Rehabilitation after gastric surgery
Surgery in the treatment of diseases of the stomach and duodenum remains the dominant method of treatment at the moment.
Most often, surgery is required for complications of peptic ulcer disease. For example, such as internal bleeding, perforation of an ulcer. Surgical intervention is also necessary if conservative treatment is ineffective for a long time. And the most important thing about this is that rehabilitation after gastric surgery is often necessary to restore not only the stomach itself, but also many related organs and systems. But unfortunately, such interventions often do not bring relief to patients. Moreover, sometimes the consequences of interventions can be more severe than the disease itself. Therefore, the issue of preventing postoperative complications becomes key.
Features of the recovery period
Healing after surgery may take longer than with other diseases...
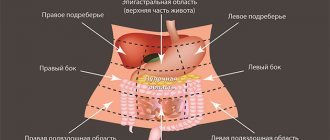
After surgery, patients may experience weakness and other painful symptoms for 2 to 3 weeks. There is heaviness and distension in the epigastric region after eating. There may also be difficulties with eating. After a deep resection, a person can rarely take more than 200 - 300 ml of liquid food at a time. Also, after any type of gastrointestinal surgery, the patient may develop concomitant functional disorders. For example, such as esophagitis, gastritis, impaired gastric motility. The functional state of the liver changes. Due to the large number of complications, the patient may remain unable to work for a long time after the operation.
The goals of medical rehabilitation after gastric surgery are two key aspects. The first aspect is the prevention of postoperative disorders. The second is to maximize the patient’s ability to work.
Physical and natural factors of rehabilitation
Rehabilitation after gastric surgery should be comprehensive and consistent. Since the therapeutic effect gives results only in the totality and compatibility of factors, both physical and natural. The key components of restorative treatment are mineral waters, mud applications, physical therapy and massage.
- Mineral waters help reduce the secretory function of the stomach, namely acidity. They also improve motor function and help normalize the functioning of the liver and pancreas. Carbon dioxide, bicarbonate sodium-potassium waters are recommended. For example, such as “Essentuki 4”, “Moskovskaya”, “Smirnovskaya”.
- Mud applications also help normalize the motor function of the stomach. The best effect of therapeutic mud is 3-4 weeks after surgery.
- Physical therapy is a whole medical area that deserves to be considered separately. However, we will indicate the key positive aspects that exercise therapy gives us. Therapeutic exercise has a general tonic effect and helps strengthen the abdominal muscles. Which in turn leads to the elimination of constipation and accelerated healing of the postoperative scar.
Material and methods
We have the immediate results of treatment of 646 patients with PJ of the stomach and duodenum who were in the clinic for the period 2004-2013. 86.6% of patients were delivered within the first 4 hours from the onset of the disease, which is associated with the severity of abdominal pain. 90.6% of patients were operated on within the first 2-4 hours from hospitalization. Of the surgical methods of treatment, simple suturing of the perforation hole clearly predominated - in 358 (55.5%) patients, the rest underwent vagotomy of various types - in 215 (33.3%), gastrectomy - in 73 (11.2%) patients.
The main stages of exercise therapy during the recovery period
- Due to the nature of gastric surgery, increased breathing may cause pain in the first days after surgery. Therefore, breathing these days should be predominantly chest. There is no particular need for increased or deep breathing at the moment.
- On the third day after surgery, you can add a light massage, rubbing the chest. Starting from 4-5 days, general tonic and strengthening exercises are included. You can also sit on the bed with your legs down starting from 4 to 5 days.
- Full exercise therapy sessions can be carried out from 9 to 10 days after surgery. The emphasis is on restoring diaphragmatic breathing. The complex of classes also includes exercises to strengthen the abdominal muscles. The duration of classes is no more than 20-25 minutes.
Restorative measures at the hospital stage
Now we will consider in more detail the complex of measures at each stage of postoperative recovery. Let's start with the early, hospital stage. In addition to the already mentioned approaches of physical therapy and breathing exercises at the hospital stage, other elements are no less important. For example, nutritional therapy.
Patients begin to feed regular food 4–5 days after surgery. The nature of the meal is fractional. You can drink weak tea, eat 1 - 2 raw eggs. It is allowed to take foods rich in protein, meat and fish dishes, vegetable and fruit purees. From 3 - 4 days you can connect low mineralization mineral water. At this stage, mineral water helps reduce swelling of the gastric mucosa and normalizes the functioning of the liver and pancreas.
Otherwise, during the hospital stay, medication support plays the main role. Depending on the patient’s condition, you can get a psychologist and autogenic training. The next stage is sanatorium-resort treatment.
Restoration activities at the sanatorium-resort stage
Rehabilitation after gastric surgery in a sanatorium can begin from 2 to 3 weeks. It is worth noting that there are enough special gastroenterological institutions and sanatoriums in many regions. Patients can be referred for sanatorium-resort treatment only after all indicators have normalized and the postoperative wound has completely healed without complications.
