Analysis of the intestinal group is a popular test. It is prescribed both for the diagnosis of acute diseases and for the purpose of identifying the hidden course in carriers of the disease. When an adult or child develops diarrhea, fever, abdominal pain, and vomiting, it is impossible to make a diagnosis based on the clinic alone, since many intestinal infections occur with similar symptoms.
In addition, to prescribe optimal antibacterial treatment, it is necessary to know the specific causative agent of the disease. According to the existing instructions of the sanitary service and the Ministry of Health, all people who work in the production of food products or come into contact with them during transportation, sale, packaging, food preparation, and cleaning the premises are regularly tested for intestinal group.
The result is noted in their “Sanitary Book” along with the doctors’ conclusion. We will try to explain in this article why you should pay so much attention to stool analysis.
What is included in the "intestinal group"?
About 500 species of microorganisms live quietly in the intestines of a healthy person. They quite successfully coexist with the macroorganism, help it perform a number of important functions, and themselves feed from the intestinal contents. It is customary to divide all flora into 3 types based on the principle of danger.
Useful - in any conditions they support digestion, produce vitamins, and provide immunity. Among them are the main ones:
- bifidobacteria;
- bacteroides;
- lactobacilli;
- Escherichia;
- mushrooms.
There are 15 such microorganisms in total. Conditionally pathogenic microorganisms are harmless if a person is strong and healthy, but if the protective forces fall, they become an additional aggressive factor and can cause significant harm.
“Enemies” can be:
- staphylococci;
- enterococci;
- coli;
- clostridia;
- mushrooms of the genus Candida.
Pathogenic are the causative agents of an infectious disease, which should not normally exist, but they can take such well-protected forms that they live for a long time in the intestines of the carrier in the form of cysts. And the person does not even suspect that he is a carrier of the infection. These include:
- salmonella;
- shigella;
- dysenteric amoeba;
- intestinal trichomonas;
- balantidium;
- Vibrio cholerae and others.
The presence of bacteria in the intestines is considered an absolute norm.
If a doctor prescribes a stool test for the intestinal group, then he is primarily interested in the likely causative agents of the disease. After all, knowing their features and damaging properties, you can:
- find out the source of infection;
- limit the spread of the outbreak of the disease;
- examine contact persons;
- prescribe a course of optimal therapy.
Analysis of stool for helminth eggs and protozoan cysts
Helminths (worms) are parasitic worms that live in the body of humans and animals and cause diseases called helminthiasis (helminthic infestations). The disease in humans is most often caused by roundworms (nematodes) and flatworms (platytodes), which are divided into tapeworms - cestodes and flukes - trematodes. Helminths change their host in the process of life development, and the range of hosts, routes and mechanisms of transmission are individual.
Clinical manifestations are largely determined by the localization of the parasite, its number and feeding habits. Helminths, parasitizing in the human body, can have a mechanical effect, damaging the tissues and organs of the host, toxic and allergic phenomena, metabolic disorders, closing the lumen of the intestines, excretory ducts of the liver, gall bladder, pancreas, disrupting intestinal motility, irritating the receptors of the intestinal wall.
Protozoa are single-celled organisms. Like helminths, during the development process protozoa go through several stages and change hosts. Many protozoa have two forms of existence - vegetative and cystic. The cyst has a durable shell and ensures the survival of the protozoan in unfavorable, and even extreme, conditions. It is cysts that usually infect humans.
A stool test for helminth eggs and protozoan cysts must be taken if a parasitic infection is suspected, to monitor the effectiveness of antiparasitic treatment, before hospitalization, when preparing a medical record, or certificates. For example, for children before visiting the pool.
In the CMD laboratory, stool analysis for helminth eggs and protozoan cysts is carried out using two different methods:
- Feces for helminth eggs and protozoan cysts: microscopic method; "thick smear" method and Kato staining
- Modified sedimentation method using PARASEP concentrators (enrichment method). Analysis of feces for helminth eggs and protozoan cysts using a Parasep concentrator: the use of PARASEP concentrators makes it possible to identify helminths and protozoa even in small quantities.
