ligaments stretch.
The pelvic bones slowly but systematically move apart, as the body produces the hormone relaxin at an accelerated pace. It helps soften bones and move them apart. Naturally, this process can cause some pain in the groin and pubic area. They are always accompanied by a feeling of heaviness.
Sometimes pregnant women complain of hip pain. Its cause is compression of the femoral nerve by the enlarged uterus. In some cases, the pain can be very intense and reach the kneecap.
At this stage of pregnancy, a woman should listen carefully to her own feelings. If she has even the slightest suspicion that the pain is not associated with natural processes occurring in the body, then she must consult a doctor.
Possible problems
A woman should not leave home for a long time. Moving is prohibited. This is due to the fact that by disturbing the rest of the body, a pregnant woman can provoke the onset of labor. Childbirth at 40 weeks of pregnancy is, of course, not a terrible phenomenon, but only if the woman can be quickly hospitalized.
But diarrhea at 40 weeks is not a problem, but the body’s real preparation for childbirth. The intestines begin to empty themselves spontaneously to make it easier for the baby to exit.
Every woman should remember the points that require an urgent call to the doctor at home:
- blood pressure has risen;
- blurred vision appeared;
- large swelling appeared (hands, face);
- Strong headache;
- loss of consciousness;
- the temperature has risen.
Discharge
As throughout the entire pregnancy, at 40 weeks a woman needs to carefully monitor the nature of her discharge. The absence of pathology is indicated by light or milky discharge, which may contain some mucus. The discharge may become more stringy and thick, which is explained by the release of part of the mucus plug.
The discharge may contain bloody streaks. They appear there because the cervix becomes softer before childbirth, the smallest capillaries burst, and a small part of the blood gets into the discharge.
However, truly bloody discharge is a reason to immediately consult a doctor. Blood coming out of the genital tract of a pregnant woman at such a late stage is a sign of placental abruption. This condition requires prompt medical attention, so the woman should immediately call a medical team. You cannot hesitate, as there is a direct threat to the life and health of the fetus and the expectant mother.
Foamy discharge of green or yellow color, leucorrhoea with admixtures of pus require an urgent trip to the doctor. They clearly indicate an infection that needs to be treated. If this is not done, then there is a high risk that the baby will become infected. Moreover, there is still time left to get rid of the disease.
Thin, watery and copious discharge indicates the breaking of water. This process indicates the imminent onset of labor, so you need to go to the maternity hospital, taking with you everything you need.
A woman should know one thing: the water does not always recede en masse. Sometimes they leak a little, but contractions do not begin. If you detect leaking amniotic fluid, you should immediately contact a doctor. This occurs when the membranes surrounding the baby become thinner and fluid begins to leak out. This condition requires medical supervision, as the risk of infection of the fetus increases significantly.
Pain
Pain at 40 weeks of pregnancy is normal. Any housework is a burden for a woman; it is difficult for her to walk, sit and even lie down. But you can’t endure the discomfort for long, because childbirth is just around the corner.
At this stage, the woman has pain in the lower back, stomach, and legs (especially the hips and knees). Joint pain does not go away, the pelvic bones and pubis hurt, there is pressure and distension in the groin. Pinching of the sciatic nerve is not uncommon. The breasts become full, painful, and colostrum is released.
You cannot completely limit physical activity due to pain; you need to move. This will speed up the birthing process.
Ultrasound
If a woman feels well and does not have any pregnancy pathologies, then an ultrasound examination is not required at this time. Although some experts recommend undergoing an ultrasound to assess the condition of the placenta. After all, every day it wears out more and more and ages. Naturally, this affects its functioning, and therefore the child’s well-being. For example, he may begin to suffer from oxygen starvation, which leads to depression of brain activity, disturbances in the functioning of the heart, and sometimes even to the death of the fetus.
If an ultrasound is performed to assess the condition of the placenta, then the doctor will definitely examine the baby himself, clarify his parameters, and eliminate the slightest possibility of the umbilical cord entwining the baby’s neck. It is equally important to monitor the quality and volume of amniotic fluid and the readiness of the cervix for the upcoming birth.
