Causes of heartburn during pregnancy
According to statistics, from 20 to 50% (according to other sources - from 30 to 60%) of the population experiences heartburn. In the countries of Asia, Africa and Latin America, this figure is several times lower. During pregnancy, heartburn bothers up to 80% of women.
There are two main explanations for this.
The expectant mother actively produces progesterone, the “pregnancy hormone”. Its task is to relax all muscles and ligaments for childbirth. Therefore, the esophageal sphincter begins to cope with its function worse. The second point is that a growing baby puts pressure on the stomach. All that remains is to patiently wait for his birth and carry out symptomatic treatment. But there are causes of heartburn during pregnancy that require more serious drug therapy or even surgical intervention:
- gastroesophageal reflux disease. It is associated with disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, primarily with improper peristalsis of the esophagus and involuntary relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter. If left untreated, GERD can lead to narrowing of the esophagus, bleeding and ulcers;
- hiatal hernia. This muscle separates the chest and abdominal cavity. The esophagus passes through an opening in it. If it is increased in size, then part of the stomach ends up in the chest cavity. This protrusion is called a diaphragmatic hernia. It is often accompanied by belching, the entry of stomach contents into the oral cavity, pain as with angina pectoris - appearing in the lower part of the sternum and radiating to the back, left shoulder and arm.
- increased intra-abdominal pressure. It can be caused by an enlarged liver or spleen, as well as obstructive pulmonary disease;
- peptic ulcer and other disorders of the stomach, pancreas, gallbladder or duodenum (gastritis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, etc.);
- tumors of various locations and origins.
Do not self-diagnose or self-medicate. When heartburn occurs more than twice a week (especially if sleep disturbances and anxiety occur along with it), consult a physician. He will tell you which examinations to undergo and which specialists to contact.
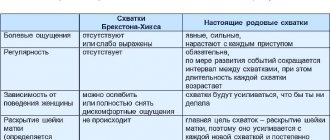
Why do expectant mothers so often complain of heartburn and indigestion?
There are two main causes of heartburn and indigestion during pregnancy:
Hormonal changes in the body of the expectant mother
During pregnancy, the amount of progesterone produced increases, causing muscle relaxation. Accordingly, increased production of progesterone provokes relaxation of the muscles of the lower esophageal sphincter. The sphincter is a ring of muscle that prevents stomach contents from entering the esophagus. As a result, when the sphincter muscles relax, the contents of the stomach (including gastric juice) can freely pass into the esophagus, causing irritation of its mucous membrane. The esophageal mucosa is not designed to accept large amounts of gastric acid for a long time. This is why we feel pain.
Child's height
As your baby grows, it begins to put more and more pressure on the organs of your digestive tract, stomach and intestines. This pressure can cause stomach acid to flow into the esophagus.
Most often, problems with the digestive system during pregnancy are faced by those who had similar problems before pregnancy, as well as those for whom this is not their first baby.
Heartburn and indigestion can also be caused by other reasons. For example, some foods and drinks also cause excessive stomach acid production, which can destroy the protective lining of the stomach. The protective layer is the mucous membrane, which is in direct contact with the contents of the stomach, including gastric juice. If its destruction occurs, it can lead to discomfort and unpleasant sensations.
How to get rid of heartburn during pregnancy at home
If there are no pathological problems, then specific treatment for heartburn during pregnancy is not required. An obstetrician-gynecologist will recommend medications to relieve symptoms and adjust your lifestyle and diet.
Most often, antacids are prescribed (they contain magnesium, calcium, aluminum salts, neutralize hydrochloric acid, so the esophageal mucosa is not irritated) and alginates (when interacting with the contents of the stomach, they form a protective barrier that does not allow excess into the esophagus). Antisecretory drugs that suppress the formation of hydrochloric acid in the stomach and prokinetics that increase the tone of the esophageal sphincter and stimulate contraction of the esophagus are used during pregnancy only under strict indications and under the supervision of a physician due to the risk of side effects.
First trimester
Heartburn in the first trimester of pregnancy is usually associated with an increase in progesterone levels, so it is not very disturbing and goes away quickly on its own.
Second trimester
If heartburn during pregnancy did not bother you at the beginning, then there is a high probability of encountering it after the 20th week. During this period, the uterus begins to actively grow and put pressure on neighboring organs. The stomach has nowhere to stretch, so even the usual amount of food can lead to overflow and backflow into the esophagus.
Third trimester
As the fetus grows, heartburn will become more intense. But closer to childbirth it will become a little easier - the uterus will descend and “free up” the stomach, progesterone will no longer be produced so actively.
Diet recommendations
Heartburn and nausea at 38 weeks and later require not only drug treatment, but also dietary adjustments. Experts believe that if a pregnant woman follows a diet from the moment of conception, she has a better chance of avoiding digestive problems, which are sometimes difficult to get rid of.
A burning sensation occurs when a woman eats in too large portions, as at this time an increased amount of gastric juice is produced. To solve the problem and get rid of discomfort, it is enough to switch to fractional meals. Soups, cereals, meat and side dishes should still serve as main courses, and light snacks are introduced between meals. For this purpose, they eat natural yoghurts, fresh fruits that do not provoke allergies, and it is useful to make salads from vegetables.
Treatment of heartburn also involves a number of dietary restrictions. The symptom appears if the menu includes foods that provoke an increase in the level of acidity inside the stomach or negatively affect the integrity of the mucous membranes:
- sour fruits and berries;
- spices;
- vinegar;
- canned food;
- sauces;
- smoked meats.
