Source: Managing the menopausal midsection: is it even possible? by Lyle McDonald (Alan Aragon Research Review, September 2017)
Translation: fitlabs.ru
It is believed that even women who are slim in their youth are “doomed” to gain excess weight during menopause, especially around the waist. Is this an inevitable effect of hormonal changes or is it because people become less active as they age? What can you do about it?
Menopause is the cessation of a woman's reproductive function. The body runs out of viable eggs, menstruation stops (this process begins several years before menopause and is called peri-menopause), and estrogen and progesterone drop to very low levels.
When estrogen decreases, several important things happen. The first is weight gain. The second is the redistribution of fat deposits. In a “normal” situation, most of a woman’s fat deposits are not located in the abdominal area and especially around the internal organs (this fat is called visceral).
The latter is more common in men due to the influence of testosterone. Although in women with some types of polycystic ovary syndrome (which is often accompanied by increased levels of androgens), obesity also develops according to this type.
Excess visceral fat is harmful to health and increases the risk of cardiovascular disease. So before menopause, when estrogen levels are high, women have much lower risks.
Finally, during menopause, lipolysis occurs worse - the mobilization of fats from cells into the bloodstream for further oxidation. But this can easily be compensated for by caffeine taken before cardio training.
In general, estrogen is usually blamed for all problems, although it does many good things. As mentioned above, it affects the distribution of fat in the body, and also maintains muscle and bone mineral density. As estrogen levels decline during menopause, women begin to lose both muscle and bone mass at a much faster rate. This is also why they suffer from osteopenia and osteoporosis more often than men.
Regarding fat redistribution, there is a theory that explains this. Fat cells are the main site where testosterone is converted to estrogen by aromatase. It is believed that the increase in visceral fat in menopausal women is an attempt by the body to maintain at least some estrogen signaling pathways.
Hormone replacement therapy, when estrogen and progesterone are replaced with synthetic analogues, eliminates the problems listed above. Excess weight does not increase, muscle loss and bone density do not occur. Even the decrease in metabolic rate differs between women on and without replacement therapy. For the former, it decreases by 4 calories every year. For the second, 14 calories per year. By the way, this shows that the age-related decline in metabolism is overestimated: for 10 years after menopause it is only minus 140 calories. A large part of the decline in metabolism with age is that a woman begins to move less and becomes less active. Loss of muscle mass is likely part of this.
There is a lot of debate about replacement therapy during menopause. There was once a Woman's Health Initiative (WHI) study that was stopped early due to an increased risk of breast cancer with estrogen. But more recent research has shown that a lot depends on age and when you start taking hormones. If it occurs soon after menopause and only lasts for a few years, it is considered safe. Taking estrogen for a long time or in older women is indeed unsafe. The WHI study pooled all women, which masked this difference.
Reasons for weight gain during menopause in women
Closer to 45 years, all women gradually decrease the production of sex hormones.
This process is called menopause, which leads to a complete cessation of reproduction - menopause. During this period, serious changes occur, the hormones estrogen and progesterone are synthesized less and less. These hormones are very important for women's health: they are responsible for the maturation of eggs, the condition of the uterus, skin elasticity and metabolic processes in the body.
Estrogens make tissues more sensitive to insulin, which is responsible for processing sugars. If there is not enough estrogen, cells stop absorbing sugar normally, and glucose levels in the blood rise. This is a dangerous condition, so the body strives to remove sugar in any way, urgently converting it into fats.
Leptin is a hormone produced by adipose tissue. It controls appetite and satiety. The level of leptin depends on estrogen, and if there is little of the latter, the concentration of leptin also decreases. This provokes hunger, despite the fact that objectively there are still enough energy reserves. Because of this, a woman eats more and unknowingly chooses high-calorie junk food.
It is precisely because of metabolic disturbances during menopause that obesity often begins, even if the woman was not previously inclined to this. The balance between calories received and expended is disrupted, and the excess is stored in fat reserves. Fat deposition in the abdominal area is especially dangerous - so-called visceral obesity. Fat forms in the abdominal cavity around the organs and disrupts their function. Excess visceral fat provokes the development of diabetes.
DON'T PUT LIFE ON PAUSE
Phytoestrogens - plant analogues - will help fill the lack of female hormones. For example, soy isoflavones. They are part of the Mense and are enhanced with a complex of amino acids and vitamins. Mense improves the body’s renewal processes and helps reduce the risk of developing undesirable consequences of menopause.
The greatest effect of the drug is achieved with a course of treatment - 1-2 capsules per day for a month.
Find out the price
Dietary supplement NOT A MEDICINE.
Summarizing
Nutrition: more protein, carbohydrates and fats in moderation. Strength training: 2-3 times a week. They should be fairly heavy (8-12 reps per set) and consist of compound exercises with free weights. Leg press or squats - for legs and spine. Chest press or overhead press for arms and so on. Isolation exercises can also be useful, but only as a bonus. Cardio: 3 times a week, moderate intensity. This helps get rid of visceral fat. Caffeine before cardio - to improve fat mobilization. Medications: Consider taking phytoestrogens with your doctor along with melatonin at bedtime and possibly DHEA.
