Pain syndrome accompanies many diseases. There is a common misconception that shingles pain in the back occurs only with diseases and injuries of the spine. However, experienced rheumatologists and therapists draw patients’ attention to the fact that the cause of pain may be diseases of the internal organs. Specialists at the Yusupov Multidisciplinary Hospital provide daily medical care to patients experiencing this symptom. Comprehensive treatment programs are based on highly accurate diagnostic data, which increases the effectiveness of the chosen therapy.
Shingles in the back: causes
Girdle pain in the abdomen and back is most intense; it can be short-term or long-lasting, depending on the causes of development. It is difficult to independently determine the cause of pain, since the appearance of this symptom can occur due to various disorders:
- Spinal diseases are characterized by increased pain when moving. As the pathological process progresses, other symptoms appear: numbness, increased sweating, tingling and burning in the affected area. In addition, these signs may indicate compression of the nerve roots;
- intercostal neuralgia appears with injuries, prolonged stay in a stationary position, or muscle strain. With this disease, the girdle pain is localized under the ribs or between them, so breathing is difficult;
- lung diseases, which are accompanied by fever, cyanosis of the skin. Diseases such as pneumonia and pulmonary tuberculosis can cause serious consequences if left untreated;
- urolithiasis disease;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- heart attack;
- diseases of the digestive system, characterized by pain under the ribs; this symptom can be combined with nausea, vomiting and fever.
If you have back pain, you need to consult a general practitioner who will examine the manifestations of the pathological condition and prescribe diagnostic measures. The multidisciplinary Yusupov Hospital employs experienced rheumatologists, who are most often approached for help by patients experiencing shingles pain in the back. Specialists are ready to develop an individual treatment program for each patient and begin its implementation after receiving consent from the patient.
Abdominal pain as a symptom of heart disease
It is important for people with heart pathologies and a tendency to problems with blood vessels to know that a sudden attack of sharp or cutting pain in the upper abdomen can be the initial manifestation of a heart attack, therefore, even in the absence of other symptoms, it is recommended to sit in a sitting position with your legs extended forward and take a Nitroglycerin tablet
" The product must be taken sublingually - under the tongue. Repeated administration is allowed after 5-7 minutes, if necessary.
Important!
An abdominal infarction is often accompanied by severe nausea, as well as a single vomit. These symptoms usually appear at the beginning of an attack.
What to do if you have a heart attack?
Timely provision of emergency care is of great importance in the prognosis of life and health after a myocardial infarction. The patient must be seated on a chair or placed in bed, but in such a way that the legs and head are elevated. There must be enough air in the room to restore respiratory activity and prevent acute hypoxia, so windows and vents must be open. Any restrictive clothing and accessories that can compress blood vessels and arteries must be removed from the patient.
Nitroglycerin" are used as an emergency medicine
", as well as metered spray and aerosol "
Nitrosprey
".
If there are signs of acute respiratory failure, intravenous administration of the bronchodilator drug " Eufillin
" is allowed, but only after familiarization with the recommended dosage regimen and the list of contraindications.
Girdle pain in the abdomen and back
Synchronous pain in the back and abdomen is a dangerous symptom, as it occurs rarely. Pain in the abdomen and back at the same time can indicate diseases of the digestive system, for example, with a peptic ulcer, it appears after eating and is accompanied by nausea and vomiting. Unbearable pain in the abdomen and back is observed during exacerbation of pancreatitis; pain can spread to the area of the shoulder blades or heart.
Inflammation of the appendix can occur suddenly; the pathological process is indicated by symptoms such as nausea, a slight increase in temperature, diarrhea and pain that simultaneously appears in the abdomen and back. The danger of appendicitis is that when the appendix ruptures, peritonitis can occur, so only surgical treatment is performed.
Simultaneous pain in the back and abdomen in women is observed with gynecological diseases:
- ectopic pregnancy;
- development of fibroids;
- endometrial proliferation;
- twisting of the legs of a cyst or fibroids;
- spontaneous termination of pregnancy.