What pathogenic microorganisms are most often detected?
A patient with an acute digestive disorder and suspected infection is sent to an inpatient infectious diseases department. Children are hospitalized together with their mothers. In a hospital setting, it is possible to isolate the patient and conduct the most complete examination and treatment.
The most common intestinal pathogens are manifested by the following diseases:
- Dysentery - caused by Shigella, the main “blow” is dealt to the stomach and large intestine. The pathogen is characterized by good adaptability to environmental conditions. They live in garbage and feces for up to two months. A person gets the infection through dirty hands or contaminated food.
- Salmonellosis - the favorite site of infection is the small intestine. The disease is accompanied by severe intoxication. For young children it is especially dangerous because it causes severe complications (pneumonia, meningoencephalitis, general sepsis). Pathogens are divided into types, except for salmonellosis, typhoid fever is caused by infection through the fecal-oral route, through insufficiently processed foods, and dirty water.
- Coli infections are diseases caused by E. coli of different serotypes. Occurs more often in infants. Affects the large intestine. They are transmitted from carriers or sick adults if the basic rules of hygiene and baby care are not followed.
These examples show how important it is to timely analyze not only feces, but also food, drinking water, and swabs from the hands of personnel. Especially if the disease is detected in children's institutions.
References
- Pokrovsky, V.I., Pak, S.G., Briko, N.I. and others. Infectious diseases and epidemiology. Textbook. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2007. - 816 p.
- Yushchuk, N.D., Vengerov, Yu.Ya. Infectious diseases. National leadership. Brief edition. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2022. - 1056 p.
- Mazankova, L.N., Gorbunov, S.N. Diagnosis and treatment of acute intestinal infections in children. Methodological recommendations for doctors, 2012. - 93 p.
- Ejidokun, T. Principles and Practice Recommendations for the Public Health Management of Gastrointestinal Pathogens, 2022. - 85 p.
How to get tested?
To obtain reliable results, the patient should first be prepared:
- It is recommended not to eat meat dishes for 4–5 days, not to drink alcohol, to eat only dairy products, cereals, potatoes, white bread;
- three days before collecting stool, stop taking antibiotics, laxatives, iron supplements (one can assume in advance a negative result in patients who independently began treatment with antibiotics), and administering rectal suppositories.
It is better to use a standard container purchased at a pharmacy; it has a closing stopper and is sterile
Collection rules include:
- prevention of foreign impurities (urine, blood during menstruation in women) entering the test material; the child should be given the opportunity to urinate first; women should use a clean vaginal tampon if the analysis cannot be rescheduled;
- containers for the material being tested cannot be treated with disinfectants (bleach); the jar must be washed thoroughly with soap and poured with boiling water;
- the baby's potty is treated in the same way;
- No more than two hours are allowed for delivery to the laboratory; storage in the refrigerator allows for a 4-hour delay; the longer the delay in transportation, the less effective the data obtained will be, since some of the pathogens die.
The analysis is taken:
- at home - in a sterile container, the volume should be approximately a full teaspoon;
- in the infectious diseases room or in the hospital, a rectal smear is taken with a swab, with the patient in the lateral position, the laboratory assistant inserts a sterile swab on a stick into the rectum to a shallow depth and turns it, then immediately places it in a test tube with a special medium;
- For a small child, you can take the material directly from the diaper.
A prescription filled out by a doctor is attached to the container.
How is the research conducted?
For a more likely result, three stool samples are taken for testing. All methods used are of the “in vitro” type, which means “on glass”. Another “in vivo” possibility, carried out by infecting animals, is not needed in this case.
The collected material in small quantities is placed on a nutrient medium for 4–5 days. Colonies grow here, from which a smear can be prepared for the intestinal group even with a very small number of microorganisms.
