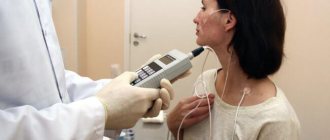
Probing is a manipulation in medicine. It can be performed both in the hospital and at the patient’s home. The process itself consists of inserting a probe into the stomach area through the oral cavity or nasal cavity. The procedure itself is not very pleasant. Although it is carried out without causing pain. It may be accompanied by the following symptoms: Probing is a procedure that is done using a special tube called a probe. It can be of different thickness and length. At the end of the probe there is a small camera and a light fixture. Such a tube is connected to a pump or screen.
Contraindications
It is worth noting that probing is a procedure that has its own contraindications. Cannot be carried out in the following cases:
- during pregnancy;
- for diseases of a hypertensive nature;
- with stomach bleeding;
- when there is varicose veins in the esophagus;
- if the presence of a cough reflex is not observed;
- when there are burns in the gastrointestinal tract;
- in the presence of epilepsy;
- when there is the slightest curvature of the spine in the cervicothoracic region.
Indications for use
Probing is one of the most informative and safe methods of examining the stomach, therefore the procedure is prescribed for diagnosing almost all diseases of the stomach:
- peptic ulcer;
- gastritis; reflux disease;
- other stomach diseases;
- They feed patients who cannot feed themselves through a tube, and wash out the stomach in case of poisoning.
Probing has a number of contraindications: pregnancy, stomach bleeding, severe diseases of the cardiovascular system. In this case, one of the alternative research methods is used: according to one of the methods, the patient drinks a special substance that colors the urine. The more intense the color, the higher the acidity. But none of the alternative methods provides the completeness of information that sounding can provide.
Preparation
Before starting the procedure, preparation for probing is necessary. Its main goal is to completely empty the stomach. This is necessary so that the specialist can examine the presence of the slightest pathologies in the gastrointestinal tract without obstacles. To do this you should:
- eat the last time only before six o’clock in the evening before the morning manipulation;
- It is strictly forbidden to eat food that causes gas formation;
- to flush the stomach on your own, you need to drink only water throughout the evening;
- You should also not smoke in the morning.
Who needs gastroscopy?
Gastroscopy of the stomach is prescribed by doctors for any pain in the epigastric region, associated or not associated with food intake, unclear nausea, vomiting, frequent belching, a feeling of fullness or heaviness in the abdomen after eating, heartburn, blood in the vomit or in the stool.
An examination of the stomach must be carried out if there is a suspicion of a pathology such as:
Which doctor should I contact if my stomach hurts?
- acute or chronic gastritis - it is necessary to determine the type of inflammation to choose a treatment method;
- peptic ulcer - the ability to establish localization, condition of the edges, size of the mucosal defect, stage of the process, probability of malignancy;
- gastric and intestinal bleeding from the veins of the esophagus and stomach in liver diseases;
- pyloric stenosis;
- polyps and cancer - to choose treatment tactics.
Fibrogastroscopy is indicated for patients with questionable subjective signs when all tests are normal. An annual stomach check is recommended for people at risk, those with a family history of a malignant tumor, and patients who have undergone surgery.
The procedure helps to identify atrophic gastritis in the latent stage in people associated with toxic substances by profession. As a desirable examination, it is included in the list of medical examinations for those working with hazardous substances (chemicals, acids, alkalis, poisons).
At the same time, endoscopic pH measurements can be performed to determine the acidity of gastric juice.
An important point is that during the procedure it is possible to take samples of mucous membrane material for a biopsy. Typically, sampling is carried out from five points, including from areas with obvious changes. Subsequent histological and cytological diagnostics make it possible to detect cancerous degeneration of cells at an early stage.
A biopsy sample can be subjected to bacteriological analysis for Helicobacter. The collection is made with special forceps. This is not painful at all, since the mucous membrane has no pain sensitivity.
Gastroscopy can be performed at the request of the patient in private clinics without first contacting a doctor and the need to justify the referral. But it’s still better if the gastroscopist knows what to look for and what to pay attention to. If you have concomitant diseases (hypertension, diabetes, epilepsy), you must notify your doctor.
What is done before the procedure?
Before probing, the specialist must check with the patient about possible diseases, as well as the presence of allergic reactions to medications. After clarifying all the necessary information, a mouth dilator is inserted into the oral cavity. Since during the procedure this part of the face must be in an open position. A test is also carried out for the presence of an allergic reaction to Lidocaine. If it is not observed, then the back of the pharynx is irrigated to create anesthesia. The patient is placed on the couch, in a side position, legs bent at the knees, one arm bent at the chest. A cushion is placed under the head. Only then do they begin to insert the probe either into the duodenum or into the stomach. The specialist uses a camera to observe all the changes inside, which he views on the screen.
