Antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment for many infectious and inflammatory diseases. In most cases, these drugs suppress pathogenic flora, ensure rapid recovery and prevent infection.
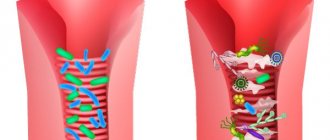
However, such strong drugs have side effects, and in many cases, antibacterial therapy disrupts the balance of intestinal microflora: there are fewer beneficial bifidobacteria and lactobacilli that inhibit the growth of opportunistic flora.
As a result, antibiotic-associated diarrhea and dysbacteriosis may develop. Probiotics contribute to the restoration of intestinal microflora after antibiotics in adults.
Reaction of intestinal microflora to antibiotics
The reaction to antibacterial therapy from the gastrointestinal tract may vary. Thus, the development of antibiotic-associated diarrhea is explained by a disruption in the functioning of the intestinal microflora: the number of beneficial bacteria decreases, which leads to an increase in the number of opportunistic flora, in particular Clostridium difficile.
As a result, a dangerous disease develops - pseudomembranous enterocolitis. In other cases, diarrhea can be caused by a change in the intestinal microflora after antibiotics in the form of active reproduction of Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella, Candida fungi, and Salmonella.
There are other mechanisms for the development of diarrhea: due to a decrease in the number of beneficial bacteria, metabolic processes are disrupted, including the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates and fiber. The secretion of water into the intestinal lumen leads to dilution of the stool.
But a decrease in the number of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli does not always lead to diarrhea. Sometimes dysbiosis is accompanied by constipation or alternating stool retention and diarrhea. Symptoms of dysbiosis also include bloating, rumbling in the stomach, nausea, loss of appetite and other manifestations.
Why does diarrhea occur after taking antibiotics?
The development of complications during antibacterial therapy in the form of diarrhea is associated with a decrease in beneficial microflora, which is involved in a complex of digestive processes:
- breakdown and absorption of nutrients from food;
- evacuation of the contents of the stomach and intestines;
- residual digestion of food;
- removal of toxins and metabolic products;
- secretion and absorption of water in the intestine;
- formation of feces, regulation of their excretion.
Even with standard antibacterial therapy, leading to a slight imbalance, side effects may occur in the form of disruption of intestinal function.
In addition, bacterial infections themselves can contribute to diarrhea, which is the basis for taking antibiotics. The waste products of pathogenic bacteria have a toxic effect, and stool liquefaction may be associated with an increase in body temperature. Antibiotics fight the underlying agent and root cause of the disease, and in many cases they are truly necessary. However, this group of medications can worsen the digestive system.
Nutrition and drinking regimen to restore microflora
To restore the intestinal microflora after antibiotics, probiotics are usually prescribed - preparations based on live lacto- and bifidobacteria. In addition, some foods and drinks will help improve digestive function and restore the balance of microflora:
- Yogurts and fermented milk drinks are natural sources of beneficial bacteria that the intestines need.
- Fermented foods. For example, sauerkraut.
- Fiber-rich foods. It is important to remember that insoluble dietary fiber serves as a substrate for the vital activity and proliferation of beneficial bacteria. These products include fresh vegetables, fruits, and prunes.
When stool retention is associated with intestinal dysbiosis, it is important to adhere to the optimal drinking regime. An adult requires an average of 30 ml of liquid per 1 kg of weight per day - as a rule, this norm fits into the recommended 1.5-2 liters. This amount of water will help normalize intestinal function.
The main symptoms of dysbiosis:
- pain in the stomach;
- nausea and belching, frequent heartburn;
- particles of undigested food in the stool;
- dry skin, there are cases of rashes;
- brittleness and layering of nails;
- dry hair;
- weight loss, decreased immunity, deterioration of general condition.
Problems can intensify in the presence of stress, chronic diseases, including gastrointestinal diseases, poor nutrition, consumption of alcohol, carbonated water. That is why many patients who have been treated with these drugs ask the question of how to restore the gastrointestinal tract after antibiotics.