Pain syndrome is also observed in women after childbirth. The localization of pain in the back and abdomen is explained by the fact that during labor the muscles experience severe strain.
Patients seeking help at the Yusupov Hospital can be confident that specialists will accurately determine the cause of the pain syndrome and select the most effective and safe methods to eliminate the problem.
Inflammation of the pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system responsible for producing the hormone insulin, which regulates carbohydrate metabolism. Inflammation of organ tissue is called pancreatitis
. The pathology is most often diagnosed in men aged 25-45 years who lead an unhealthy or sedentary lifestyle or abuse high-calorie and fatty foods. The pathology is predominantly chronic, but if all doctor’s prescriptions are followed, stable long-term remission can be achieved. Exacerbation of the inflammatory process and the appearance of dull pain in the upper abdomen usually results from drinking large amounts of alcoholic beverages or overeating, especially if the food consumed contains a lot of fat and simple carbohydrates.
It is not always possible to recognize an attack without laboratory and hardware diagnostics, despite the fact that the disease has a fairly clear clinical picture. This is due to the fact that the main symptoms of inflammation of the pancreas are identical to the manifestations of other diseases of the digestive system, and only an experienced specialist can differentiate them from each other. Signs of exacerbation of pancreatitis include:
- repeated, profuse vomiting with an unpleasant odor, containing pieces of undigested food;
- blue discoloration of the facial skin (in rare cases, signs of cyanosis can be observed on the upper and lower extremities, neck, abdomen);
- irradiation of pain to the lumbar region, collarbone, interscapular area;
- increased pain in the first few minutes after vomiting.
During the inflammatory process, enzymes accumulate in the tissues of the pancreas, which quickly corrode it and destroy the tissue structure. This phenomenon causes typical symptoms of intoxication: hemorrhages in the form of small dots or small spots of arbitrary shape that appear in the central umbilical line, on the lateral abdomen and on the surface of the buttocks. It is by this symptom that a doctor can diagnose an acute attack before conducting an examination.
How to treat?
The basis for the treatment of pancreatitis and other inflammations of the gastrointestinal tract is a diet using mechanical, chemical and temperature gentle methods. To stop the attack, the patient is prescribed complete rest and bed rest. The drug treatment regimen is shown in the table below.
Treatment of pancreatitis in adult patients (after relief of an acute attack)
| What are they for (goals and objectives)? | What medications should I take? | Image |
| Neutralization of excess hydrochloric acid, protection of mucous membranes from additional damage, restoration of normal acidity | "Gastal", "Almagel", "Almagel-Neo", "Maalox", "Rennie", "Phosphalugel" | |
| Blocking enzymes that destroy pancreatic tissue | "Rabelok", "Omeprazole", "Omez", "Pantripin" | |
| Relieving spasms and relaxing smooth muscle fibers, eliminating pain | “Spazmalgon”, “Maksigan”, “No-shpa”, “Papaverine”, “Drotaverine” | |
| Reducing the load on the inflamed organ, restoring the natural secretion of pancreatic enzymes | “Biozyme”, “Gastenorm”, “Creon 10000”, “Pancreatin” |
To relieve repeated vomiting, Cerucal
“, but it is better to do them in a hospital setting, since the drug can have a negative effect on the functioning of the heart and the functioning of the respiratory centers.
Ways to identify the causes of girdle pain
Modern diagnostic methods make it possible to determine the cause of pain localized in the back and under the ribs. When patients who have experienced back pain come to the Yusupov Hospital, the existing symptoms are studied, after which an examination is prescribed.
The main diagnostic measures for back pain are:
- urine and blood tests. The Yusupov Hospital has its own laboratory, so the results are delivered to the attending physician in the shortest possible time;
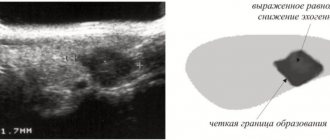
- Ultrasound of internal organs to detect pathological changes;
- examination of substances discharged from the lungs to exclude diseases of the respiratory system;
- X-ray of the upper limbs and lungs;
- gastroscopy.
