Removal of rectal polyps is the only effective method aimed at combating such a serious disease. Conservative approaches rarely help to cope with the disease, especially in cases of an advanced stage of development, in the presence of many formations or particularly large growths. An operation performed by real professionals can help here. The effectiveness of such a radical measure is confirmed by numerous reviews from people who have already gone through such an intervention.
Despite the fact that in the medical classification polyps are usually classified as benign formations, this does not mean that when they appear, the disease can be ignored. To prevent problems in the intestines, whether they are genuine or inflammatory in nature, from developing into something more, you need to get rid of the source of the problems at an early stage.
Polyp classification
Content:
- Polyp classification
- Cause of occurrence
- When should you go to the doctor?
- The right preparatory approach
- Polyp removal
- Complications after surgery
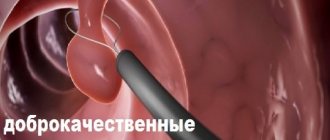
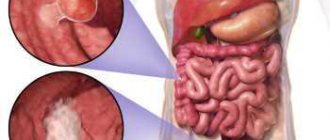
A polyp localized in the rectum is a benign tumor that consists of the mucous membrane of both the rectum and colon. Such a growth likes to “settle” on the wall of a hollow organ, attaching to the surface due to the base or a strong leg. Although it grows from epithelial tissue, it contains other cells inside.
The cost of measures aimed at neutralizing such formations depends on their number, characteristics and severity of the lesion. The cost will also be affected by the specific type of polyp and the method by which it will be removed. Taking into account all of the above, it is difficult to say exactly how much the entire set of procedures costs. Because of this, doctors recommend that you first undergo a preliminary examination and discuss the price directly with your doctor.
It is believed that all benign tumors of this kind have only three main geometric shapes. Most of it falls on the ball. There are options that look like a mushroom with an extensive cap. The least common are branched versions without a clearly defined shape. It is precisely such proposals that surgeons usually have the most difficulty with.
The consistency of the polyp is close to a soft composition, which is pink, burgundy, and dark red in color. The exact shade depends on how well the nutrient supply has been established between the lesion and the blood vessels nearby.
In general, polyps can choose any organ of the digestive tract as their location, not just the rectum. Moreover, they are almost equally common in men and women. According to statistics, representatives of the stronger sex are approximately one and a half times more susceptible to this disease. In rare cases, they make themselves felt even in children.
Before referring a victim for endoscopic removal of an unhealthy area, the doctor must first establish the specific class of the lesion. In addition to division according to the quantitative component, experts use another classification. It relies on differences in structure:
- fibrous;
- adenomatous;
- villous.
Variations of the fibrous polyp are usually created on the basis of connective tissue, choosing for the site of attachment those areas of the mucous membrane that are often inflamed. These kinds of processes often become the cause of an extensive inflammatory process with initially healthy tissue being drawn into it. Also, the fibrous component often becomes an ideal environment for triggering the mechanism of suppuration. However, it quite rarely transforms into a malignant neoplasm that metastasizes throughout the rectum. Doctors advise not to test the theory in practice and treat the original source of the disease with a laser or another method according to medical indications immediately.
The adenomatous class is distinguished by its ability to grow up to 3 cm in diameter, attaching to the wall with its leg. It has glandular tissue inside. Unlike its fibrous counterpart, it much more often becomes the cause of a full-fledged oncological neoplasm. To prevent the development of the worst scenario, it is worth immediately removing the detected growth.
Even in the initial phase of development, an adenomatous polyp is a precancerous condition, so it is worth quickly deciding on the optimal excision technique. But treatment with folk remedies is not worth practicing, since education usually progresses very quickly. In attempts to correct the situation by self-medication, you can only miss the chance for a successful recovery.
The villous category includes processes that are round or slightly elongated. It has a velvety surface, which is made possible by the many fibers. Due to the fact that its structure is very soft, it is quickly injured even with slight pressure.
In the future, it becomes one of the fundamental causes of the development of malignant oncology of the digestive tract. Any medical forum where there is expert advice from experienced doctors will confirm these concerns.
Multiple polyps are considered separately, which are represented by mixed classes, ranging from mucocystic to villous-glandular. If the victim was diagnosed with diffuse polyposis, this indicates the growth of a large group of polyps. They literally stick to the inner surface of the intestine, which makes it much more difficult for processed food to pass through.
Treatment tactics
If a small polyp is detected, a wait-and-see approach may be prescribed - the doctor monitors the dynamics of tumor growth for a year, and if no significant changes are detected, surgery to remove the polyps is not performed. However, in this case, it is imperative to continue to be examined regularly in order to eliminate the risk of degeneration in time.