Important! The appearance of pain and other symptoms is a signal for immediate examination and treatment by a gastroenterologist. Diagnosis of this disease consists of anamnesis, patient complaints, clinical picture, results of gastroscopy of the stomach and laboratory tests. The main thing is to take timely measures aimed at restoring the gastrointestinal tract after antibiotics.
When restoring microflora, gastroenterologists advise including fermented milk products, baked or boiled fish and lean meats, various pureed soups with grated vegetables, compotes, jelly, and slimy porridges in the diet.
Prohibited:
- alcohol;
- smoking;
- dry food;
- fatty meat and fish;
- boiled and fried eggs;
- fresh white bread;
- milk and freshly squeezed juices;
- sauces and seasonings.
Restoring intestinal microflora with probiotics
Restoring the intestinal microflora after taking antibiotics will most likely be necessary against the background of the following diseases and conditions:
- bacterial infections requiring antibacterial therapy, especially long-term;
- rehabilitation after surgery, when prophylactic antibiotic therapy is recommended;
- infectious diarrhea;
- previous viral infection;
- complex treatment of allergic and dermatological diseases;
- irritable bowel syndrome.
Get rid of intestinal problems
The natural British drug is not addictive and works immediately
Find Fitomucil with benefits
Probiotics help normalize intestinal microflora. They contain normal intestinal microflora, which has a therapeutic effect and eliminates the phenomena of dysbiosis. Such drugs should be taken in a course. Beneficial bacteria populate the intestines and successfully cope with opportunistic microflora.
What else can you do to restore the intestinal microflora after antibiotics? Prebiotics are of particular importance in this matter. They act as a substrate for nutrition and reproduction of beneficial flora. Bifidobacteria and lactobacilli restore normal functioning of the digestive system.
In addition, probiotics help strengthen the body's defenses, improve digestion, promote the production of vitamins B and K, and have other therapeutic effects.
The mechanism of development of diarrhea after a course of antibiotics
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea (AAD) develops as a result of the death of both pathogenic bacteria and beneficial microorganisms. An imbalance of microflora is called dysbiosis. According to statistics, the source of such digestive disorders can be up to ⅕ of the types of antibiotics used in medical practice. Typically, this phenomenon occurs as a result of taking broad-spectrum drugs.
Typically, this type of diarrhea does not have other symptoms, unlike food poisoning. The main symptoms of antibiotic poisoning include watery or loose stools, and less commonly, cramping abdominal pain. Most often, the intestinal condition returns to normal after 2-3 days.
In very rare cases, antibacterial therapy can cause colonization of the mucous membranes by pathogenic microorganisms - Clostridium difficile and Salmonella. They cause severe infections with persistent diarrhea, which increases the risk of dehydration and can lead to serious health consequences.
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea can occur with long-term use of suitable doses of the drug, and not necessarily in tablet form - injections can also lead to this result. However, poisoning can also occur due to an overdose. Each antibiotic has a toxic effect on different organs, so the category of the drug is taken into account. Common symptoms of overdose include the following:
- high body temperature (up to 39–40 ˚C);
- diarrhea;
- vomit;
- muscle pain;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- changes in blood pressure;
- tachycardia or bradycardia;
- joint pain;
- dizziness, etc.
With toxic damage to the liver, the following symptoms may appear: yellowness of the skin and sclera, itching of the skin, bloating, etc. With kidney damage, the volume of urine decreases significantly, and a strong feeling of thirst occurs. Poisoning with aminoglycosides leads to the appearance of signs of toxic otitis: acute pain in the ears, decreased hearing acuity, a feeling of congestion, etc. All conditions associated with an overdose of antibiotics require immediate treatment of poisoning . It is important to call an ambulance as soon as possible.
Is there an alternative to antibiotics?