***
Of course, the older we get, the more difficult it is to maintain a regimen, but regular exercise and attention to diet compensates for most age-related and hormonal problems.
How to stop weight gain during menopause in women
Do not think that weight gain during menopause in women is inevitable. Only the predisposition to this increases, and the accumulation of fat reserves occurs due to unnoticed changes in lifestyle and nutrition.
Psychological attitude
It is important to calmly accept the changes that are now taking place. All women go through menopause, and it is inevitable. Menopause does not mean the onset of old age and does not make you ugly if you follow some rules.
Excessive worries about menopause result in stress and depression, which are often unnoticed by eating junk food. According to statistics, women usually choose sweets, fatty or salty foods to comfort themselves. During stressful conditions, the hormone cortisol is actively produced. It increases appetite, making it even more difficult to refuse food.
Therefore, it is very important to reduce your worries. You can contact a psychologist if you can’t do it yourself.
Balanced diet
Now you need to pay special attention to your diet, even if you didn’t pay attention to it before. To prevent weight gain, you don't need to go on strict diets. It’s enough just to eat often, in small portions, and choose healthy foods. Avoid high-calorie foods, give up pure sugar. It is better to replace it with fruit.
If obesity has begun, try to calculate the calorie intake for the day. Special exercises will simplify the task. Next, you can contact your doctor or nutritionist to adjust your diet. You may need to take a couple of tests.
Physical exercise
After 45, energy consumption inevitably decreases; the loads are not enough to process all the calories received. Due to a passive lifestyle, muscles weaken and muscle tissue is gradually replaced by fat.
To avoid this, you need to give yourself feasible loads. You can start with simple exercises and stretching, gradually adding active exercises when the body gets used to it. At the same time, take into account the characteristics of age - bones become more fragile, so it is better to avoid active jumping and other things.
Mense will help you sleep soundly and carefree . It contains a plant analogue of female hormones (soy isoflavones), enhanced with a complex of vitamins and amino acids. Including vitamins B6 and B12 - they improve the condition of the nervous system, normalize sleep, and reduce fatigue. And the amino acid 5-hydroxytryptophan, being a moderate antidepressant, reduces despondency, depression, tension, anxiety, and normalizes biorhythms.
Find out the price
Dietary supplement NOT A MEDICINE.
Healthy sleep
Sleep often worsens during menopause, not only because of nervous worries. Physical symptoms appear: sweating, fatigue. At night, the feeling of hot flashes and stuffiness is especially annoying.
With a lack of sleep, the level of cortisol, the stress hormone, also increases, which worsens the situation with excess weight. Such a dream does not restore strength, and of course there will be no desire to exercise or eat right.
To improve sleep, it is recommended to take a contrast shower in the evenings, fall asleep before 11 pm, and sleep with an open window for good air ventilation. If all else fails, you should consult a doctor. Perhaps mild herbal sleeping pills will suffice.
Regular medical examination
Since hormonal changes increase the risk of various diseases, you need to regularly visit your gynecologist, as well as an endocrinologist. Using tests, doctors will evaluate your hormone levels and, if necessary, prescribe additional tests.
It is important to monitor your blood glucose levels to avoid diabetes. If the tests are not very good, menopause is difficult and the health risks are too high, the doctor may prescribe hormonal medications. But this is usually a last resort. It is important to understand that synthetic hormones do not reduce weight or suppress appetite; there is no such magic pill. Such drugs only alleviate the symptoms of menopause, which indirectly helps to cope with increased appetite.
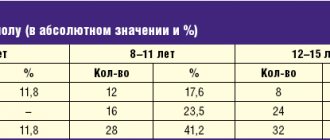
Why do you need to know these values?
To prepare for menopause. In addition to prescribing replacement therapy, a woman should introduce calcium-containing foods into her diet: cottage cheese, fermented milk products, cheese to prevent osteoporosis. You need to undergo a gynecological examination: take a smear for oncocytology, do an ultrasound of the pelvic organs and mammography. You should donate blood for sugar and cholesterol levels. Adjust your diet, move more, follow a sleep and rest schedule. Your doctor may prescribe vitamins or supplements to relieve menopausal symptoms.
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category. Chernovskaya Rosa Uranovna
Popular questions and answers
Since all changes in the female body with the onset of menopause are associated with hormonal levels, understanding physiology will help prepare for this period. Gynecologist Irina Budnik answers popular questions from patients .
If a person was initially inclined to be overweight, will the situation worsen with the onset of menopause?
As menopause approaches, every woman faces the problem of weight gain. An increase of 6-7 kg is considered the physiological norm. During this period, a mechanism is activated in the body designed to compensate for the deficiency of female sex hormones: adipose tissue takes over part of the functions of the ovaries, which no longer produce estrogens in the same quantity. With changes in hormonal status, metabolism slows down, calories are no longer burned as actively. Therefore, if preventive measures are not taken to correct lifestyle and nutrition, weight gain may become more significant.
Is it possible to understand in advance whether weight gain will occur during menopause?