During an ultrasound, a woman will be able to clearly see her baby, if the equipment allows it. At this time, his facial features and all parts of the body are perfectly formed.
Immediately after birth, the mother may be embarrassed by the baby's appearance. For example, his body is sometimes covered with fluff, his skin is spotted or bluish in color, his genitals are often swollen, and fluid is released from his nipples. The baby's head may be irregular, slightly elongated. There is no need to worry about this; in the near future all these “frightening shortcomings” will go away on their own.
After birth, you need to insist that the baby be put to the breast immediately. This is very important not only for the baby, but also for the woman herself. With the first drops of colostrum, the intestines will be populated with beneficial bacteria; in addition, this is a very emotional and touching moment.
Immediately after birth, the baby is washed, the airways are cleared, dressed, and drops are placed in the eyes to prevent the development of infection. The condition of the newborn is assessed by doctors using the Apgar scale. Then a tag is put on the baby, which indicates the mother’s last name, medical card number, height and weight of the child, as well as his gender. From this moment you can begin to enjoy the great happiness in the life of every woman - motherhood.
Other tests.
At this time, the woman will need to undergo a general urine test and a general blood test, which will ensure the normal functioning of the body. She also needs to visit a gynecologist who will take measurements of the abdomen and pelvis. As necessary, the cervix is examined and its readiness for childbirth is assessed.
Readiness for childbirth
The 40th week of pregnancy is the final stage of bearing a child, and the expectant mother’s body is almost ready for the upcoming birth. Now you should have everything ready for the birth of your baby - from a bag to the hospital and documents, to complete order in the apartment and the presence of everything necessary to care for your baby. Fear of childbirth, increasing stress, anxiety - all this negatively affects your baby. Try to set yourself up positively, because very soon you will be able to see and hold your long-awaited son or daughter in your arms!
Important Tips
- When contractions last for 1 minute, and the interval between them is about 4 minutes, and this condition persists for an hour, you need to go to the maternity hospital.
- Although the wait for your baby to be born seems excruciatingly long, you need to stay in good spirits. Everything goes as expected, but excessive nervousness can affect the child’s condition. In the future, the woman will suffer from sleepless nights due to the increased anxiety of the baby. Therefore, it is important to control yourself even during pregnancy.
Tests and studies during pregnancy
Visiting a doctor monitoring pregnancy: once a week.
Weighing, measuring blood pressure, measuring the height of the uterine fundus, listening to the fetal heartbeat. General urine test - before each visit to the doctor. Indicates the quality of kidney function.
Dopplerography (a study that allows you to evaluate blood flow in the vessels of the uterus, placenta and main vessels of the child) - in the last weeks of pregnancy or if the expected date of birth has already passed, according to indications . The study allows you to find out whether the child is getting enough oxygen and nutrients.
Cardiotocography (CTG, synchronous recording of fetal heartbeats and uterine contractions) - in the last weeks of pregnancy or if the expected date of birth has already passed, according to indications. The child’s condition is assessed and intrauterine hypoxia is excluded.
Principles of proper nutrition
It is imperative to adjust the menu of a pregnant woman. It should be focused on facilitating childbirth and achieving normal lactation after it.
All substances from the food that a mother eats will be received by her child. This occurs first through the placenta and then through breastfeeding.
It is extremely important to completely exclude highly allergenic foods, trans fats, spicy and fried foods from your menu. You should eat more vegetables and fruits; dairy products are no less healthy.
Almost all women in late stages of pregnancy often visit the toilet at night in order to empty their bladder. This does not allow you to get a full night's sleep, so you can reduce the amount of liquid you drink a couple of hours before going to bed.
Fortieth week: what changes occur in a pregnant woman’s body?
The 40th week of pregnancy is the last period of the third trimester. Most often, it is in the fortieth week of pregnancy that children are born; if a pregnant woman passes her due date, the child will be considered post-term. During this period, the woman’s body is actively preparing for the birth process, the expectant mother experiences strange sensations that are nothing more than preparation for childbirth.