The complex of rehabilitation measures in the sanatorium includes:
- therapeutic and dietary nutrition
- sanatorium regime
- drinking mineral waters
- mud - and balneotherapy
- physiotherapeutic procedures
- therapeutic exercises and massage
Spa treatment begins with the appointment of mineral waters. Mineral waters help reduce inflammation in the stomach and improve secretory function. The use of mineral waters has virtually no restrictions or contraindications.
Also, in addition to the internal use of mineral waters, medicinal baths are actively prescribed. Chloride, sodium, iodine-bromine baths are recommended. In general, baths of any chemical composition act unidirectionally. They help improve general condition, normalize muscle tone, and oxygen metabolism. You can also alternate taking therapeutic baths with mud therapy.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are also prescribed at the stage of spa treatment. But it is necessary to take into account the adaptation factor at the resort. As a rule, the body adapts within 3-4 days at least, especially when moving to another region. These days, the appointment of severe physiotherapeutic procedures is not recommended. And also, physiotherapy is not recommended for 10 - 14 days after surgery in principle. And if a trip to a sanatorium occurs immediately after discharge from the hospital, then physical treatment is prescribed in the following days or already at the stage of outpatient rehabilitation.
Surgical and conservative treatment of giant gastric ulcers
IUlcerative lesions of the stomach are not only a medical, but also a social problem due to the widespread prevalence of the disease and the high cost of treatment. With regard to giant gastric ulcers (GPG), the approach to choosing treatment (surgical or conservative) has not yet been determined [1], and there are also no results of long-term observations of patients after various types of treatment [3].
Materials and methods
In order to develop treatment tactics and criteria for predicting the effectiveness of various approaches to the treatment of GYG, we spent 10 years (1985-1994) in the medical departments of the State Military Clinical Hospital named after. N.N. Burdenko comprehensively examined and observed 223 patients with this pathology. The presence of GNG in all patients was confirmed by fibrogastroscopy; the malignant nature of the ulcerations was excluded based on the results of multiple biopsies and long-term follow-up (for 2-9 years). All patients underwent a thorough examination using clinical, instrumental and laboratory methods, including fractional examination of gastric contents and pH measurements. Control fibrogastroscopy was performed 2-4-6 weeks from the start of treatment and 1, 6 and 12 months after ulcer healing. The male to female ratio was 27:1, with patients over 60 years of age accounting for 47%.
results
In 187 (83.8%) patients, gastric ulcers had a diameter of up to 5.1 cm, in 25 (11.2%) patients - more than 6.1 cm. The distribution of gastric ulcers and their localization are presented in Table. 1. Most often, GGS were localized in the body of the stomach - in 149 (66.8%) patients. During the analyzed period, 32 patients underwent surgery for GCT. Indications for surgery, their scope and timing of surgical treatment from the moment of diagnosis of thyroid cancer are presented in table. 2. Even when providing surgical care for urgent reasons (the development of life-threatening complications - bleeding, perforations) - the volume of the operation was quite large (from gastric resection to gastrectomy). All gastric resections according to Billroth I were also performed in urgent conditions. The duration of surgical treatment for developed complications ranged from 1 to 4 days. The main indications for surgical intervention in 56.3% of cases were developed complications, which forced the performance of rather large and crippling surgical interventions. When choosing surgical treatment tactics, we were guided by the results of endoscopic and morphological studies of biopsy specimens, which did not allow us to clearly judge the absence of malignancy of the ulcer during the initial examination of the patient. The average duration of treatment for patients with OTG after surgery was 43.8±9.6 days. Conservative treatment of HTN in the absence of complications was carried out according to general principles: gentle physical activity, restriction of mechanically and chemically irritating foods for 2 weeks. In the first days of the week, in the presence of pain, selective M1-cholinergic receptor blockers (gastrocepin) or injectable forms of H2-blockers (quametol and neutron) were used until the pain subsided and long-acting antacids (Almagel and Maalox). After the disappearance of pain (usually on the 2-3rd day) or when it was of low intensity upon admission, patients were treated with tableted secretion blockers. Thus, since 1992, H2-blockers of the second and third generations (ranitidine, Zantac, ranisan and famotidine) have been used, which provide the necessary therapeutic effect when used twice a day. The first control gastroscopy was performed 10-14 days after the primary one. Upon receipt of an unequivocal conclusion from morphologists about the benign nature of the gastrointestinal tract, the next control gastroscopy was performed at an interval of 2 weeks. During the final fibrogastroscopy (determining the healing of the ulcer), biopsies were also taken from the scar at the site of the ulcerative defect. The main treatment was supplemented with physiotherapeutic procedures only after receiving the results of a repeated histological examination of the biopsy specimens. The average healing time for GJ was 38.6±4.3 days. In 99 patients with thyroid cancer, the course of the disease was complicated by bleeding, 84 of them were placed in the intensive care unit. In table Table 3 presents data on indications for placing patients in the intensive care unit. To stop bleeding, general measures were used - bed rest, fasting, cold on the abdomen, ingestion of finely crushed ice (in 100% of patients); intensive care measures - intravenous administration of a 5% solution of aminocaproic acid, 200 ml per drip infusion, total volume up to 400-550 ml/day, administration of fresh frozen plasma, 2 doses per infusion 1-2 times a day, crystalloid solutions under the control of circulating blood volume (BCC) until it normalizes (in 79.8% of patients); replacement of blood loss by transfusion of single-group red blood cells in 47 (55.9%) patients; local endoscopic methods of stopping bleeding - irrigation or application of adhesive compositions or film-forming aerosols (MK-6, MK-7, gastrosol, etc.) to the area of the ulcer in 17 patients, coagulation of the bleeding site or vessel in the ulcer (in 38.9% of patients) , alkalization of gastric contents. Until 1987, they resorted to drip administration of sodium bicarbonate through a rubber or polymer probe inserted into the gastric cavity under control of the pH of the gastric contents. Currently, drip administration of a suspension of liquid antacids (Almagel, Gelusil-varnish, Maalox), diluted at the rate of 100 ml of suspension per 50-70 ml of physiological solution, is carried out. The use of this method of treatment of HTG in the development of bleeding allowed 81 (96.4%) patients to achieve stable bleeding control within a period of 2 to 5 days.