Weight gain will be inevitable due to physiological reasons. How significant depends on the presence of diseases. It is important to monitor biochemical indicators in the blood and sugar levels so as not to miss the onset of diseases of the endocrine system, for example, diabetes.
Is it possible to avoid such unpleasant changes as weight gain?
You can reduce such manifestations at the initial stage of menopause by correcting your diet. You need to consume less sugary foods, reduce the calorie content of your food, and ensure that your intestines are functioning normally. Physical activity is also necessary. It is impossible not to mention hormone replacement therapy - the earlier a woman starts taking medications, the less problems with excess weight arise. Diseases of the cardiovascular and urinary systems, diabetes mellitus, and calcium metabolism disorders leading to bone fragility are also less common. Women can take such drugs up to 60 years of age, and possibly longer, under the supervision of a gynecologist and only as prescribed.
How to take a hormone test correctly?
Blood tests are taken on certain days of the cycle - the day of the test will be calculated by the doctor. So tests for FSH and LH are taken at the beginning of the cycle - on days 4-5. Analysis for estradiol - 19-22 days. Progesterone test at the same time. There are a number of restrictions before donating blood for hormones; they must be observed, otherwise the result will be distorted. Avoid alcohol and physical activity a week before the test. Do not have sex the day before the test day. Take the test strictly on an empty stomach - in the morning, the break from the last meal should be at least 8 hours. You can drink water. Do not take medications.
Testosterone free
Free testosterone is mistakenly considered an exclusively “male” hormone, but the woman’s body also requires it in small quantities. The level of free testosterone drops with the onset of menopause; normally its levels are in the range of 0.1-1.7 pg/ml.
The concentration of testosterone may increase due to tumors of the endometrium, ovaries, adrenal glands, polycystic ovary syndrome, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome.
The prices for analysis of female hormones are low, and the effectiveness is 5 points.
Estradiol
Estradiol plays one of the key roles in the regulation of the cycle and ensures the normal functioning of the female reproductive system. Its indicators change with the onset of menopause; normally they range from 0-54.7 pg/ml.
The level of estradiol can increase with the formation of tumors of the adrenal glands, ovaries, liver cirrhosis, and hyperthyroidism. A drop in the concentration of a substance in a woman’s body can be a sign of polycystic ovary syndrome, anorexia nervosa, hypogonadism, hypopituitarism, etc.
Menopause affects microflora
An age-related decrease in the level of female sex hormones also negatively affects the vaginal microflora . Beneficial lactobacilli are especially sensitive to a decrease in the natural level of estrogen - they simply disappear . As a result, lactic acid ceases to be produced. The acid-base balance in the vagina (pH) is disrupted. As a result, the vaginal environment becomes dry and, accordingly, favorable for the occurrence of various genital infections . Let's look briefly at the most famous and common ones.
Thrush. In medicine, this disease is called candidiasis, named after the opportunistic yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida albicans, which are its causative agents. The disease can affect the mucous membranes of the mouth, intestines, and nails, but is more common in the genital area (including men). Female thrush is manifested by burning and itching in the genital area, white, curd-like discharge from the vagina, pain during sexual intercourse and urination.
Gardnerellosis. Or, in other words, bacterial vaginosis. The disease is quite common among women, representing vaginal dysbiosis. Under normal conditions, the basis of the vaginal microflora is lactobacilli (they are also called lactobacilli, Lactobacillus spp.). They convert glycogen contained in the vagina into lactic acid and also produce hydrogen peroxide. Both of these compounds suppress the activity of opportunistic microflora, namely streptococci, staphylococci, anaerobic bacteria, E. coli and Gardnerella vaginalis itself. It is she who first begins to take a leadership position if the level of lactobacilli decreases. Bacterial vaginosis causes a grayish-white vaginal discharge that smells like rotten fish. Gardnerellosis, if it occurs during menopause, can provoke inflammatory diseases of the uterus and appendages, namely endometritis, myometritis, endomyometritis, salpingitis, oophoritis and others.
When does menopause start?
Menopause is usually preceded by what is called perimenopause . It usually begins around age 50 . A characteristic feature of premenopause is a decrease in the number of eggs to a minimum . Thus, the onset of this stage indicates a natural decline in ovarian function . During this period of life, a woman feels the onset of changes in her general well-being, and delays in the menstrual cycle begin . The onset of menopause, as well as pregnancy and ovulation, is determined by a special test. But it is appropriate if irregular periods have been occurring for six months.
Interruptions with menstruation ultimately lead to the complete disappearance of menstruation, which indicates the end of the premenopausal period and the onset of menopause itself . This period lasts, as a rule, two years . But there are many cases where nature stretched it out to five years. With the onset of menopause, a completely new stage begins in a woman’s life. From a social point of view, it can be great: ladies rejoice at the success of their children, happily nurse their grandchildren, and they have more time for their family and social responsibilities. However, from a health point of view, things are not so smooth. This is all due to the notorious hormonal changes in the body. Sometimes it is so radical that it cannot be called anything other than revolutionary.