Feelings of the expectant mother
By the end of pregnancy, a woman on average gains 10–15 kg. The fortieth week is difficult; almost all the time the expectant mother is accompanied by pain caused by internal changes:
- pulling in the lower abdomen as during menstruation, the stomach becomes hard, pressure is felt in the perineum;
- nausea occurs periodically;
- the back hurts, especially the lower back, due to the characteristic posture of a pregnant woman - it is caused by the need to bear the weight of the abdomen;
- legs swell, varicose veins worsen, walking long distances becomes increasingly difficult;
- the expectant mother suffers from constipation and hemorrhoids - a consequence of the pressure of the uterus on the intestines;
- the urge to urinate becomes more frequent – the bladder has very little space left in the abdominal cavity.
However, there are also positive changes in the body. Due to the fact that the baby goes down to the perineum, it becomes easier for the woman to breathe, heartburn goes away, and she no longer feels as sick as in the first and second trimesters.
Allocations during this period
Vaginal discharge at 39–40 weeks of pregnancy should be treated with the utmost care (we recommend reading: 39–40 weeks of pregnancy: harbingers of labor in multiparous women). They can become both harbingers of labor and a sign of danger to the fetus.
What discharge is considered normal at 40 weeks? Normally, the discharge is transparent and watery. A day or two before the expected delivery, they may turn white. Although white flake-like lumps on underwear often indicate the presence of candidiasis, it is better to see a doctor.
If the expectant mother notices spotting bloody or brown discharge on her underwear, she should not worry. At such a late stage of pregnancy, blood smears are normal; they indicate that the mucus plug is gradually beginning to separate before childbirth (for more details, see the article: the passage of the plug before childbirth in primiparous and multiparous women). The mucus plug protected the uterus from infections throughout pregnancy, blocking their path to the cervical canal.
Condition of the uterus
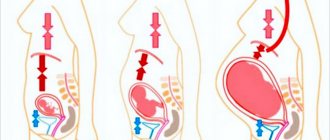
In the last period before childbirth, the uterus is actively preparing for delivery. The organ is enlarged to its maximum size, the muscles are tense. The volume of the abdomen often exceeds 100 cm. You can see what the abdomen looks like before childbirth in the photo.
The fundus of the uterus is located approximately 36–40 cm from the pubic symphysis. Before the baby is born, the organ descends slightly towards the perineum, and pressing sensations appear in the intestines, pelvis and bladder. On the other hand, it becomes easier for a woman to breathe, and shortness of breath goes away.
Why does my stomach get hard?
At 39–40 weeks of pregnancy, many women complain of a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, as if it turns to stone and becomes very hard. Why does my stomach become hard at 40 weeks? The abdomen becomes hard due to contraction of the uterine muscles. The organ is in good shape, so when palpating the tummy, the expectant mother feels petrified.
When there are still a few days left before giving birth, doctors can inject the pregnant woman with the drug Ginipral. It relaxes the muscles of the uterus and promotes gentle cleansing of the intestines before the birth process.
Answers to questions about 40 weeks of pregnancy
- Training contractions at week 40 are painful, but do not become more frequent. Is this normal?
This is the norm. If training contractions become more noticeable, this indicates that labor is approaching. You need to continue to monitor the time intervals between contractions. If contractions occur at least once every 10 minutes, this indicates the beginning of the labor process.
- The lower back hurts, but the water has not broken, there are no contractions. Is this how labor can begin?
Many women note that their contractions began with the appearance of nagging pain in the lumbar region. This is due to the location of the nerves in the uterus, as well as the position of the baby in the stomach. At the same time, lower back pain, which is characteristic of the onset of labor, will differ in a certain frequency. To do this, you just need to time it and everything will become clear. If the pain intensifies, then you need to go to the maternity hospital.