Patients may be referred for additional consultation to other specialists at the Yusupov Hospital, a cardiologist, a neurologist, or a rheumatologist. Self-medication for back pain can provoke serious consequences, since without special equipment and knowledge it is impossible to accurately identify the cause of the disease and its manifestations.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis of abdominal pain on the right, the doctor prescribes the following tests.
Blood tests
A clinical blood test reveals signs of inflammation (increased leukocytes, accelerated ESR). Appendicitis is characterized by a sharp increase in the level of leukocytes to 15x109/l. Liver tests evaluate liver function.
Analysis of urine
A general analysis and, if necessary, urine culture exclude/confirm kidney inflammation and the presence of stones.
Stool tests
The coprogram diagnoses gastrointestinal diseases. If an intestinal infection is suspected, a stool culture is performed. A test for occult blood is prescribed when bleeding is suspected (for example, in Crohn's disease). Children who complain of abdominal pain are tested for dysbiosis and worm eggs.
Instrumental methods
Ultrasound (including Doppler mode) is the safest method for examining the abdominal cavity, pelvic organs and kidneys. The study is carried out for abdominal pain of any location in adults, pregnant women and children of all ages. If you suspect a disease of the stomach and gallbladder, it is advisable to undergo an FGDS. Pathology of the small intestine is diagnosed using x-rays. For colitis, colonoscopy is prescribed. However, the doctor receives the most accurate information about organic changes in the gastrointestinal tract using CT/MRI.
High-quality treatment for pain in the back and under the ribs
Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe comprehensive treatment to eliminate the girdle pain under the ribs and in the back, as well as possible disorders. For some diseases, the patient needs emergency care, which specialists from the Yusupov Multidisciplinary Hospital are ready to provide. Round-the-clock operation of clinics allows diagnosis and hospitalization immediately after treatment.
Medicines are used to treat pain and its causes. Experts draw the attention of patients to the fact that painkillers and medications to relieve spasms have a temporary effect, in addition, they can complicate diagnosis. To eliminate pain, medications in the form of ointments, injections and tablets can be used.
If the patient’s health and life are in danger, surgeons at the Yusupov Hospital can perform surgical intervention. With this method of treatment, experts prefer minimally invasive techniques, after which recovery occurs faster.
Shingles in the back can appear due to insufficient physical activity; rheumatologists recommend leading an active lifestyle, observing personal hygiene rules, and also paying attention to the psychological state to prevent diseases. The Yusupov Hospital employs specialists who develop nutrition programs taking into account the client’s taste preferences.
At the Yusupov Hospital you can receive a wide range of medical services. Specialists pay attention to each patient and accompany him during the treatment process and make the necessary adjustments. If you are concerned about pain in the back area, do not delay visiting a specialist. An appointment with a general practitioner and other specialists can be made by calling the Yusupov Hospital.
Abdominal pain on the right side in men
Dull abdominal pain in men most often occurs due to an inguinal or umbilical hernia. The reason is excessive physical activity. A bulge in the groin often develops in boys under 1 year of age due to weakness of the ligamentous apparatus, so babies should not be allowed to cry angrily for a long time. Umbilical and inguinal hernias are eliminated with plastic surgery (suturing the hernia opening or strengthening it with a special mesh). Without timely surgical intervention, strangulation of the hernia is highly likely. The pain increases, spreads to the entire abdomen, patients note frequent vomiting, stool retention and bloating. The surgery is performed on an emergency basis.
Pain in the lower back, radiating to the groin and leg, is characteristic of protrusion and herniation of the intervertebral disc. Patients often complain of weakness and numbness in the legs. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor will prescribe an effective course of anti-inflammatory drugs. If necessary, a therapeutic blockade or surgery is performed.
Diseases of the genitourinary system in men (cystitis, prostatitis, prostate adenoma) are manifested by pain in the lower abdomen, which subsides after defecation and urination. However, sometimes the pain is worse on the right or left.
With orchitis (inflammation of the testicle) and vesiculitis (an inflammatory process that develops in the seminal vesicles), the temperature suddenly rises, a sharp or dull pain radiates to the groin and perineum, and intensifies when walking down the stairs and physical activity. The damaged testicle swells. Inflammation of the testicles often complicates the course of sexually transmitted diseases and is fraught with infertility.