All of the foods listed should be excluded from the diet during pregnancy. This measure is designed to help avoid burning, sour belching and stomach pain.
There are foods that can help treat the burning sensation. Dairy products are considered useful for increasing acidity. They are consumed if they do not cause intestinal upset and are well absorbed by the body. In the last weeks of pregnancy, it is recommended to include fruit jelly in your diet. It is enough to drink one glass to protect the mucous membranes from destruction and saturate the body with vitamins.
Heartburn in pregnant women is a common condition that causes discomfort to women. If discomfort occurs occasionally, then there is no need to do anything. If the sensations become intense, treatment must begin.
Preventing heartburn during pregnancy
An increase in progesterone and growth of the uterus are objective reasons that cannot be influenced. But there are several tips for preventing heartburn during pregnancy, which will once again avoid causing discomfort.
Photo: pixabay.com
Adjust your lifestyle:
- do not bend over suddenly, especially after eating;
- do not lie down for one and a half to two hours after eating;
- When sleeping, place a second pillow so that your head is higher than your stomach;
- remove tight belts, corsets, and tight clothing from your wardrobe;
- do not lift heavy objects;
- give up bad habits (smoking, alcohol, drinking strong tea and coffee in large quantities), although without heartburn during pregnancy it is important to do this for the normal development of the baby.
Adjust your diet:
- do not overeat, it is better to eat less, but more often (divide the usual volume into 5-6 meals);
- Chew your food thoroughly;
- make sure that the food is not too hot and not too cold;
- have dinner no later than 2-3 hours before bedtime;
- choose foods and drinks wisely.
Analyze what causes heartburn most often and eliminate this factor. What has no effect on one person may be too much for another person's stomach.
How to cope with heartburn and indigestion during pregnancy?
Independent methods of treatment
As already mentioned, most pregnant women experience heartburn and indigestion, but there are simple and useful tips that will help you experience these unpleasant sensations less often:
Try to give up bad habits
- Stop smoking and drinking alcohol - both of these can only contribute to the appearance of heartburn and stomach discomfort, not to mention the fact that this is simply contraindicated during pregnancy.
Eat right
- Proper nutrition is an integral part of pregnancy. It is very important to maintain a balance of proteins, high-starch foods, vegetables and fruits. However, the best way to relieve heartburn is to avoid trigger foods. Spicy and fatty foods, caffeine, chocolate and tomatoes are the most common foods that most often cause heartburn.
Change your eating habits
- It is recommended to divide your daily diet into small portions and eat more often throughout the day. This way of eating will bring more benefits than three large meals. This will prevent overfilling and can ultimately prevent stomach acid from getting into your esophagus.
- If you experience heartburn and indigestion at night, you may be a late-night eater. If this is true, then gastric juice will continue to be produced even after you go to bed. To avoid this, it is better to eat 2-3 hours before bed: this time is just enough to digest the food.
Pregnancy doesn't mean you have to eat for two. Excess weight can cause you discomfort in the later stages. For women whose weight was normal before pregnancy, it is recommended to gain no more than 10-14 kg.3
Get plenty of rest
- Pregnancy is a blessing for expectant parents and the whole family, but sometimes you have to be nervous. Since stress can also cause heartburn and indigestion, try to regularly set aside time for yourself to relax. This way you can reduce the likelihood of the negative effects of stress.
Think about the body position you are in
- After eating, try to stand or sit for a while, do not lie down immediately after eating. Also try to avoid strenuous activity after eating, especially if it involves bending.
- Try to avoid putting additional pressure on the waist and abdominal area. In particular, do not wear compression belts. Don't forget about this when children or pets ask to sit on your lap.
- Get used to the correct sleeping position, which will allow you to avoid unpleasant sensations while you sleep. When you lie on your back, stomach acid is more likely to enter your esophagus. Some people find that raising the head of the bed can also help. Always pay attention to the position of your body - this is important both during pregnancy and in any other condition!
Treatment with medications
During pregnancy, expectant mothers are wary of taking medications. This is completely justified; no one wants to harm their unborn baby. However, there are medications that you can take during pregnancy without worrying about the baby's health. Despite this, always read the instructions before using a new drug and pay attention to special advice and side effects of drugs.
Antacids
Such drugs usually contain calcium carbonate, magnesium carbonate or aluminum hydroxide; they neutralize stomach acidity. They are used to treat mild attacks of heartburn and indigestion and are available in several forms, including liquid and chewable tablets.
alginates
"Gaviscon® Double Action" is a well-known drug related to alginates and has a neutralizing effect on excess gastric acid. Sodium alginate in its composition forms a protective barrier that prevents the contents of the stomach (including gastric juice) from entering the esophagus, due to which discomfort and pain disappear.
In addition, Gaviscon® Double Action contains calcium carbonate, which quickly neutralizes excess stomach acid. The result will be a reduction in discomfort in the stomach area. Gaviscon® provides long-term relief from heartburn and indigestion4 and has a longer-lasting effect on acid reflux than simple antacids.5,6
Gaviscon® Double Action can be used during pregnancy. The possibility of its use is explained by the fact that the drug is not absorbed into the blood.
If you are taking antacids or alginates (eg Gaviscon® Double Action), remember not to exceed the recommended dose. Follow the instructions carefully.