Qualified bacteriologists are able to identify pathological pathogens, focusing on appearance and mobility under a microscope. The method is called bacterioscopy.
When viewing a drop of feces diluted with water, a specialist can give a preliminary result on the first day
To be sure, you will need to examine the pathogen that has grown on the nutrient medium.
The microbiological method is accompanied by mandatory inoculation of feces on special media (for example, any universal medium is suitable for dysentery pathogens; salmonella grows well in bile broth). If it is not possible to do urgent sowing, material samples are preserved in a solution with glycerin or phosphoric acid salts.
Bacteriological testing allows not only to identify the infectious agent, but also to analyze its sensitivity to antibiotics. This is especially important for the choice of treatment for carriers.
Biochemical tests allow you to calculate the amount of fatty acids secreted by microorganisms in the intestinal contents. Based on their content, conclusions are drawn about the quantity and qualitative composition of the intestinal group.
Bacteriological research for the population
CENTER FOR HYGIENE AND EPIDEMIOLOGY Our services Laboratory research, testing, measurements Bacteriological research for the populationThe bacteriological laboratory of the FBUZ “Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in the Lipetsk Region” provides services to the population to conduct bacteriological research:
- intestinal microflora for dysbacteriosis;
- for the intestinal group of infections (disgroup);
- urine test for sterility;
- swabs from the pharynx and nose for microflora, diphtheria, Staphylococcus aureus (material is collected by hospital staff) with determination of the sensitivity of the isolated microorganisms to antibiotics.
Material for research can be submitted directly to the laboratory, bypassing various medical centers.
Urine microflora analysis
Biomaterial: urine, collected in a disposable sterile container with a screw cap.
This test is aimed at identifying microbial cells in urine. In a healthy person, the urine in the kidneys and bladder is sterile. • Indications for use: diagnosis of infectious inflammatory diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract (pyelonephritis, cystitis, urethritis, etc.).
Units of measurement: The type of pathogen identified, its quantity, as well as its sensitivity to antibiotics are indicated.
Normal values (adults): Normally there are no bacteria in the urine.
Urine collection rules
1. Take material for analysis before starting antibacterial treatment, or 2-3 weeks after discontinuation of these drugs.
2. Sampling of morning urine sample after overnight abstinence.
3. Carry out a thorough toileting of the external genitalia.
4. Open the sterile jar without touching the inner surface of the lid.
5. Collect an average portion of urine in the amount of 3-5 ml.
6. Deliver to the laboratory within 2 hours.
Stool analysis for the study of intestinal microflora for dysbacteriosis
Biomaterial: Cal.
Feces for dysbacteriosis is a modern laboratory diagnostic method that allows you to assess the state of the intestinal microflora.
Indications for use: diseases of the intestines, liver, pancreas, immune disorders, long-term therapy with antibiotics, immunosuppressants, steroid hormones.
Units of measurement: CFU (colony forming units) per 1 g of feces.
Rules for collecting stool for dysbacteriosis
1. 7-10 days before the test, stop taking antibacterial and bacterial medications (containing bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, E. coli, etc.).
2. The material is feces after natural defecation, which is collected from different places of feces in the amount of 1-2 grams (pea) in a sterile disposable container with a screw cap and a spoon.
3. Before collecting the analysis, urinate into the toilet, then collect the stool by natural defecation into a bedpan (be careful not to get any urine).
4. The material is delivered to the laboratory within 2 hours from the moment the analysis is collected. In special cases, sampling can be done in the evening (the day before), in which case the bottle with feces should be stored in a cold place at a temperature of +5 +10 C 0 (refrigerator conditions).
Analysis for intestinal infections
Biomaterial: Cal.
Stool culture for disgroup is a common test performed in the laboratory. It is carried out if there are suspicions of intestinal diseases, a sign of which may be, for example, abnormal stool, vomiting, etc. In other words, this is an early diagnosis of acute intestinal diseases, including for the purpose of confirming the diagnosis of salmonellosis, dysentery, etc.
