What inconveniences and limitations await a person with an ostomy? How to care for your stoma? We tried to collect as complete information as possible.
Author:
- Agapov Mikhail Andreevich Head of the surgical department, surgeon, oncologist, coloproctologist
3.5 (Votes: 9)
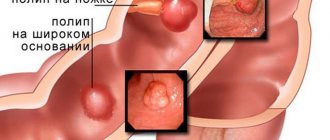
What is a stoma after intestinal surgery?
A patient's ostomy is a necessary measure to create the opportunity to have a bowel movement. It is used for many surgical interventions:
- after removal of intestinal tumors;
- during reconstructive operations, for faster healing of intestinal sutures and anastomoses;
- in some cases with peritonitis (after trauma, wounds, colitis, diverticulitis, etc.);
- with acute intestinal obstruction, which developed as a complication of cancer, inflammatory processes in the intestine;
- for chronic inflammatory bowel diseases - nonspecific ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, ischemic colitis.
Complications
Forming a colostomy is a complex operation that requires high skill of the surgeon. However, proper care in the postoperative period is no less important. Colostomy is accompanied by the risk of complications that require referral to a specialist. Such situations include: abscess (inflammation of tissue near the colostomy), necrosis (death of tissue), retraction or prolapse of the intestine, eventration (separation of the wound with prolapse of the intestine). A qualified doctor knows how to treat inflammation of a colostomy. When the first signs of complications appear, you should immediately seek help.
It is necessary to know in what cases pain occurs around a colostomy. Medical personnel provide information about this to the patient in the postoperative period, teaching the patient how to independently care for the colostomy. Pain occurs when tissue nutrition is disrupted, the inflammatory process develops, or the wound heals poorly. Spasms after colostomy removal may also be accompanied by pain. If your colostomy is bleeding, you should see a doctor immediately. This condition can be dangerous and requires urgent elimination.
The narrowing of the excreted hole occurs as a result of scarring of the wound. In advanced cases, this leads to difficulty in defecation or obstruction. A change in the diameter of the outlet is considered a normal process if regular bowel movements occur and the patient does not experience discomfort. What to do if there is no bowel movement during a colostomy? It is necessary to urgently consult a doctor to clarify the situation and receive timely treatment.
Complications after closing a colostomy are mainly associated with leaks in the sutures connecting the intestinal walls. After stitching the intestine, the tightness of the connection is checked using contrast. This is important to avoid divergence of the sutures on the intestine.
Types of stomas
If surgery is performed on the small intestine, an ileostomy is formed. If it’s thick, there’s a colostomy.
The stomas of the small and large intestines differ both in size, traditional places of excretion on the anterior abdominal wall, and in the nature of the intestinal discharge, the time of release of the contents from the gastrointestinal tract.
There are single-barreled stomas (when one opening from the intestine is formed on the abdomen). Or double-barreled (the adducting and efferent ends of the intestinal tube are removed). Double-barreled stomas provide drainage of intestinal contents from the overlying parts of the gastrointestinal tract and outflow of contents from the rest of the intestine (secreted by the tumor). Through the second opening of the stoma it is possible to administer medicinal solutions.
The stoma may be temporary
measure until healing and restoration of intestinal patency.
Or permanent
, when there is no possibility of natural emptying without the prospect of recovery - when removing the anal sphincter, terminal parts of the rectum, after operations for “low” colorectal cancer, after palliative operations for advanced oncological processes in the intestine.
Ileostomy
The size (diameter) of the stoma depends on the part of the intestine that is being ostomized. The small intestinal stoma - ileostomy - is smaller in size, since the lumen of the intestinal tube in this section of the intestine is from 2.5 to 6 cm. The secretion of the ileostomy has a liquid consistency and is released into the colostomy bag continuously. This is due to the digestive processes in this section of the gastrointestinal tract.
The site of ileostomy formation is most often on the right side of the anterior abdominal wall, at the level of the navel, slightly above or below it. The exact location of removal depends on the pathological process in the abdominal cavity and the surgical need.
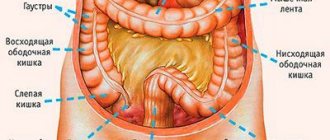
Colostomy
A colonic stoma - colostomy - is usually larger in diameter, because the lumen of the colon is from 5 to 8 centimeters. The masses discharged from the colostomy have a thick consistency and are released at intervals of 2-3 times a day. This feature is associated with propulsive contractions of the walls of the colon and the nature of digestion in the colon: here water is reabsorbed into the intestinal wall and the digestion process is completed.
The location of the artificial opening (colostomy) directly depends on the location of the lesion and follows the anatomical location of the transverse rim and terminal sections of the large intestine.
Remember that you are a healthy person just like everyone else
Is your belly bag making a huge difference in the lives of your partners, friends, family or colleagues? Are you really any different from them as a person? The answer is no.