Varicocele (varicose veins of the spermatic cord) is diagnosed in every fourth man under the age of 30. The disease is often asymptomatic and is diagnosed during clinical examination of adolescents. Only in severe cases does aching pain occur on one side of the scrotum and in the groin. Pain increases with overheating, physical exertion and during sexual intercourse.
When testicular torsion occurs, a sharp pain suddenly occurs in the scrotum on one side, radiating to the groin, perineum and lower back. In young boys, the disease is accompanied by nausea and vomiting. Palpation reveals a higher position of the testicle in the scrotum. The pathology is eliminated urgently.
Important! If you suspect prostatitis, prostate adenoma or testicular disease, you should contact a urologist-andrologist.
What to do
When acute pain appears, spreading throughout the abdominal cavity, as well as around the body to the back, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible. After all, most often such sensations appear in serious conditions that require medical attention, and sometimes even surgical intervention.
Sometimes you need to call an ambulance. Before the doctor arrives, it is necessary to ensure complete rest for the patient. He should lie down, preferably on a flat surface. It is important to immediately stop eating, since such sensations are often caused by poisoning or pancreatitis. You are only allowed to drink clean water without gas. If the pain is acute and unbearable, you can take an antispasmodic tablet. But you should not get carried away with painkillers, as their use can complicate the diagnosis.
In many pathologies, cold helps reduce pain. Therefore, it is recommended to apply a cold heating pad or ice to the area of the most intense pain. Under no circumstances should you apply warm compresses or take a bath, as this can worsen the condition and intensify the inflammatory process. It is not advisable to take any medications, especially laxatives, before diagnosis.
Many pathologies that cause abdominal pain are treated in a hospital setting. After all, conditions such as acute pancreatitis, cholelithiasis or urolithiasis often require surgical intervention. But if you consult a doctor in a timely manner, you can get by with conservative therapy. It usually includes medication, a special diet, and traditional methods.
All treatment is prescribed by a doctor after examination. After all, medications should not only relieve symptoms, but also eliminate the causes of pain. Therefore, antibiotics are used for infectious pathologies, enzyme agents are used for overeating or poor circulation, and antacids are used for ulcers or gastritis. It is undesirable to take even painkillers without a doctor’s prescription. Only antispasmodics are allowed, for example, Platyfillin or Dustpatalin. It is dangerous to dull the pain with pills, as you can miss peritonitis or an attack of appendicitis.
Types of pathologies
Pathological changes in different parts of the intestine, dysfunction of the stomach, pancreas, and organs of the genitourinary system can provoke the occurrence of abdominal pain. Here are just some examples of pathologies that can cause stomach pain:
- Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the colon. In addition to pain, there is a general deterioration in health, the appearance of blood in the stool, and rapid heartbeat. Ignoring pain and not seeking medical attention increases the risk of developing peritonitis;
- enteritis - inflammatory processes in the small intestine. The patient may believe that it is a more intestinal infection, since the nature of the pain and other symptoms are very similar;
- Crohn's disease is an inflammatory process in one or more parts of the intestine. In addition to intense pain, intestinal obstruction may develop. Therefore, you should not get sick at home and self-medicate; you should immediately consult a doctor;
- Dysbacteriosis is a pathology in which the intestinal microflora suffers. Pain is accompanied by intense gas formation and stool disturbances;
- pancreatitis is a pathology of the pancreas. The upper abdomen hurts, problems with digestion arise;
- cystic fibrosis - damage to the pancreas and respiratory tract. Characterized by abdominal pain without inflammatory processes;
- gastritis is an inflammatory process in the gastric mucosa or in its individual areas. There are discomfort in the abdomen, and burning and cramping in the upper part. The pain may be accompanied by a feeling of overeating or, conversely, a feeling of hunger. In advanced cases, intense pain, nausea, and vomiting are observed;
- stomach ulcer – a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane. The pain is accompanied by a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, pain in the upper part of the abdominal cavity;
- “reflux” is a decrease in the tone of the valve connecting the stomach to the esophagus. Characterized by pain and burning sensations;
- appendicitis - inflammation of the appendix. The pain is localized in the right part of the abdominal region, below the navel;
- Diverticulitis is the formation of spherical capsules in the walls of the colon. Abdominal pain is accompanied by chills, cramps, and fever;
- cholecystitis – inflammatory processes in the gallbladder. Characterized by abdominal pain that worsens after eating.
