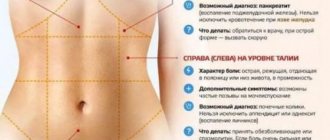
Most women experience nagging pain before menstruation. Such sensations are familiar to them, so they do not frighten the fair half of humanity. Sometimes pain begins to bother you in the middle of the cycle, a week or two before the start of menstruation. Most often, such pain indicates past ovulation. The woman begins to wonder if this is normal and whether it is possible to get rid of the pulling sensations that bring discomfort.
What happens in the body?
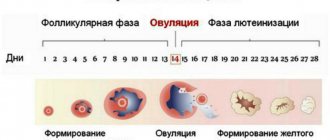
If a woman has no health problems, ovulation occurs exactly in the middle of the menstrual cycle. For most women, the cycle lasts 28-30 days, that is, the rupture of the dominant follicle occurs on the 14-15th day of the cycle. In some cases, the cycle can be 26 days or 32-34 days. You can determine the exact date of ovulation using an ultrasound (this method is used during pregnancy planning) or by keeping a basal temperature chart. The second method is less accurate, since the indicators are affected by hormonal fluctuations, endocrine problems and infectious diseases.
The egg matures and prepares for fertilization during the first half of the cycle. For follicle growth to occur, a woman's brain produces FSH. This is follicle-stimulating hormone (follitropin), which is responsible for the functioning of the reproductive system and the maturation of the dominant follicle. On the 14-15th day of the cycle, the follicle ruptures, the mature egg begins to move through the fallopian tubes, where, after meeting the sperm, fertilization occurs.
Premenstrual syndrome is associated with hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle. It is not known why it is more pronounced in some women than in others. However, it has been established that there is a hereditary predisposition to this pathological condition. The likelihood of nagging pain a few days after ovulation increases if a woman does not receive enough vitamin B6, calcium or magnesium from food. Stress, lack of physical activity and excessive consumption of caffeine-containing drinks increase discomfort.
Key Causes of Pain
- A follicle breakthrough is a microtrauma inside the body
. In which of the ovaries the rupture occurs, nagging, aching pain may appear on that side. Bloody discharge (from bright red to dark brown) may also appear - implantation discharge. Some women don't notice a breakthrough. - Defective ovulation
. Interruption of the process of rupture of the follicle or release of the egg into the tube can be accompanied by severe nagging pain. - The appearance of pain as the first sign of pregnancy
. The implanted egg can affect the female body. Immediately at the moment of attachment, cramping tingling sensations appear in the lower abdomen. A spotting discharge interspersed with blood may appear. - One of the reasons for the appearance of nagging pain is female gynecological diseases
. Polycystic disease, infections, ovarian cysts, inflammation of the genitourinary system and others. Pain occurs due to the weakening of the body as a whole during periods of ovulation. It is worth paying attention to this if there are unusual sensations such as discharge, burning sensation and itching.
After ovulation, before a delay or the onset of menstruation, you can do a test to determine pregnancy with high sensitivity. Tests show the presence of a fertilized egg 7-14 days after expected ovulation.
Is bleeding likely to occur?
A slight discharge of blood in the form of mucous blood streaks or spotting is acceptable in the first 1-2 days after ovulation. Drops of blood can enter the mucus from a wound formed at the site of rupture of the follicular walls, as well as the wound surface of the uterine walls to which the egg is attached.
In case of heavy bloody or brown discharge, as well as bloody spotting that lasts more than 2 days after ovulation, you should immediately go to the hospital, as the possibility of internal bleeding cannot be ruled out.
Symptoms
Women with low weight and unstable psyche often suffer most from primary pain. Secondary pain appears in women over 30 years of age who have had cases of abortion, infectious diseases, or operations.
In such cases, pain due to menstrual irregularities begins the day before menstruation and lasts from 2 to 24 hours. The pain can be of different types - cramping, sharp, aching. In some cases, it can spread to nearby organs.
Painful sensations are conventionally divided into several types:
- Mild pain syndrome. Unpleasant sensations do not cause inconvenience, the woman’s lifestyle and performance do not change. With a mild degree, a pulling, aching pain is felt, which continues during heavy bleeding.