Discussion
As can be seen from the above data, conservative treatment of thyroid cancer is longer than surgical treatment. However, despite this, we still prefer conservative treatment. The correctness of this approach is confirmed by the results of long-term observations (over a period of 2-9 years) of patients with thyroid cancer discharged from the hospital after treatment. In particular, after surgery, patients sought medical help 2 times more often than after conservative treatment. The number of hospitalizations after surgical treatment was also significantly higher than after conservative treatment, which is explained by the development of disease of the operated stomach in patients due to the disabling nature of the operations and the large volume of surgical intervention (gastric resection or gastrectomy). Some authors [1,3] take into account the state of trophism of the gastric mucosa when conservatively treating GAG. In 79 patients with gastric ulcers, in whom the leading element of ulcer formation was insufficiency of trophism of the gastric mucosa, we added hyperbaric oxygenation to the main treatment in courses of 10 sessions every other day, which made it possible to reduce the treatment time by an average of 7.0 ± 0.5 days.
conclusions
1. The indication for surgical treatment of HTG is the development of life-threatening complications - perforations and bleeding that are not amenable to intensive hemostatic therapy in a specialized hospital; long-term indications are non-healing of the ulcer for more than 3 months from the start of therapy. 2. In the absence of absolute indications for surgery, conservative treatment of gastric ulcer is carried out according to the principles of therapy for peptic ulcer disease, taking into account the clinical and morphological variant of the course and the presence of concomitant diseases.
Literature:
1. Bagmet I.I. Giant stomach ulcers: causes of formation and features of clinical manifestations. Fourth All-Union Congress of Gastroenterologists. M.; L., 1990. T. 1; C. 363.
2. Grebenev A.L. Guide to gastroenterology. M.: Medicine. 1996. T.2.; 710 c.
3. Spesivtsev V.N. Evaluation of the effectiveness of modern antiulcer drugs. Proceedings of the conference “Clinical aspects of pharmacotherapy and presentation of new things in gastroenterology.” Smolensk; M., 1992. p. 170-3.
Physiotherapy and types of procedures
The main techniques used for recovery after gastric surgery:
- galvanization - does not have a stimulating effect on the secretory function of the stomach, but at the same time helps to improve its bioelectrical activity. Which in turn improves blood circulation, normalizes the blood coagulation system, improves blood circulation in the liver, and has a beneficial effect on the immune system. If it is necessary to administer any drug, electrophoresis is prescribed.
- ultra-high frequency therapy (microwave) is a more deeply penetrating method of exposure to an electromagnetic field. It has the property of generating endogenous heat in tissues, which helps normalize a number of physiological reactions. Improves metabolic processes, blood microcirculation in tissues. But mainly, microwave helps to normalize the function of the thyroid gland and the endocrine system as a whole. In addition to restoring digestive functions after surgery, microwave helps stimulate reduced immunity and rapid healing of the postoperative scar.
- magnetic therapy - has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, trophic effects. But mainly it normalizes blood circulation, enhances the recovery process, and restores metabolism in the gastric mucosa.
Rehabilitation after gastric surgery, as we see, is not a quick process. And its peculiarity is that in addition to restoring the stomach itself, there is a need to restore many other organs and systems, as well as body functions. For example, such as digestion, endocrine regulation. Not only the above methods can be prescribed, but also many others.
It is also necessary to take into account that after surgery on the stomach, a person’s lifestyle may be completely different than before the operation. This mainly depends on the reason for which the operation was performed, as well as the type of operation performed. Depending on the complexity of the surgical intervention, a lot can change - from diet to loss of ability to work. Therefore, at certain stages of rehabilitation, psychological rehabilitation and medical and social control may be involved. And of course, some parts of rehabilitation need to be repeated periodically. Especially sanatorium-resort treatment and physiotherapy courses in the clinic at the place of residence.