- At 40 weeks of pregnancy, a pulling sensation appeared in the abdomen, but there was no pain and the water did not break. The mucus plug has come out, the stomach has dropped, and labor has still not begun. Is it dangerous?
There is no danger. Childbirth is considered normal even if it begins at 42 weeks of pregnancy. Everything is individual. However, if there are any doubts, it is best to dispel them with a doctor. The main danger of a post-term pregnancy is the aging of the placenta, which becomes unable to provide the child with all the necessary substances. However, 40 weeks is a normal pregnancy period.
- At 40 weeks, spotting appeared. What could it be?
Discharge with blood indicates placental abruption, which occurs at the wrong time. It is necessary to call an ambulance as quickly as possible.
- At 40 weeks the discharge became thinner. What does it mean?
Most likely, the woman’s water began to leak. To refute or confirm this fact, you need to go to the maternity hospital. A prolonged anhydrous period should not be allowed, as this can be dangerous for the fetus.
Author of the article:
Lapikova Valentina Vladimirovna | Gynecologist, reproductive specialist
Education: Diploma in Obstetrics and Gynecology received from the Russian State Medical University of the Federal Agency for Health and Social Development (2010). In 2013, she completed her postgraduate studies at NIMU named after. N.I. Pirogova.
Our authors
Signs of surgical pathology
The risk of surgical pathology during pregnancy is small, but if there is a delay in making the correct diagnosis and does not start adequate therapy on time, this threatens the life of both the pregnant woman and the child.
Emergency assistance is necessary for any pathology that causes “acute abdomen” syndrome. This symptom complex includes impaired motor function of the intestines, tension in the abdominal wall and severe cutting pain in the abdomen. Similar signs appear if the inflammatory process rapidly develops, as well as if blood circulation in the mesenteric vessels is impaired.
Pain in the lower abdomen after childbirth
An “acute abdomen” during pregnancy can develop with the following pathologies:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (inflammation of the appendix, cholecystitis, perforation of ulcers, ischemia and infarction of the intestine);
- gynecological disorders (torsion of the cyst pedicle or rupture of the cyst);
- complications of pregnancy and childbirth (uterine rupture, placental abruption, septic complications);
- dysfunction of organs located outside the abdominal cavity (lungs, kidneys, heart).
According to statistics, if the operation is performed within the first 6 hours after the appearance of an “acute abdomen”, then the likelihood of developing complications is reduced by 5–8 times
The problem is that during pregnancy it is quite difficult to determine surgical pathology, which is explained by the following factors:
- abdominal organs are displaced;
- it is impossible to palpate organs due to an enlarged uterus;
- changes in immunity and reflexes of the abdominal wall;
- atypical picture of the course of the disease;
- nausea, vomiting, abnormal bowel movements, pain in the lower back and abdomen can be perceived as features of the course of pregnancy.
All this provokes diagnostic errors and delays in providing adequate medical care. In order to correctly establish the cause of the pathology, the pregnant woman must be examined by a surgeon and a gynecologist; this is the only way to exclude an obstetric or gynecological disease.
Inflammation of the appendix
In 9 out of 10 cases in pregnant women, an “acute abdomen” is caused by inflammation of the vermiform appendix of the cecum. Appendicitis is quite difficult to diagnose because there are no specific symptoms. It is determined by palpating the abdominal area, which is quite difficult to do in a pregnant woman, especially at this stage.
Acute appendicitis is clinically manifested by pain in the right side (at the beginning of the inflammatory process, pain can be felt in the lower abdomen), a pulse rate of up to 100 beats per minute, hyperthermia, frequent vomiting, belching, bloating, and uterine tone. Symptoms of peritoneal irritation are mild or absent altogether.
If the disease develops at 40 weeks of pregnancy, then first delivery is performed, and then appendectomy. If there are indications for a caesarean section, the operations are performed simultaneously.
Inflammation of the gallbladder
During pregnancy, women often develop gallstones, which is explained by changes in the composition of bile, as well as a deterioration in the motor activity of the bile ducts, which causes the secretion to stagnate.