Recovery after the procedure
The examination, which was carried out according to all the rules by a qualified gastroenterologist, does not require any recovery after its implementation.
After removing the probe, the patient is observed by the doctor for another hour. This is necessary in order to quickly and effectively eliminate possible negative consequences: injury to the esophagus or stomach.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Perforation of the stomach or injury to the mucous membrane can occur if the procedure is performed incorrectly. In this case, gastric bleeding often occurs. In this case, it is necessary to urgently take a number of actions:
- intramuscular injection of dicinone;
- intravenous injection of calcium chloride;
- blood transfusion (in case of large blood loss);
- applying ice to the stomach area.
In case of gastric perforation, urgent surgical intervention is necessary. However, such complications are extremely rare. This procedure almost always goes smoothly and painlessly.
Other purposes of sounding
Probing is a medical procedure during which you can take juice from the stomach for a more thorough analysis. For this purpose, either a syringe or a pump designed for this process is attached to the tube. The stomach is washed out using intubation. Here a special tube is used, at the end of which a funnel is attached. It is designed for pouring in and pouring out purified water.
While probing of this nature is being done, the patient is in a sitting position. The exception is the unconscious patient. Then a thin tube is inserted through his nose and rinsed.
Interpretation of survey results
This procedure is aimed mainly at studying the secretory function of the stomach. It can be used to diagnose most diseases of the digestive system:
- a clear, non-viscous liquid with normal acidity indicates a completely healthy stomach;
- the predominance of yellow or green in the liquid indicates an admixture of bile, red and brown - an admixture of blood;
- food residues in the pumped out fluid and an increased total volume make it possible to judge hypersecretion of gastric juice;
- increased fluid viscosity indicates the presence of gastritis;
- depending on the content of hydrochloric acid, treatment is directed either to limit its production, or, conversely, to stimulate it;
- The acidity of the stomach is determined: low or high.
Probing for rinsing at home
Probing for the purpose of lavage is mostly done in the hospital during poisoning, but in some cases people do it themselves at home. This procedure is quite simple:
- you need to drink warm boiled water;
- after a minute, artificially induce vomiting.
This manipulation should be done several times, with each approach using at least one and a half liters of water. For a child, such washing should be done carefully. At the same time, make sure that the drunk liquid leaves the body completely. To induce vomiting, you need to stick two fingers into the oral cavity so that the urge to vomit appears. They should be maintained for some time. If food poisoning occurs, then a little potassium permanganate is added to the water. Before use, strain through cheesecloth. Since undissolved crystals of the product can cause a burn in the gastrointestinal tract. Such manipulations are aimed at removing harmful substances from the body from food before they have time to enter the bloodstream and have a negative impact on other internal organs.
It is worth noting that if a sick person is not sure what nature of his poisoning is, then it is not advisable to rinse the stomach at home. Why? When the cause of the disease is petrochemical products, together with water they can not only provoke an even greater poisoning process, but also form burns of the mucous membrane in the gastrointestinal tract.
Gastric probing technique
Diagnostic probing is performed on an empty stomach or after a test breakfast (see Test breakfast). The patient should not eat, drink, or smoke the evening before.) Removable dentures must be removed before the procedure. 3. g. carried out with the patient sitting (his head slightly tilted forward), in case of a severe or unconscious condition of the patient - lying down. In extremely rare cases, with a pronounced gag reflex, it is necessary to resort to anesthesia of the mucous membrane of the pharynx and pharynx, which is lubricated with a solution of dicaine, novocaine, etc.
Being on the right side of the patient, a warmed, moist thick probe is inserted along the back wall of the pharynx with the right hand. As the end of the probe approaches the level of the epiglottis, the patient is asked to make a swallowing movement: the probe passes into the upper part of the esophagus. Using gentle rhythmic movements without violence, the probe is pushed through the esophagus into the stomach; at this moment the patient breathes deeply through his nose. When the probe is passed 40-45 cm from the level of the teeth, it usually reaches the stomach. To determine the required depth of insertion of the probe, you can also use a figure equal to the patient’s height in centimeters, minus 100-105 cm. When inserting the probe in an unconscious patient or if he is unable to perform swallowing movements, the probe may get into the larynx, signs of which include wheezing, cyanosis, restless state of the patient. In this case, you should immediately remove the probe and try to insert it again.
After the tube enters the stomach, its contents begin to flow through the tube. If this does not happen, you need to rinse the probe and force the patient to strain slightly or induce gagging by moving the probe.
