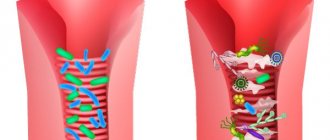
Probiotic preparations are widely used for the treatment and prevention of various intestinal disorders in children from infancy to older age. The correct choice of product is especially important for recently born babies, but older children also need careful selection of probiotics.
The little person’s own defense does not begin to work immediately; the immune system takes time to “get acquainted” with the foreign flora that meets the child first in the maternity hospital, then at home, and then in preschool and school institutions. To help the immune system, you should protect your own beneficial bacteria, ensure an influx of “fresh forces” - lacto- and bifidobacteria, as well as auxiliary substances and prebiotics, so that microorganisms can act in full force.
This is why doctors recommend probiotics from an early age. Such products are harmless because they contain bacteria that make up the normal intestinal flora. However, you should consult your pediatrician about taking medications and strictly follow medical instructions.
Probiotics for newborns
The neonatal period is short and is about 28 days. It is at this time that the baby’s immune system adapts to the new environment. It should be borne in mind that throughout the pregnancy the baby was protected by the walls of the amniotic sac and the fetus existed in an almost sterile environment. The rupture of a bladder and childbirth are a huge shock for the baby, as well as for his immune system, which, like its owner, can do almost nothing at first. Microorganisms that meet a newborn settle on the skin and mucous membranes, multiply and create colonies.
It should be recalled that this is a normal process, that sterile cleanliness is unacceptable even for a child’s room, since it interferes with the formation of protection.
The formation of the correct microflora is facilitated by bacteria that enter the intestines with mother's milk. Mostly it will be useful, but among this “army” there may also be pathogens. In addition, there is a risk of dysbiosis in newborns if the mother took antibiotics during breastfeeding.
Modern children experience health problems almost from the first days of life. As a rule, they are easily corrected by mild means, which include probiotics.
If in the last century, in the 70-80s, the normal microflora of a newborn was formed already on the 8-9th day from the moment of the first breath, then in the 2000s, complete formation is completed only by one and a half to two years. The immune system does not work at full strength, children get sick more often and longer.
The use of probiotics helps with predisposition to:
- allergies;
- dysbacteriosis;
- constipation, diarrhea, and other stool disorders;
- frequent illnesses.
Probiotics, which include Biovestin, can be given to infants in the first year of life. This measure will help the beneficial microflora cope with its task and deliver the required amount of lacto- and bifidobacteria. The drug is effective and safe, easy to use and comes in liquid form, which allows you to add the required dose to breast milk, formula or water.
Lacto- and bifidobacteria, as well as the products of their metabolism, are the main helpers of the newborn’s immunity. It is especially important to receive probiotics for children who, for one reason or another, are bottle-fed. Deprived of breast milk, and therefore of immune protection transmitted from the mother, such babies are prone to more difficult adaptation to foreign flora in the first months.
What role do beneficial bacteria play in a child’s body?
A 2 year old child is actively growing and developing. In order for the baby’s tummy to work like a clock, beneficial microflora must predominate in the intestines. It is involved in many vital processes:
- synthesis of digestive enzymes necessary for the breakdown of carbohydrates and proteins,
- production of B vitamins and protein,
- absorption of calcium, iron and vitamin D by the intestinal walls,
- processing and removal of toxic substances,
- strengthening natural defenses through the synthesis of immune bodies,
- fight against pathogenic organisms.
Probiotics against colic in children
Colic is the scourge of modern parents. The child cries for days on end, folk remedies bring short-term relief. Often the cause of colic is intestinal immaturity and a lack of beneficial bacteria in the intestinal microflora. If colic is caused by other reasons, probiotics are also useful; they will help the immune system and provide symptomatic relief to the baby’s condition.
Most often, Linex, Bifiform or Biovestin are prescribed - the safest drugs, the composition of which allows you to quickly improve the functioning of the intestinal flora. Children are prescribed a solution of powder, drops and even suppositories. If colic affects an older child, it is permissible to give him probiotics in capsules and tablets.
Probiotics for children: how to choose
Today, pharmacies have a wide selection of drugs on their shelves. First of all, of course, you should follow the recommendations of the pediatrician observing the child. Intestinal disorders can have different causes and purposes, and often there is a specialized drug for a specific problem that helps best. The pace is no less. Parents also need to have an idea of what probiotics can be given to their beloved children.
- It is important that the composition does not contain flavorings or dyes.
- The number of beneficial bacteria should not be less than 10⁷ CFU.
- The shelf life of liquid preparations is short (no more than two months), if it is longer, then live bacteria are unlikely to retain their viability and the product should not be purchased for a child.
You can also choose probiotics based on what specific problems your baby has.