The vast majority of antibiotics used in medicine . They have become so firmly established in everyday life that many doctors, out of habit, prescribe them even for minor reasons (say, for a simple cold). And people who are accustomed to trusting people in white coats regularly follow all the recommendations. With all the ensuing consequences that are described above. However, it is encouraging that recently there has been a tendency to abandon the use of synthetic antibiotics “for all occasions.” Today there is an understanding that if, in the treatment of a particular disease, an artificial antibiotic is not a mandatory drug and, in principle, one can do without its use, then it is better to turn to an alternative - antibiotics of plant origin. Moreover, the medicinal properties of plants have been known for a very long time.
Many of them - for example, elecampane, licorice and bearberry - contain glycosides. Many of these organic compounds (they are also called theol glycosides or phytoncides) are similar in their action to antibiotics . Their use has proven effective in the fight against harmful microorganisms, but there are no side effects, not to mention addiction and complications. Experts recommend: if treating your disease in an acute form is impossible without synthetic antibiotics, then use natural antibiotics for its chronic course. Having, of course, agreed on this issue with your doctor, because medications should also not be taken uncontrolled. In addition to the above-mentioned plants, onions and garlic, horseradish and cranberries, apples, citrus fruits and dogwoods . Garlic also contains the substance allin. Interacting with food enzymes, it turns into allicin, which is known for its pronounced bactericidal properties.
Pathogenic microorganisms do not feel very comfortable in the vicinity of phytoalexins - substances that are a type of phytoncides . Their amazingness is that at first they are simply absent from plants. But as soon as pathogenic microbes appear “on the horizon,” the process of their synthesis immediately begins. Phytoalexins can be formed in potatoes, carrots, peppers and a number of other vegetable crops.
Another effective alternative to artificial antibiotics is called bacteriophages . They have not yet found widespread use, but in medical circles they are sure that everything is moving towards this. Bacteriophages are some types of viruses that have a selective effect on certain bacteria. That is, when they treat specific diseases, only causative microorganisms will be destroyed. Since each illness has its own bacteriophage, there is no need to fear damage to beneficial intestinal microflora. Bacteriophages, unlike conventional antibiotics, do not have any effect on internal processes in the body and certainly do not disrupt their course. But there are also disadvantages: it is difficult to select “their” viruses for certain pathogenic bacteria. And treatment with bacteriophages usually takes longer than a traditional course of antibiotics. But both doctors and patients are inclined to believe that these disadvantages can be easily accepted and lived with. The main thing is that bacteriophages do not cause damage to the human body, which is already weakened due to the underlying disease.
Ultrasound results
Ultrasound of the gallbladder dated January 12, 2019: the shape is irregular due to the presence of kinks in the projection of the neck and body, dimensions 63*25*25 mm. The walls are not thickened, uniform in density, single-layer. The hepatic choledochus is 3.4 mm (the norm is 6 mm), it is not traceable throughout its entire length, it is passable, the contents are heterogeneous, the walls are moderately compacted. The contours are smooth and clear. The cavity is heterogeneous due to hypoechoic fine suspension. The initial volume of the gallbladder is 18.81 cubic cm. After giving a trial breakfast at 30 minutes, the gallbladder decreased by 51%.
According to ultrasound and clinical data, it was possible to conclude that the patient has a congenital deformation of the gallbladder in the neck and body with signs of bile stagnation - dyskinesia of the hypotonic type ("flaccid" gallbladder) with the presence of hypoechoic fine bile (sludge).
Symptoms of constipation from antibiotics
Constipation after taking antibiotics, which is one of the negative consequences of treating an infectious-inflammatory disease, is called drug-induced. Due to dysregulation of intestinal motor function, the process of bowel movement is accompanied by pain and straining. Often, after completing a bowel movement, there is a feeling of incomplete passage of the contents. The amount of excreted feces decreases significantly; they acquire a hard consistency and fragmented shape (the so-called sheep feces).
Due to stool retention, rotting processes develop in the intestines. The toxic substances formed in this process are absorbed into the blood and often cause intoxication of the body. This can lead to a partial or complete lack of appetite, weakness, increased fatigue and headaches. Almost always, constipation after antibiotics is accompanied by increased gas formation, bloating, pain of varying intensity and colic in the lower abdomen. With anal injuries, often caused by excessive straining and the passage of hard stool, blood may be found in the stool.