- Moderate pain. Occurs regularly during menstruation, accompanied by other signs of cycle disruption. Such pain cannot be ignored, because it significantly reduces performance and worsens well-being. In most cases, painkillers help relieve the symptom.
- Extremely severe pain syndrome – a woman finds it difficult to get out of bed due to very severe pain in the pelvic area. With such pain, self-administered medications do not alleviate the serious condition.
The cause of pain during menstruation is most often associated with a cycle disorder, and in order to establish the source of the problem, a series of diagnostic measures will often be required.
Disorders that accompany pain during menstruation are conventionally divided into:
- Autonomic – migraine, tachycardia, heart pain, vomiting, swelling.
- Psycho-emotional – bad mood, anxiety, sleep problems, depression.
The appearance of secondary pain is always associated with signs that signal the presence of a particular disease. In most cases, the sources of problems and pain in menstrual irregularities are the following diseases:
- Endometriosis is a pathology in which pain occurs a week before the start of menstruation and subsides by the middle of the cycle. In addition to unpleasant painful sensations, bloody discharge may appear in the lower abdomen.
- Uterine fibroids are formations that block the ability of the uterus to contract. This causes severe pain.
- Adhesions in the abdominal cavity or pelvis - this phenomenon causes a change in position, as well as mobility of the internal genital organs. In this case, pain is present not only during menstruation, but throughout the entire cycle. Painkillers do not provide relief.
Laboratory tests play an important role in the process of investigating secondary pain. With their help, you can find out the cause of cycle disruption and establish the source of pain, determine the level of estrogen, progesterone and other hormones.
Women who suffer from menstrual pain should undergo a pelvic ultrasound examination. Using this examination, you can assess the condition of the uterus, endometrium, and determine the presence of cysts, fibroids or polyps.
Pain as a sign of pregnancy
When pregnancy occurs, global changes begin to occur in a woman’s body, which is due to preparation for the upcoming pregnancy and labor. At this time, various kinds of signs may appear that a new life has arisen inside. Among the main symptoms are nagging pain in the lower abdomen. And it is this sign that most often causes anxiety in expectant mothers.
Often, when the stomach pulls at the beginning of pregnancy, this causes considerable anxiety in the pregnant woman, because such a symptom can predict a premature termination of pregnancy. And indeed there is a risk, but provided that the nagging pain is accompanied by bloody discharge from the vagina. Physiologically, such pain is normal during fertilization.
This is due to a rush of blood to the uterus and increased blood circulation. Also, such painful sensations are associated with swelling and stretching of the uterine ligaments. They, along with the growing uterus, must constantly stretch, which, in fact, can cause a certain kind of discomfort. However, not all women who are in an “interesting situation” observe such a symptom.
Video - First signs of pregnancy
Pain from rupture and torsion of the cyst
Rupture of an ovarian cyst or torsion of a pedicle is an acute condition accompanied by circulatory disorders and requiring urgent surgical treatment. If qualified medical care is not provided in a timely manner, peritonitis may develop, accompanied by a deterioration in the general condition, hypotension, tachycardia, fever and positive peritoneal symptoms.
Typically, pain when an ovarian cyst ruptures begins sharply and suddenly in the lower abdomen, then quickly moves to the upper sections, involving the entire abdomen in the pathological process. The appearance of such pain can be triggered by sexual intercourse, heavy physical exercise, or a pelvic injury. When performing minimal movements, the pain intensifies, accompanied by an uncomfortable sensation in the back, lower back or pelvic area, and a feeling of heaviness. Abdominal pain when an ovarian cyst ruptures can be so severe and intense that it contributes to shock and loss of consciousness.
Pathological causes
If a woman experiences alarming symptoms after ovulation, she should immediately go to the hospital, as many gynecological diseases can lead to dangerous consequences and serious complications. Warning signs include:
- severe pain (possible stabbing and cutting pain);
- bleeding;
- dyspnea;
- dizziness;
- painful bowel movements or urination;
- hypertonicity of the abdominal muscles.
In many pathologies, a woman may experience symptoms of general intoxication: fever, weakness, vomiting and nausea. Pain due to pathologies caused by disturbances in the functioning of the organs of the reproductive and reproductive systems is difficult to relieve with medications and can radiate to the coccyx, shoulder and even the interscapular area.