- Mono-composition (one strain of bifidobacteria) characterizes the drugs that are most effective for the treatment and prevention of dysbiosis. The most commonly prescribed medications for dysbacteriosis are: Linex, Hilak Forte, Bifiform.
- Acute intestinal infections require complex treatment with the participation of combination drugs, such as: Biovestin, Bifidumbacterin.
- Constipation can be treated with Symbifer, Biogay, Bifiform.
Don’t forget to check what age the product is suitable for children.
Probiotics for children: names
Parents are wondering which probiotic preparations are best to use for children? It is quite difficult to answer this question unambiguously: each product has its own “specialization”. But there are proven probiotic options.
- Bifiform is produced in the form of powder, drops, capsules, and chewable tablets. This drug is often prescribed for disorders (of various origins) of the gastrointestinal tract, deterioration of the immune system, and constipation. The uniqueness of this drug is that it contains a nutrient medium for the growth and reproduction of beneficial bacteria.
- Linex - thanks to advertising and frequent prescriptions, can easily be considered the most recognizable probiotic. Belongs to the combined type. Produced in the form of powder and capsules. That is why it is easy to take for babies from 1 year old. Despite the fact that they prefer to prescribe drugs for infants in the form of drops, Linex is also recommended for use even at such a tender age.
Probiotics for children under two years of age are prescribed in the form of powder or drops, sometimes in suppositories. After two years, you can give the product in capsules, and three-year-olds are quite capable of coping with chewable tablets. Bifido-containing probiotics recommended for babies include: Bifiliz, Biovestin, Bifidumbacterin, Probifor.
Probiotics for infants: names
Probiotics recommended by doctors for newborns differ in composition from those that can be taken by older children. Infants are vulnerable, drugs for them require additional research. Exclusively liquid forms and powders are used.
- Hilak Forte is often prescribed for the treatment of dysbiosis, bloating, and constipation. This probiotic is often used to restore children after a course of antibiotics. You can take it literally from the first day of life. The composition contains only metabolic products that are normally produced by healthy intestinal flora.
- BioGaia drops are often recommended for use for children from the very beginning of life. The drug helps in getting rid of colic and constipation. Doctors often prescribe drops for infants who are bottle-fed. Contraindications: diabetes mellitus, renal dysfunction.
- Symbiter is acidophilic with the maximum amount of benefits for a newborn in its composition. The release form is in powder form, which must be mixed with breast milk, infant formula or warm water.
Why is it important to restore the microflora in time?
When taking antibiotics, poor nutrition, or frequent infectious diseases, a 2-year-old child may develop dysbiosis - a condition in which the composition of the intestinal microflora is disrupted. This negatively affects the health and well-being of children:
- digestion suffers from a lack of enzymes,
- the synthesis and absorption of vitamins and other nutrients is impaired,
- immunity decreases,
- hidden infections become active,
- diarrhea or constipation, abdominal pain, atopic dermatitis occur.
To quickly restore the intestinal microflora in a 2-year-old child, it is important for parents to take timely measures.
Features of the use of drugs for microbiological correction of intestinal dysbiosis in children
Yu. A. Kopanev Research Institute of Epidemiology and Microbiology named after. G. N. Gabrichevsky, Moscow L. G. Kuzmenko, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor
RUDN University, Moscow
In the complex therapy of intestinal dysbiosis in children, the following areas are distinguished: immunocorrection, microbiological correction, correction of dysfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), treatment of concomitant diseases (primarily parasitic and chronic infectious) [1, 3, 4].
The use of complex treatment regimens, including drugs from these areas, provides more
pronounced and persistent clinical and microbiological effect than treatment covering only one of these areas
As a result of observations for three years of children receiving treatment for intestinal dysbiosis (1-1.5 thousand patients per year), we identified some features of microbiological correction in children.
Microbiological correction includes antimicrobial drugs and preparations of bacteria of normal intestinal flora (eubiotics).
Antimicrobial drugs in the treatment of dysbiosis are prescribed for selective decontamination, i.e., targeted reduction in the number of opportunistic microorganisms. For this purpose, bacteriophages, intestinal antiseptics (furazolidone, intetrix, enterol, etc.), herbal antiseptics (chlorophyllipt, rotokan), and antifungal drugs are used [1]. The direct antimicrobial effect of a complex immunoglobulin preparation (CIP) has been proven [2]. The use of antibiotics to correct dysbiosis is undesirable, since these drugs often lead to worsening microbiological disorders of the autoflora. Nevertheless, the use of antibiotics is justified when dysbiosis is a consequence of a chronic infectious disease (chlamydia, yersiniosis).
Features of the use of antimicrobial drugs
1. The use of any drugs for selective decontamination can lead to a worsening of the condition. This is due to the toxic effect of decay products of opportunistic microorganisms. If the number of autoflora bacteria performing a barrier function in the intestinal microbiocenosis is reduced, the likelihood of complications increases. If the condition worsens, which may be significant, symptomatic therapy should be initiated or decontamination should be suspended.