Problems of the lower abdomen are typical for the fair sex. Severe pain before and during menstruation may indicate that a woman has endometriosis. If there are inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs, the lower part of the abdominal cavity may hurt. There are a number of other pathologies that can only affect women (ovarian cysts, neoplasms in the uterus, and others). They are also causes of specific pain.
Abdominal pain can occur due to hernias. Particularly insidious in this case are diaphragmatic hernias, which are outwardly invisible. In this case, the patient may believe that he has gastritis, since the symptoms are similar.
Rectus abdominis syndrome
Abdominal pain or abdominal pain is a common reason for patients seeking medical help. Over a 5-year follow-up period, up to half of individuals experience abdominal pain.
There are several types of abdominal pain:
1) visceral - associated with damage to internal organs, most often the digestive organs. It is characterized by unclear localization, i.e. the pain zone only approximately corresponds to the affected zone. This pain is often associated with eating, defecation, etc.
2) parietal - occurs when the parietal peritoneum is involved in the process of inflammation. The pain is usually clearly localized, sharp, cutting, stabbing, and is accompanied by symptoms of peritoneal irritation.
3) referred pain - occurs when several zones are innervated by one segment of the spinal cord. For example, abdominal pain can occur with myocardial infarction.
4) projection pain - occurs when nerves are damaged, and the place of pain perception corresponds to the zone innervated by this nerve.
This article will discuss one of the diseases that is characterized by projection pain, namely anterior cutaneous nerve entrapment syndrome . It is also called rectus abdominis syndrome. In the English-language medical literature, the term ACNES is used (anterior cutaneous nerve entrapment syndrome, which translated into Russian means anterior cutaneous nerve entrapment syndrome), which we will use further in this article.
ACNES is one of the common causes of abdominal pain that remains unrecognized. On average, the prevalence of this syndrome is 1:1800-2000. In adolescents, one out of eight cases of chronic abdominal pain is caused by anterior cutaneous nerve entrapment syndrome. Up to 2% of cases of patients visiting a hospital emergency room with acute abdominal pain are caused by ACNES.
Pathogenesis of ACNES.
In ACNES, the lower thoracoabdominal intercostal nerves (Th8-Th12) are involved in the pathological process. They pass between the internal oblique and transverse abdominis muscles to the point where they reach the rectus abdominis muscles. Here the nerves turn to enter the rectus abdominis channels. It is assumed that compression of the nerves in the rotation zone is the leading mechanism for the development of ACNES. Pinching occurs due to muscle contraction, which can cause additional compression of the nerve, its ischemia, and, as a result, leads to severe pain.
Clinical picture of ACNES.
Pain (dull or sharp) is usually localized in a certain area - along the edge of the rectus abdominis muscle in the umbilical region or in the right hypochondrium. The pain is usually chronic, constant or frequent, less often in the form of individual episodes. The area of pain in most cases can be easily identified by palpation in the painful area. In rare cases, when the ilioinguinal and iliohypogastric nerves (Th12-L1) are pinched, the pain may have an atypical localization: in the iliac region and groin. Localization of pain in the right hypochondrium can simulate an attack of biliary colic.
The pain may vary depending on the person's posture, worsening when lying on the side of pain or sitting. Pain sensations are reduced when lying on your back. Coughing, laughing, bumpy driving, running, wearing tight belts and corsets, as well as exercise lead to increased abdominal pain.
Diagnosis of ACNES.