People in the subway, in shops, cinemas and other public places will not even realize that you can go to the toilet standing or sitting next to them at any time. No matter how it sounds, it is a fact. And high-quality rehabilitation means will help you feel safe.
I'm not suggesting you start stripping and changing your bag in front of your friends and colleagues - let's face it, seeing someone's bowels is a bit like seeing someone naked. However, I actually think it's quite healthy to not hide it completely from the public. This gives people the idea that we are all different and there is nothing wrong or unpleasant in the fact that someone's body works a little differently. And it certainly shouldn’t constrain and constrain your life.
Everyone has their own problems. For some people, the fear and anxiety you feel when talking about your ostomy is the same as when they tell you about their problems with their bosses, children, or past breakups. We all have our secrets and fears.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Colostomy bags: what they are, their advantages and disadvantages
Whatever type of ostomy is performed on the patient, in any case, the stoma requires daily care and it must begin from the very first day after the operation. For hygienic purposes, colostomy bags have been created to collect contents from an artificial hole.
Conventionally, they can be divided into:
- disposable: two-component (conditionally reusable);
- one-component;
During use, the patient and those caring for him will gradually determine the preferences, availability and ease of use of certain colostomy bags.
The main pros and cons of various modifications of colostomy bags
Disposable colostomy bags
Single-component products are produced - a plate attached to the body and a receiving bag-container, which form one whole and are removed together as the bag is filled (up to half the volume).
Two-component colostomy bags consist of an adhesive-based plate and a replaceable bag. The plate is changed every 2-4 days. And the bag as it fills (up to half). The bag and the plate are firmly connected to each other using a flange.
Both receivers can be drainable or not.
Photo: Drainable one-component colostomy bag
Drainable bags have a channel (at the end opposite the attachment point) for discharging the contents. The drainage is closed with a clamp or other means. Through the drainage, as necessary, the contents of the collection are evacuated directly into the toilet, the hole is wiped and closed again with a clamp.
Photo: Non-drainable one-component colostomy bag
Pros:
- the flexible plate gives greater freedom
of movement to the patient, tightly adhering to the skin and ensuring odorlessness and confidence in fastening; - almost invisible under clothes
.
Minuses:
- more expensive to use (the cost of one product is from 100 rubles); the cost of use is also increased by the barrier paste for ostomy required for tightness (from 250 rubles);
- the adhesive base of the plate can cause irritation on the skin, despite the use of hypoallergenic compounds.
Reusable colostomy bags
There is also an option for containers for collecting intestinal contents. There are few similar offers in pharmacy chains and online stores.
Flaws:
- The main drawback of the design is its “unreliability”. A non-flexible ring with eyes is used. It is fixed to the body by pressing with an elastic band. The ribbon is worn around the torso. When changing body position (tilting, turning the body), leakage of the ring to the skin may occur. This causes the contents of the container to leak and produce an unpleasant odor. The solution in some situations is specially designed overlay plates that prevent excessive movement and maintain the stability of the connection.
- Another issue that confuses patients is its considerable size. The ring and the elastic band that holds it in place may be visible under clothing.
Advantages:
- Reusable colostomy bags are cheaper to use, since the main component of the product is used for a long time and repeatedly. Can be subjected to hygienic treatment (washing, sterilization). Only polymer bags with a ZIP clamp are regularly replaced with new ones; their cost is relatively low (20-40 rubles).
Photo: Reusable colostomy bag with fixing tape
Transversostomy. Transverse variety
For malignant neoplasms, a transverse colostomy is performed.
The main location is the upper abdomen, where the transverse colon is located.
Depending on the circumstances, it is done in different parts of the colon.
But the best option is considered to be close proximity in the splenic flexure, passing on the left.
Here there is the least chance of harming the nerve trunks, since there are not many of them in this area. A transverse colostomy is performed in the following cases:
- malignant neoplasms;
- inflammation of diverticula - diverticulitis, leading to the formation of scars, abscesses, narrowing the intestinal passages, and also capable of causing intestinal ruptures;
- intestinal blockage;
- injuries;
- physiological abnormalities.
In most cases, transverse colostomies are done temporarily, for the period of treatment of the existing pathology. This is necessary to protect the area being treated from complications that may arise if stool passes through this area. But if part of the colon is removed, then a permanent colostomy is made above the removal site.
Ostomy care
It is quite possible for the patient to take care of the stoma at home. The ostomy hole is not a wound and does not require sterile conditions or sterile gloves.
Before changing the colostomy bag, check that everything is at hand. You will need:
- paper napkins, soft fabric non-sterile napkin;
- plastic bag for used colostomy bag;
- mirror (if the patient provides care himself);
- scissors for a hole in the plate;
- template (stencil) for determining the size of the stoma;
- soap;
- if necessary - non-sterile wipes, barrier paste and skin treatment products.
It is rational to care for your stoma in the evening, before bed. The colostomy bag should not be changed immediately after eating, as intensive separation of intestinal contents may begin.