Due to the psychology of Russian patients, in most cases, endoscopic removal is immediately prescribed instead of expectant management. People believe that there is no need to worry about small polyps and ignore doctors’ orders for repeated examinations, so specialists immediately take a radical approach to the problem - this is the safest option. Even a small tumor can quickly become malignant.
There is no conservative treatment for intestinal polyps - it is simply ineffective.
If there are other possible complications of polyps - bleeding, incessant diarrhea, excessive mucus secretion or severe inflammatory processes - expectant management is not used, surgery is prescribed immediately.
Cause of occurrence
Doctors insist that when going through the methods of treating a given disease, it would be more logical to first identify the original source of the problem. In the future, this will allow us to carefully work on prevention in order to block all chances of relapse.
In clinical practice, there is no one hundred percent correct factor that prompts the development of defects that are so painful for a person. Usually several aspects come together, including:
- disruptions in the psycho-emotional state;
- chronic inflammation of the intestinal mucosa;
- bad heredity;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- sedentary lifestyle with little physical activity.
But the most important point is still poor nutrition. When a person's daily diet does not include enough plant fiber, the rectum begins to protest. It bleeds, signaling that it is gradually becoming covered from the inside with destructive growths.
Some researchers adhere to the theory that the harbinger of polyps is chronic inflammatory processes localized in the colon. The following diseases also become indirect catalysts for failure in the body:
- enteritis;
- ulcerative colitis;
- dysentery;
- haemorrhoids.
Frequent constipation or any other disorders of the digestive system can provoke the development of pathology. Also, with reduced immune functions, the body turns into an optimal environment for pathogens of viral infections, which often have consequences in the form of effects on the rectum. The victim’s passion for food that contains a high amount of fat is taken into account separately. Drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking, as well as age-related changes, add risks.
When should you go to the doctor?
In order for modern methods of therapy to work with an increased likelihood of a positive outcome, it is necessary to contact the hospital as early as possible. To help patients, doctors have developed a kind of map of alarming symptoms.
As soon as the patient experiences at least a few of the above dangerous signs, this becomes a reason to seek qualified help.
The only difficulty that will arise here is the asymptomatic course of the first stage of development. But as soon as a benign tumor is injured or surrounded by inflamed tissue, a person will face:
- anal itching;
- frequent urge to go to the toilet;
- pain after or during bowel movements;
- mucus in the stool, and sometimes even blood is present;
- chills, high body temperature, which signals the start of the inflammation mechanism.
In rare cases, the polyp may come out on its own during bowel movements. But if it falls off due to pressure or mechanical trauma, then an open wound surface forms at the site of its connection.
Not only will it become an excellent place for the reproduction of infectious pathogens, but it will also bleed. Additionally, the victim will experience pain, since the fallen off appendage will be pinched by the sphincter.
Doctors also highlight a list of symptoms that are characteristic of larger formations, the size of which reaches 3 cm. They often belong to the camp of villous adenomas. Then the patient will be haunted by:
- blood in stool;
- pathological mucous admixture;
- pronounced pain in the abdominal area;
- constipation;
- sensation of a foreign object in the anus, if the polyp has already fallen off and is now blocking the natural release of processed waste products.
Often victims experience sudden weight loss and exhaustion of the body, which is caused by water and electrolyte imbalance. This is typical for neoplasms of gigantic size. No amount of proper nutrition will help here. You just need to urgently make an appointment with a proctologist to minimize the risks of possible side effects.
Against the backdrop of all of the above, patients have to confront constant fatigue. If you do a general blood test at this time, it will show a reduced hemoglobin level. When the variant is neglected, the victim develops an anal fissure, which leads to paraproctitis.
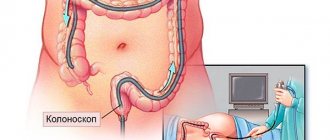
Endoscopic polypectomy of the sigmoid colon
Surgery also requires the use of a colonoscope. The patient is under general anesthesia. The instrument is inserted into the patient's anus, the polyp is removed and the area is cauterized. A few hours after the operation, the patient goes home. As a preventative measure, it is recommended to visit a proctologist and gastroenterologist twice a year. If you have complaints such as rectal bleeding, stool problems, flatulence, or pain in the intestines, you should immediately consult a doctor.
If endoscopic polypectomy is not performed on time, the disease will develop into malignant.
The right preparatory approach
Before finally choosing the mode of excision of the lesion, the proctologist is obliged to send his ward to undergo a preliminary examination. It is aimed at eliminating contraindications. Some diagnostic measures make it possible to qualitatively visualize polyps in order to assess their number, size, and characteristics.