Anovulation
Speaking about ovulation, one cannot help but touch upon the problem of its absence or anovulation. Normally, anovulation is observed in pregnant women and premenopausal and menopausal women. And, of course, ovulation cannot occur while taking hormonal birth control pills.
If a woman of reproductive age does not ovulate for several cycles in a row (2 or more), she should start sounding the alarm, because no ovulation - no egg - no possibility of getting pregnant.
As a rule, the cause of anovulation is hormonal imbalances in the body, which, with appropriate treatment, are stopped and the woman has a chance to become a mother. To clarify the date of ovulation, you can use ovulation tests or undergo an ultrasound, where the doctor will accurately see the mature follicle and the release of the egg from it (of course, ultrasound is performed several times during the period of expected ovulation).
Urogenital infections in women
The most common diseases of the genitourinary system:
Chlamydia
. Inflammation of the genitourinary system in women manifests itself in the form of cervicitis, cystitis, and pyelonephritis. The inflammatory process provokes ectopic pregnancy and female infertility.
- Adnexitis
. The infection affects the female appendages and is caused by pathogenic microorganisms. Immediate treatment is required to avoid serious consequences. - Urethritis
. Inflammatory processes that affect the urinary tract and cause discomfort. - Vaginitis
. Discomfort, burning and foul odor are the first signs of inflammation. - Gonorrhea
. In women, characteristic pain during sexual intercourse and urination, discharge becomes yellow or red, fever and hemorrhages. - Cystitis
. Diseases of the urinary system and bladder. Causes repeated trips to the toilet, which is painful. - Pyelonephritis
. These are diseases of the kidneys and urinary system. Harmful bacteria, when the disease worsens, cause attacks of sudden pain in the lower back.
The genitourinary system experiences disorders in a variety of diseases. Antibacterial medications and antispasmodics are not the only method of treatment for inflammation. When temperature and fever are observed, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used: Cefekon, Ibuprofen, Nimesulide.
Prevention of diseases of the urinary system is that you need to monitor proper nutrition, lead an active lifestyle, and avoid hypothermia. From time to time you need to use diets in order to reduce the load on your organs. Herbal teas will be useful for treatment and prevention. It is important not to forget about vitamins. And most importantly, maintain personal hygiene and have order in your sex life.
Sexual infections
In some cases, the lower abdomen may feel tight due to the development of sexually transmitted infections. Pain is usually the first clinical sign; other symptoms begin to appear within 2-5 days. The duration of their occurrence depends on the type of pathogen and the incubation period. In addition to pain, a woman may also notice a change in the nature and color of the discharge, the appearance of an unpleasant odor and pain. Characteristics of the main sexually transmitted infections are presented in the table below.
| Group of infections | What diseases are included? | Characteristic |
| Fungal | Candidiasis (thrush) | Discharge from thrush has a white, cream or milky beige hue. The consistency is cheesy interspersed with small white particles. The smell is usually reminiscent of kefir products. Additional symptoms include burning and itching in the perineum and vaginal tract |
| Viral | Genital herpes | With viral infections, the discharge has a mucous consistency and a transparent tint (may be cloudy). The discharge is abundant, rarely has a pungent odor, and resembles thick, coagulated egg whites. Mucus lumps may be present |
| Bacterial | Gonorrhea, chlamydia, bacterial syphilis, etc. | The discharge is thick, yellow, green or brown. They have a sharp putrid odor, reminiscent of rotten fish. Accompanied by severe itching and burning. The skin in the perineal area is irritated, ulcers may appear |
Pain syndrome during sexually transmitted infections usually appears in the first 1-3 days, after which it weakens, and other signs characteristic of this group of diseases appear.
Uterine diseases
Pathologies in the functioning of the uterus are one of the most common causes of prolonged postovulatory syndrome. The following diseases can cause pronounced pulling sensations after the release of a mature egg from the ovary:
- uterine fibroids
- a pathology of the myometrium (muscular layer of the organ), characterized by the growth of benign formations; - endometriosis
- proliferation of the mucous membrane of the uterine walls and penetration of endometrial cells into other tissues; - endometrial hyperplasia
- pathological growth of epithelial cells lining the inner surface of the uterus; - cervical erosion
is a defect in the mucous membrane of the cervix that is benign in nature; - Uterine polyposis
is the growth of benign tumors (polyps) on the walls of the uterus.