2. Antimicrobial therapy may be ineffective without concomitant immunocorrection.
3. Long-term continuous (more than two weeks) use of antimicrobial drugs, including bacteriophages, is not justified, since in this case disturbances in the composition of the intestinal autoflora occur. In particular, E. coli with normal enzymatic activity, as well as lactobacilli, are inhibited.
4. In the case when intestinal dysbiosis is caused by a focus of chronic infection (chlamydia, yersinia), antibacterial therapy will be more effective if it is started in the acute stage, and less effective if it is started in the remission phase.
Eubiotics (probiotics) - preparations of live bacteria of normal intestinal flora - are used to correct intestinal dysbiosis with a deficiency of these microbes as part of the intestinal microbiocenosis [5]. Drugs of this group are also used in situations where it is necessary to maintain microbiocenosis due to any unfavorable factors: intestinal or respiratory infections, the use of antibacterial drugs, as a preventive measure for post-vaccination complications, during teething, etc.
The most widely known eubiotics: domestic - dry bifidumbacterin, lactobacterin, acylact, acipol, bificol, colibacterin; imported - primadophilus, floradophilus, linex. Liquid forms have appeared relatively recently and have proven themselves well: liquid bifidumbacterin (liquid concentrate of bifidobacteria, LCB), liquid lactobacterin (liquid concentrate of lactobacilli, LCL). Primadophilus drugs and the lactase enzyme are used in various age groups to correct disturbed microflora and reduce fermentation in the digestive tract. Sometimes flatulence and bowel movements occur even in breast-fed children. To correct such disorders, often associated with age-related enzyme deficiency, it is possible to prescribe a lactose enzyme preparation. You can add the contents of the capsule directly to milk or dairy products.
Primadophilus is used to correct dysbiosis in any age group, since each of the four forms of the drug includes specially selected types of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli that are normally found at a given age. The drug is available in enteric capsules and powder for infants.
Recommended: the usual dose is one capsule, in powder - once a day, a teaspoon with meals.
The powder can be added to any type of food, including baby food.
Features of the use of eubiotics
1. Therapeutic doses to restore bifido- and lactoflora with a very significant decrease in the number of these bacteria (bifidobacteria less than 107, lactobacilli less than 105) - 5 doses of each drug twice a day for a course of treatment of at least three weeks. The use of smaller doses or short courses of treatment in this situation is often not effective enough.
2. With a moderate decrease in bifido- and lactoflora (bifidobacteria no less than 107, lactobacilli no less than 105), the use of eubiotics 5 doses once a day is effective. As maintenance drugs, eubiotics can be successfully used in short courses (7-10 days).
3. Autoflora is restored better with the combined use of eubiotics and enzymatic preparations (Abomin, Mezim-Forte, Creon, etc.) [4]. JCB and JCL preparations contain enzymes.
4. During the use of eubiotics, a short-term deterioration in the child’s well-being is possible, which does not require discontinuation of the drugs. The more active the drug, the more likely it is to worsen during treatment. Treatment with the most active of modern eubiotics - GSD and GCL - often leads to abdominal pain, exacerbation or the appearance of skin rashes, and changes in the character of stool. All these phenomena almost always disappear within a week, without requiring any adjustment in therapy.
5. With long-term use of single-component preparations for therapeutic purposes (for example, those containing only bifidoflora), it is advisable to jointly use preparations of other autoflora bacteria in a maintenance dose. Otherwise, according to our observations, an undesirable bias in the microbiocenosis may develop towards one of the three main groups (bifidoflora, lactoflora, E. coli with normal enzymatic activity) with the suppression of the others.
Knowledge of these features can help to more competently prescribe therapy and correctly assess the changes in condition that occur during microbiological correction.
Literature
1. Korovina N. A., Vikhireva Z. N., Zakharova I. N., Zaplatnikov A. L. Prevention and correction of intestinal microbiocenosis disorders in young children. M., 1995.
2. Kopanev Yu. A., Sokolov A. L., Aleshkin V. A., Pozhalostina L. V., Efimova O. G. Effect of a complex immunoglobulin preparation on opportunistic flora // Doctor. 1998. No. 5. P. 38.
3. Mukhina Yu. G. Diagnosis and correction of dysbiosis in children // Russian Medical Journal. 1999. No. 11. pp. 487-494.
4. Tabolin V. A., Belmer S. V. et al. Rational therapy of intestinal dysbiosis in children. M., 1998.
5. The use of bacterial biological preparations in the practice of treating patients with intestinal infections. Diagnosis and treatment of intestinal dysbiosis. Guidelines. M., 1986.