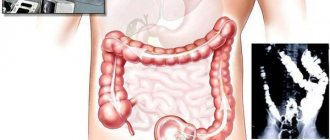
Typically, preparation includes digital examination of the rectum. But since this is often not enough, the doctor issues a referral for an endoscopic examination of the colon. We are talking about sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy.
It cannot be done without histological examination of the biopsy material. The procedure is aimed at eliminating the possibility of an ordinary benign tumor degenerating into a malignant one.
If the information picture is insufficiently complete, irrigoscopy may be used. But gastroscopy is prescribed to almost everyone without exception. An endoscopic examination is designed to examine the health of the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Differential diagnosis allows you to distinguish a polyp from pathologies with similar external signs. Sometimes they can peacefully coexist in the same intestine, which significantly complicates treatment.
Most often, a classic polyp is confused with an early stage lipoma, which is localized in the submucosal layer of the right side of the colon. But as soon as it grows to an impressive size, it blocks the entire path.
It is a little more difficult to confuse the pathology with a tumor of non-epithelial size, since the latter does not have a special distinctive stalk. Also included in the list of similar ailments are large fibroids that grow in the muscle layer, angiomas, vascular tumors, and actinomycosis.
Crohn's disease is especially insidious, which is often diagnosed under the concept of pseudopolyposis. In fact, the focus of this disease is located much higher - in the upper part of the large intestine.
To determine a specific disease, as well as to minimize the chances of mixing several anomalies at once, a histological test is performed.
Rectal polypectomy
Rectal polypectomy is performed in a similar manner. The surgery is performed under general anesthesia, so the procedure does not cause discomfort to the patient. A healthcare professional makes an incision in the patient's abdominal wall. The part of the intestine in which tumors are found is removed.
In some cases, laparoscopic equipment is used. Such technologies allow you to avoid incisions on the abdomen. Endoscopic polypectomy is performed using a colonoscope, which is inserted into the anus. Polyps are separated from the rectum using a diathermy loop. This area is cauterized.
Polyp removal
Initially, medicine had only one option for conservative therapy to combat such benign lesions. We are talking about celandine juice. But as soon as researchers realized that this approach had no practical benefit, they stopped using it altogether.
Today, treatment involves exclusively surgical removal, as well as a fairly long postoperative period. It is aimed at healing and preventing the recurrence of the growth. In private medical centers and public hospitals, the following methods are used to implement the plan:
- polyectomy, which relies on the use of a proctoscope and colonoscope;
- transanal excision;
- resection of a certain piece of intestine;
- transanal resection, which involves the formation of an anorectal anastomosis;
- endomicrosurgery.
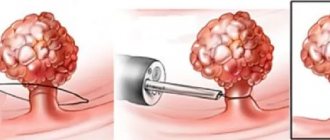
The first version is the most popular. The operation itself involves first inserting an operating device into the rectum, and then a loop is thrown over the appendage through it. Later, the loop is heated by connecting to an electric current, which allows the polyp to come out without problems.
Rehabilitation and the manipulation itself last much longer for those who have become victims of polyposis. It all depends not only on the diameter and specific location of the growths. The results of histological testing will have to be taken into account.
If visualization showed that the polyps are scattered individually, but do not exceed 0.5 cm in size, then you will simply have to undergo regular examinations at least once every six months. But as soon as the benign formation becomes more than 0.5 cm, you can move on to an active strategy. It covers polypoethmoidotomy under the control of endoscopic equipment.
This step is explained by the risk of malignancy, which means transformation into a malignant tumor. To neutralize “nests”, the same methods described above are used, with an eye to the affected area.
If the doctor preferred sigmoidoscopy with subsequent removal of the lesion, then the former site of polyp growth must be cauterized. This will protect the intestines from infection by pathogenic microorganisms.
Very rarely, doctors use the tactic of direct incision of the intestine, when endoscopic equipment acts as an assistant. The collected pathological material is then sent to a clinical laboratory.
Endoscopic colon polypectomy
Treatment of the colon occurs using the same technology. After undergoing an examination and tests, the patient adheres to a strict diet for several days, after which he is sent for surgery. The polyp is removed using special instruments. To consolidate the effect, drug treatment is prescribed to prevent relapse.
The removed tumors are sent for examination. If the polyp is benign, then the risk of recurrent disease is reduced to zero. If the polyp is malignant, then the harmful cells are located in the intestinal leg. Cancer cells penetrate deep into the intestinal wall. The risk of relapse is high, so the patient should visit the attending physician every two months to monitor the condition.