Any of these diseases can lead to serious consequences if left untreated. Any benign processes can lead to the growth of malignant cells, so such pathologies should be under constant medical supervision. If diseases of the uterus have taken a chronic course, a woman will have a pull in her stomach after ovulation and before menstruation.
Pain due to ovarian pathologies
It is inflammation that often leads to pain and a burning sensation during sexual intercourse. The disease occurs in women in acute or chronic form. Often the chronic form can be accompanied by the appearance of leucorrhoea and disruptions in the menstrual cycle. In acute cases, the temperature rises.
If your lower abdomen begins to hurt and these sensations do not go away for a long time, but only intensify, your body temperature has increased. The pain moves to the lower back and sacrum - all this indicates the presence of inflammation, requiring urgent intensive care. If no measures are taken, then in a short time the acute form becomes chronic and in this case the symptoms in women become less pronounced: aching in the lower abdomen, slight discharge, cycle disruption, decreased libido. But complications can be very serious; women are diagnosed with serious adhesions or infertility.
How to make it easier
No matter how sure a woman is that the pain that appears in the right or left lower abdomen is associated with ovulation, she should not self-medicate, but rather consult a doctor. After all, any pathology, not only gynecological, can cause pain, which accidentally coincides with the middle of the cycle.
During the examination, the specialist will rule out other causes of pain and recommend the optimal treatment (see also how to reduce pain during menstruation).
- If ovulatory syndrome bothers a woman every menstrual cycle, she is advised to relax as much as possible on the days of ovulation, eliminate stressful situations and adhere to a certain diet.
- In therapeutic nutrition, they limit dishes and products that increase the load on the gastrointestinal tract, increase intestinal motility, which aggravates pain, cause flatulence and excite the central nervous system. These are primarily spicy and fatty foods, legumes and white cabbage, chocolate, coffee and strong tea.
- Warm baths with aromatic oils or medicinal herbs help relieve pain. heat descends to the lower abdomen, which reduces contraction of the uterus and tubes and relieves pain, but only if acute infectious and surgical diseases are excluded.
- Of the painkillers of choice, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are the method of choice, which block the synthesis of prostaglandins, relieve pain and inflammation (ibuprofen, indomethacin, naproxen, ketoprofen).
- Taking antispasmodics (no-shpa, spazgan, spasmalgon) is also effective.
With constant ovulatory syndrome, the gynecologist may recommend taking oral contraceptives (pros and cons of taking them), which, by blocking ovulation, prevent the occurrence of pain. But, if a woman wants to get pregnant, their use is excluded, and it is also not permissible to use a heating pad on the lower abdomen and take any medications on the days of ovulation, as this may affect the quality of the egg.
When to worry
In the vast majority of cases, pain after ovulation is normal. Women should not worry about this. But sometimes the lower abdomen feels tight due to pathological processes. If painful sensations appear, do not panic; you must first assess their intensity, duration, and nature.
- elevated temperature;
- bleeding from the vagina;
- sharp painful spasms;
- nausea or vomiting;
- fainting;
- feeling unwell;
- periodically occurring severe pain;
- nodules in the mammary glands.
Sometimes the cause of pain can be injury to the ovaries. The pain radiates to the lower back. Unpleasant sensations intensify with any movement or physical activity; they are stabbing in nature.
Types of ovulation
There are several types of ovulation:
- premature;
- timely;
- late.
Premature ovulation is the maturation and release of an egg from the follicle not in the middle of the cycle, but much earlier and can be caused by several factors:
- excessively violent sexual intercourse (see causes of pain during sexual intercourse);
- increased physical activity or heavy lifting;
- stress and strong emotional experiences;
- various diseases, including gynecological ones;
- hormonal disorders and endocrine pathology.
The etiology of late ovulation includes various hormonal problems, including menstrual irregularities.
In connection with the described types of ovulation, pain, accordingly, does not occur, as is customary, in the middle of the cycle, but much earlier or, on the contrary, later, which can become a cause for concern for a woman (see also symptoms of premenstrual syndrome). Therefore, an indirect sign of a possible future pregnancy is pain in the middle of the cycle.