Diagnostic criteria for anterior cutaneous nerve entrapment syndrome include the following:
1) Unilateral localized pain in the abdominal wall lasting at least 1 month;
2) The presence of a unilateral painful area (“trigger point”) on the anterior abdominal wall measuring about 2 cm2, detected by pressing the index finger along the lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle;
3) Positive Carnett's sign. Carnett's sign, named after the scientist who described it in 1926, involves the examiner identifying the exact location of maximum tenderness on the abdominal wall and asking the patient to elevate the head and/or torso with the arms crossed over the chest. Increased pain or persistent pain during this movement indicates that the cause of the pain is located in the abdominal wall (positive Carnett's sign). On the contrary, a negative Carnett symptom indicates another cause of pain (for example, pathology of the internal organs);
4) Positive “pinch” test: when fingers grasp a fold of skin and subcutaneous tissue, local pain is detected;
5) A change in the tactile sensitivity of the skin in response to a light touch and/or a change in the temperature sensitivity of the skin with a decrease in the perception of cold in the area of the most severe pain;
6) Normal laboratory data (no signs of inflammation or infection) in the absence of a surgical cause of pain;
7) Absence of pathology according to imaging studies (including ultrasound, computed tomography);
A temporary reduction in pain by at least 50% after injection of a local anesthetic (usually lidocaine) at the trigger point.
Differential diagnosis of ACNES
The differential diagnosis includes various diseases in order to exclude other causes of chronic abdominal pain. The examination may reveal cicatricial changes in the skin, causing irritation and pinching of nerves, as well as hernias of the anterior abdominal wall (including those with signs of pinching).
In most cases, a thorough clinical and laboratory examination is required to exclude pathology of the abdominal organs.
Differential diagnosis with functional diseases of the digestive system, for example, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and functional abdominal pain, seems more difficult. Since there are no special research methods to diagnose these diseases, the doctor has to focus on typical clinical manifestations. Even ex juvantibus diagnosis (a diagnosis based on an assessment of the results of treatment) does not help, since therapy is not effective in all patients with IBS. The ACNES Questionnaire was developed to help differentiate functional bowel pain from pain caused by anterior cutaneous nerve entrapment syndrome. An index value of more than 10 points makes the diagnosis of functional abdominal pain unlikely.
ACNES therapy.
Treatment of anterior cutaneous nerve entrapment syndrome includes several approaches:
1) Systemic therapy - the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, weak opioid analgesics (tramadol), paracetamol, antiepileptic drugs (gabapentin) and antidepressants (amitriptyline). Unfortunately, therapy with these drugs, which often helps with other types of neuropathic pain, is usually ineffective in the case of ACNES.
2) Local therapy:
A. Trigger point injections. The trigger point in ACNES is the site of a pinched nerve, so injection of a local anesthetic into this area has both a therapeutic and (in complex cases) diagnostic effect. A 1% solution of lidocaine (10 ml) with or without the addition of steroid hormones is usually used as an anesthetic. The effect of treatment is defined as a reduction in pain severity by 50% or more, and the duration of the effect usually exceeds the half-life of the drug. The addition of steroid hormones may result in more durable pain relief, possibly due to their anti-inflammatory effects and attenuation of nerve excitation. However, their use is often associated with side effects, mainly abdominal muscle atrophy and systemic adverse reactions.
The blind method of administering anesthetic may result in an incorrect injection zone, as a result of which the use of ultrasound guidance has recently been recommended. The use of an ultrasound machine allows lidocaine to be injected precisely into the affected area, avoiding complications (entry into the abdominal cavity).
B. Chemical neurolysis. The literature describes the effect of 96% ethyl alcohol or 5-6% phenol solution for chemical destruction of pinched nerve fibers. However, there is no data on the long-term effectiveness and safety of this method.
B. Radiofrequency ablation is the treatment of nerves or nerve ganglia with high-frequency electrical impulses.
D. Ultrasound-guided injection of botulinum toxin into the trigger zone has been studied as an alternative technique, but there is no data on the long-term effectiveness of this method.
3) Surgery:
A. Laparoscopic anterior neurectomy - removal of a section of a pinched nerve.
B. Using a reinforcing polytetrafluoroethylene mesh over the problem area to prevent compression of the nerve.