For cholecystitis caused by stone movement, surgical therapy may be required
Signs of the disease include:
- abdominal pain that can last minutes or hours, usually occurring after eating;
- nausea and vomiting;
- lack of appetite;
- temperature rise to 38 ⁰C.
Conservative treatment involves refusing to eat for two days, infusion therapy, taking antispasmodics, painkillers, antibacterial and antihistamines. Indications for surgical treatment are:
- presence of symptoms of diffuse peritonitis;
- lack of effect from conservative therapy;
- complications in the form of pancreatitis, cholongitis, obstructive jaundice, degeneration of gallbladder tissue.
In case of acute cholecystitis, delivery is carried out through natural routes. Caesarean section is performed only for obstetric indications.
Inflammation of the pancreas
The pathology is caused by the presence of activated enzymes in the gland, which act aggressively and injure tissue. During pregnancy, the disease develops due to impaired motility of the gallbladder, increased secretion of enzymes (proteases, lipases, amylases), and increased intra-abdominal pressure.
Pancreatitis appears:
- increasing abdominal pain (especially after fatty or spicy foods);
- nausea;
- vomiting that does not bring relief;
- high temperature;
- tachycardia;
- blood pressure, which changes depending on whether the pregnant woman is lying down or standing;
- tension of the abdominal muscles.
The disease is predominantly treated conservatively. Surgical intervention is necessary if an abscess, secondary pancreatitis has developed, or a pseudocyst has ruptured.
Intestinal obstruction
If the intestinal lumen is blocked and feces and gases stagnate in the intestine, then surgical intervention is necessary. During pregnancy, intestinal obstruction develops as a result of:
- atony (due to the action of hormones);
- compression of the intestines and adhesions by the uterus;
- torsion of intestinal loops;
- hernias;
- tumors.
In 45% of cases, obstruction occurs precisely in the third trimester of pregnancy, which is caused by the lowering of the baby’s head into the pelvis
When the intestinal lumen is blocked, pain occurs throughout the abdomen. It can be constant or periodic. In the second case, attacks are repeated every 4–5 minutes if the obstruction is in the small intestine, or after 10 minutes if in the large intestine.
There is retention of stool and gas, and vomiting begins. With the development of pathology, the abdominal muscles are in a relaxed state. As the disease progresses, fever begins and a state of shock may occur.
Ulcer
Exacerbation of peptic ulcer disease during pregnancy is extremely rare, since gastric motility and the secretion of hydrochloric acid are reduced, and the production of protective mucus is increased.
Symptoms of perforation of an ulcer during pregnancy:
- acute pain in the abdomen spreads to the right hypochondrium and to the area of the scapula;
- no vomiting;
- forced body position;
- the muscles of the abdominal wall are tense (how severe the symptom is depends on the location of the ulcer).
If your stomach hurts at 40 weeks of pregnancy, it is recommended to consult an obstetrician-gynecologist to rule out placental abruption.
If pathological conditions of the gastrointestinal tract have developed that require the use of potent medications or surgical intervention, then labor is induced or a caesarean section is performed for obstetric indications. The child is already ready to be born, so intoxication, the consequences of hyperthermia or intrauterine infection will be more dangerous for him.
False contractions or the onset of labor?
Within a few days, or even weeks, the uterus begins to prepare for labor. Braxton-Higgs contractions are training contractions. They prepare the uterine muscles, cervix and birth canal for delivery.
First-time mothers often confuse prenatal activities and training contractions. How to distinguish them? False contractions are usually less intense than prenatal activity. They are irregular and repeat at different intervals. Pain can be easily eliminated with painkillers or a warm shower.
Prenatal activity is characterized by longer and stronger contractions. The woman feels pain, because the cervix gradually begins to open, and the uterine muscles contract intensively. The duration of the intervals is the same, gradually it begins to decrease. Unpleasant sensations can only be slightly reduced by taking a comfortable position or taking a pill. It is impossible to completely remove them during labor.