Rules for collecting stool for intestinal infections
1. The material is feces after natural defecation, which is collected from different places of feces in the amount of one teaspoon into a sterile disposable container with a screw cap and a spoon.
2. The material is delivered to the laboratory within 2 hours from the moment the analysis is collected. In special cases, sampling can be done in the evening (the day before), in which case the bottle with feces should be stored in a cold place at a temperature of +5 +10 C 0 (refrigerator conditions).
By contacting us, you can appreciate the following advantages:
- exclusion of transfer of material to other laboratories;
- storing results in electronic form, eliminating data loss;
- confidentiality;
- low prices due to all studies performed directly in our laboratory.
We are located at:
Lipetsk, st. Gagarina, 60a, 3-storey building, 1st entrance, 2nd floor (bacteriological laboratory), tel.
Extract from the price list
No.
| Name | Price, rub.) | Note | |
| Bacteriological studies: | |||
| 1 | For diphtheria pathogens | 165 | 1 biotope |
| 2 | For staphylococcus (pharyngeal, nasal discharge) | 165 | 1 biotope |
| 3 | For pathogens of whooping cough and paracough | 219 | |
| 4 | For meningococcus | 311 | |
| 5 | Blood for sterility | 384 | |
| 6 | Clinical material for microflora | 329 | |
| 7 | Sputum (quantitative method) | 434 | |
| 8 | For pathogens of dysentery and salmonellosis | 165 | |
| 9 | For pathogens of dysentery and salmonellosis and Escherichiasis | 242 | |
| 10 | Feces for opportunistic enterobacteria (quantitative method) | 384 | |
| 11 | For intestinal dysbiosis | 767 | |
| 12 | Feces for staphylococcus (quantitatively) | 187 | |
| 13 | Determination of the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics | 165 | |
Information
- The antibiotic is right on target!
- Watermelons for benefit
- Bacterial pneumonia
- Trouble that comes through the air
- Viruses vs bacteria
- Tasty does not mean safe!
- Airborne infections and their prevention
- Mushroom preparations
- To eat or not to eat... foods with antibiotics?
- Once again about whooping cough
- Cough for 100 days? Do you have whooping cough?
- Insidious infection
- Summer is the time for intestinal infections
- The best protection against pneumococcal infection is vaccination
- About the introduction of a methodology for determining milk powder in the line of dairy products.
- On measures to prevent botulism when storing mushrooms
- Danger under the lid
- Beware of campylobacteriosis!
- Open reservoirs: to swim or not?
- Memo to the population on the prevention of airborne infections
- Prevention of acute intestinal infections
- Prevention of food poisoning during the New Year holidays
- Prevention of salmonellosis
- Modern methods of studying food products for microbiological indicators of quality and safety
- Is there an alternative to antibiotics?
- Chlamydia in pregnant women
- What you need to know about salmonellosis
- What is safe food?
- What is listeriosis and why is it dangerous?
Back | Laboratory research, testing, measurements
How are results assessed?
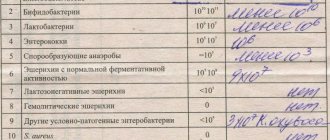
The result of the analysis for the intestinal group takes into account the presence of the entire spectrum of microorganisms.
The presence of pathogenic flora is noted separately with pluses on a standard form, recorded with stamps or included in the conclusion before the doctor’s signature
The count is measured in CFU (colony-forming units) per gram of feces. Advanced analysis allows us to judge the presence of dysbiosis among beneficial flora. This point must be taken into account, since it aggravates the course of the disease and requires correction after the acute symptoms subside.
You should not try to decipher the analysis yourself. Even doctors of various specialties not related to infections do not have enough information on this issue. Therefore, only infectious disease specialists, bacteriologists and gastroenterologists can give correct advice and assessment.