Up to contents
In what cases can you cope without antibiotics?
Doctors often mistakenly prescribe antibiotics for infections caused by viruses, or prescribe a broad-spectrum drug when it is necessary to use drugs aimed at combating only certain bacteria.
In the past, antimicrobials were used to treat chest infections, ear infections in children, and sore throats. With the development of science and medicine, it became clear that the treatment of these conditions can be done without antibiotics.
Types of diseases that are not recommended to be treated with antibiotics without a doctor's indication:
- Cold/runny nose;
- Bronchitis/chest cold in healthy children and adults;
- Flu;
- Sore throat (except for streptococcal infection);
- Fluid in the middle ear (otitis media with effusion).
Effect of antibiotics. Objectively
- satisfactory condition,
- sclera and visible mucous membranes of normal color,
- the abdomen participates in breathing, is painless on palpation in all parts, gall bladder symptoms are negative,
- liver at the edge of the costal arch.
The patient is suspected of having a violation of the contractile function of the gallbladder (dyskinesia). To clarify what dyskinesia is, an ultrasound examination of gallbladder function (cholecystokinetic test) with a test breakfast (sorbitol) was prescribed.
How to restore microflora
Complete diet
A person should eat a variety of foods per day, and not meager ones, consisting mainly of carbohydrates and fats. This is how most people eat, snacking, for lack of time, on fast foods, rolls, etc.. It is necessary to include fiber in the diet every day.
This:
- fresh vegetables;
- fruits;
- grain bread;
- legumes;
- greenery;
- nuts.
Orthodox fasting is useful for normalizing microflora. It has been observed that those who observe fasts suffer less from intestinal diseases, even cancer. Fasting excludes animal fats (meat, butter, eggs) and focuses on fresh vegetables and fruits, berries, and cereals.
It is known that inulin, which has a prebiotic effect, is found in the following products:
- garlic;
- onion;
- leek;
- asparagus;
- chicory;
- artichoke.
These products help improve intestinal microflora and defeat harmful bacteria. They must be included in your diet if you have intestinal problems.
Sources of bifidobacteria beneficial to humans are:
- apples;
- blueberry;
- artichoke;
- almond;
- pistachios.
They must be present on the table as often as possible.
Fermentation of products
It is useful to eat fermented ones, i.e. fermented products. As a result of the fermentation process, simple products become fantastically healthy because they change their composition thanks to bacteria. They help restore intestinal microflora.
The most common fermented products:
- sauerkraut;
- kefir;
- yogurt;
- tea mushroom.
It is customary for some peoples to ferment vegetables, even spicy ones. This dish of pickled spicy vegetables is called kimchi. Fermented soybeans are called tempeh.
Fermented dairy products contain lactobacilli, which are so necessary for normal microflora. People suffering from kidney disease simply need them, because... With such diseases, the microflora is disrupted.
Artificial sweeteners are harmful
Sugar substitutes (aspartame, saccharin) are harmful products. They have a destructive effect on the intestinal microflora. In addition, they increase blood glucose levels. Therefore, they must be excluded from the diet.
More prebiotics
Prebiotics contain beneficial bacteria that help evict harmful ones from the human intestines. They are found in vegetables, fruits, legumes, and grains. They should be eaten as often as possible. They also lower the level of triglycerides, cholesterol, and insulin in the body. This means that prebiotics reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases, death from heart attack, and stroke.
Whole grains
The benefit of whole grains is that they contain fiber and indigestible carbohydrates, which are not absorbed in the small intestine, but enter the large intestine. There they break down and cause the growth of beneficial bacteria.
Whole grains contain:
- B vitamins;
- iron;
- zinc;
- proteins;
- carbohydrates.
They are sold whole and are also used to make whole grain bread. They are also used to make whole wheat flour.
Artificial Probiotics
There is controversy about probiotic drugs. There is evidence of some benefits that such drugs provide. But it has not been completely proven. Moreover, there are many fakes among the drugs. You need to be careful when choosing probiotics, following your doctor’s recommendations. We recommend paying attention to Maxilac.