When removing the probe, a spasm of the muscles of the pharynx and esophagus is sometimes observed, which is eliminated by introducing a small amount of warm water into the probe.
A thin probe is inserted in the same way as a thick one, but since it is elastic, the patient must swallow it. For seriously ill patients, a thin probe is often inserted in a lying position, through the nose. Insertion of the probe takes several minutes and is easily tolerated by the patient. A small admixture of fresh blood to the gastric juice, a mild reaction to the introduction of a parenteral pathogen of gastric secretion does not prevent the continuation of the manipulation. A significant and especially increasing amount of blood is grounds for stopping the procedure. Severe reactions that force interruption of probing rarely occur.
Probing of the stomach is carried out simultaneously with a thick probe or using multi-moment (fractional) sounding methods using a thin probe.
The method of simultaneous sounding is used only if it is not possible to use more advanced methods; it gives approximate information about the juice secretion and partly the motor-evacuation function of the stomach. After 45 or 60 minutes. after a test breakfast, a thick probe is inserted and all gastric contents are completely removed. If gastric juice cannot be obtained, fractional 3. g. is necessary, since repeating the manipulations is impractical.
A thin gastric tube is inserted on an empty stomach and the entire contents of the stomach are pumped out. Then a stimulus is administered (test breakfast, injection of histamine, insulin and gastrin). In 10 minutes. pump out 10 ml and after another 15 minutes. - the entire contents of the stomach. Then, over the course of an hour, 4 portions are pumped out at intervals of 15 minutes. It is advisable to pump out the contents every 5 minutes, changing portion cups every 25 minutes. Even more accurate results are achieved with constant suction of gastric contents.
Removal of stomach contents is carried out using a thin probe inserted through the nostril. This manipulation can be carried out periodically with a syringe attached to the probe; less often, constant pumping is performed using some kind of suction.
For gastric lavage, a thick probe is used, with a glass funnel attached to the oral end. Boiled water, isotonic sodium chloride solution, sodium bicarbonate solution, etc. are used as washing liquid. The first portion of washing water is subjected to laboratory testing. Gastric lavage is also performed for diagnostic purposes for subsequent cytological, bacteriological and toxicological studies of rinsing waters.
To introduce nutritional mixtures and protein preparations into the stomach, thin (2-3 mm in diameter) polyvinyl chloride probes are used, inserted through the nose. In some patients, they are left in the stomach for a period of 1 to 4 months.
Features of application
Gastric intubation is a fairly safe and, in most cases, painless procedure. But it must be carried out according to strict indications:
Diagnosis of stomach ulcers
- with gastritis;
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- intestinal obstruction;
- reflux esophagitis;
- stomach atony;
- if bleeding is suspected;
- poisoning;
- after surgical interventions.
But this procedure is not for everyone. A probe should not be inserted in case of injury, stenosis or rupture of the esophagus, or in the absence of a pharyngeal reflex. After operations on the gastrointestinal tract, intubation can only be used according to strict doctor’s instructions. Inserting a probe through the nose is contraindicated in cases of deviated nasal septum.
Careless or incorrect insertion of such a device can lead to complications. Most often, the tube gets into the trachea, damaging it. Irritation of the pharynx or inflammation of the mucous membrane may also occur. When it is administered through the nose, nosebleeds and damage to the mucous membrane often occur. Most often, such complications are caused by a thick gastric tube.
To prevent complications, certain rules must be followed when inserting the tube.
Types of probes
Such devices come in different sizes, which depend on the thickness of the tube. In addition, they are available in lengths of 40, 80, 110, 125 cm. Common sizes are from 6 to 22. The thinnest probe has an outer diameter of 2 mm and is marked in green. Most often it is used for young children. Children's probes have sizes up to 14 and a diameter of up to 5 mm.
Gastric tube size 16 is used for adults. Its diameter is 5.3 mm, and the connector color is orange. The thickest probes, purple, green, gray and brown, are used the least often, as their use often causes serious discomfort and can cause complications. After all, the thickness of their tube is more than 8 mm.
In addition to size, there are different types of gastric tubes based on their intended purpose. They are:
- aspiration for collecting stomach contents;
- diagnostic, having an olive at the end into which electrodes are mounted;
- endoradiosondes with a built-in transmitter;
- duodenal - longer and thinner, having an olive with holes at the end;
- thin for energy nutrition.
Such devices also differ in production. Russian probes, Viroban, BasisMed, are more common and accessible. Also known are Chinese catheters from Integral Medical Products and Ningbo Greetmed Medical Instruments, and American catheters from Alba Healthcare. But the devices produced by the Dutch company Apexmed are considered to be of the highest quality.
Gastric tubes come in different lengths and thicknesses