The procedure for treating a stoma and replacing a colostomy bag:
- After washing your hands with soap, remove the used colostomy bag into a prepared bag and close it.
- Clean the stoma with a damp soft cloth. Wash your hands again.
- After which you can begin to cleanse the skin. It is enough to blot it with a soft towel. And, if possible, leave to dry for a few minutes. If there is a need to cut hair with scissors. Do not use razors or depilatory products as they cause irritation.
- Place the stencil on the stoma and trace the desired diameter with a pen.
- Cut a hole of the proper size in the adhesive sheet.
- If ulcers, wounds, or bleeding occur on the skin or intestinal mucosa, you should see your doctor. Remaining glue from the plate can be carefully wiped off with a napkin or use a special hypoallergenic leather cleaner.
- If there are unevenness or changes in skin texture, apply barrier paste around the stoma for better sealing and stick on a retainer plate.
- The choice of position of the bag for collecting intestinal contents depends on the patient’s activity - if he is constantly in bed, the bag should be oriented across the abdomen. In all other cases, the bottom of the bag should point down.
Important! To treat the skin, you cannot use products based on alcohol, ether, or aggressive antiseptic solutions.
An easy-to-care stoma is one that protrudes above the surface of the skin. In this case, it is easy to achieve tight coverage of the intestinal stump and a tight connection.
If the stoma is located in a recess and retracted, then so-called correctors are used - convex plates. They cover the intestinal stump using a tight flange. The concave shape of the products makes it possible to conveniently attach colostomy bags. For greater reliability, the plates are attached to the torso using a wide elastic band.
Photo: Convex plate, surface adjacent to the skin
Preparing for colostomy surgery
Such interventions are best carried out as planned, after a thorough examination and preparation, during which specialists are convinced of the possibility and feasibility of the operation. In such cases, the patient is prescribed a number of diagnostic procedures:
- Blood tests
to assess coagulation, general health and the quality of internal organs. - Complete examination of the intestines, including colonoscopy - an examination of tissue using a thin flexible tube with a camera and a light source at the end, or other tests.
- Ultrasound
, or
MRI
, which allows you to obtain a clear image of internal tissues. - Assessment of the condition of the cardiovascular system and other important organs.
- If necessary, doctors perform additional procedures.
A few days before the operation, antibiotics are prescribed - antibacterial agents, and diet is followed - avoidance of heavy, long-digesting foods that provoke increased gas formation. Then the intestines are cleansed using special preparations. The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach - approximately 10-12 hours before it begins, you need to give up food, chewing gum and minimize water consumption.
The patient must tell the doctor about any known medical conditions, allergies, and any medications he or she is taking, including vitamins, supplements, and blood thinners such as aspirin.
Before the intervention, during which the creation of a colostomy is planned, the surgeon marks the planned point of its placement on the skin with a marker.
- free from large scars and scars;
- sufficient for attaching a colostomy bag - a reservoir into which the stool comes out;
- convenient for placing a storage unit accumulating feces and not restricting the patient’s movement, that is, located outside the areas of the waist, groin, navel and pelvic bones.
Stoma is not a death sentence
In many countries, active work is underway to adapt people with certain characteristics to the social environment. The countries of North America and Europe have been very successful in this. Entire communities of people with stomas (urostomies, colostomies, tracheostomies, etc.) have been created and supported there. People with similar problems communicate and share their experiences and knowledge.
Under the auspices of the UN, since 1993, World Ostomy Day has been celebrated on October 2.
Thanks to new inventions and care products, patients with the consequences of operations can lead a normal, active lifestyle. These include colostomy bags and hygiene products. They are available to a wide range of buyers and are easy and convenient to use. Carrying out operations and ostomy often gives people more than one year of life, the opportunity to enjoy the world and communicate with family, friends, work and play sports. And the fullness of life of a patient with an ostomy largely depends on his optimism and the support of loved ones.
Our leading specialists
All specialists
Evseev Maxim Alexandrovich
- Deputy Chief Physician for Surgery
- Bariatric surgeon
- Surgeon
- Oncologist
- Doctor of Medical Sciences
- Professor
- Doctor of the highest category
Mirgatia Irakliy Olegovich
- Head of the surgical department
- Surgeon
- Oncologist
Vladykin Alexey Leonidovich
- Bariatric surgeon
- Surgeon
- Oncologist
- Candidate of Medical Sciences
- Doctor of the highest category
Balarev Anton Sergeevich
- Oncologist
- Surgeon
- Candidate of Medical Sciences
- Doctor of the highest category
Zhigareva Irina Stanislavovna
- Gynecologist
- Mammologist
- Oncologist
Titkov Boris Evgenievich
- Chief Physician of the Hospital Center
- Oncologist
- Surgeon
- Doctor of Medical Sciences
- Professor
- Academician AMTN
- Surgeon of the highest qualification category
Chernysheva Irina Sergeevna
- Oncologist
- Chemotherapist