The article was prepared by a specialist for informational purposes only. We urge you not to self-medicate. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
A diet for dysbacteriosis is the organization of therapeutic nutrition, whose main task is to normalize the disturbed balance of intestinal microflora. Dietary dishes must necessarily form the basis of the patient’s diet, since they are the basis for the treatment of all disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, along with drug treatment. Sometimes, simply by normalizing your menu and adjusting your lifestyle, you can achieve complete recovery. However, intestinal dysbiosis is a consequence of serious disorders in the human body, which must be eliminated together with a doctor.
It is the doctor who helps the patient create the optimal menu for his case and eliminate foods that disrupt intestinal function.
Objectives of dietary nutrition for dysbacteriosis:
- Replenishing the body's need for nutrients that are designed to compensate for energy costs.
- Restore impaired intestinal motor function.
- Restore impaired metabolism.
- Restore intestinal microflora.
The importance of diet
Doctors say that the body’s reaction to following a special diet manifests itself very quickly. Over the course of several days, the pathogenic flora decreases and improves. The intestinal environment is quite “smart” and can itself fight to maintain a healthy balance in the body. To this end, she makes certain clues in the form of food preferences.
The specialist always pays attention to which foods cause special cravings in the patient - this allows us to determine the nature of the microflora.
Supplementing therapy with a special diet makes it possible not only to eliminate the symptoms of the disease, but also to fully cure it, so it is important to follow the nutritional advice given by your doctor.
Diet for intestinal diseases in children
The child may also have intestinal diseases. Dyspeptic syndrome is quite common: diarrhea, bloating. In such cases, pediatricians, gastroenterologists and nutritionists even recommend that children adhere to the same therapeutic diet No. 4, since it is not dangerous for the child’s body, and the choice of products is really wide, so people with allergies have the opportunity to replace allergenic foods. And, of course, the diet is really effective for digestive disorders.
If doctors have prescribed a fourth diet, which is therapeutic, you should not neglect this; it is advisable to think over a high-quality diet that the child will like. For moral support, you can diet with him. Parental support is always extremely important for a child, especially since treatment table No. 4 is, in principle, a fairly suitable and gentle option for a child’s incompletely formed gastrointestinal tract.
Reasons for the development of dysbiosis
The specific reasons that can trigger the disease have not yet been established. But there are known factors that provoke dysbacteriosis:
Despite the various reasons underlying dysbiosis, their development is characterized by a number of common signs: improper diet;- taking antibacterial drugs;
- frequent stress and nervous system disorders;
- pathologies of the digestive system;
- allergic reaction;
- surgical intervention;
- parasites in the body;
- use of hormonal and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for treatment;
- infection in the intestines;
- viral diseases.
It is also known that the risks of dysbiosis increase with a weak immune system.
Symptoms
With the development of dysbacteriosis, pathological processes are formed that occur in stage 4.
- First
. Only a slight imbalance is formed between opportunistic and pathogenic microorganisms. This can occur due to the consumption of low-quality food, taking antiseptic and antibacterial drugs. Symptoms are practically not expressed. Flatulence and bloating in the abdomen may occur. Once the damaging factor disappears, the condition can return to normal on its own. - Second
. Negative symptoms appear, with which they turn to a gastroenterologist. The patient is worried about flatulence, a metallic taste in the mouth, and poor appetite. Dyspeptic disorders and impaired stool formation often occur. The latter include diarrhea and constipation. The quality of the skin deteriorates due to a deficiency of nutrients. A rash and irritation appear on it. - Third
. Due to the aggressive influence of pathogenic microflora, the intestinal mucosa becomes inflamed. This leads to pain in the center of the abdomen. The longer the condition, the more the patient is bothered by pain. The bolus of food is poorly digested, which can be seen by the nature of the stool. - Fourth
. Pathogenic microorganisms actively multiply and are completely distributed throughout the intestines. Digestion of food becomes difficult, so microelements, vitamins and minerals enter the systemic bloodstream in reduced quantities. This leads to complications such as anemia and vitamin deficiency. The patient suffers from mood swings, weakness, and constant drowsiness. The quality of immunity deteriorates, a person constantly suffers from bacterial, viral, and fungal diseases.
In order for the patient to receive quality treatment, it is necessary to see a doctor. For example, gastroenterologist, proctologist, therapist. Dysbacteriosis is a serious disorder; it can lead to complications in the absence of therapy or changes in living habits. Home treatment without a doctor is carried out only for the first and second stages. In this case, eating a good diet and taking probiotics can help.
What you can and cannot eat if you have intestinal dysbiosis
In case of dysbacteriosis, nutrition should be balanced. There are a number of foods that need to be excluded, especially at the acute stage. Refer to the lists of allowed and prohibited foods.
Authorized Products
The diet is based on the following products:
- rice and other cereals;
- dill, parsley;
- boiled potatoes;
- steamed cutlets;
- low-fat broths for meat and fish;
- boiled vegetables;
- fermented milk products;
- jelly.
Products to Avoid
During treatment, the following products are excluded from the menu:
pickles, smoked meats, marinades;
The main functions of normal microflora of the intestinal tract.- spicy food;
- fresh fruits and vegetables;
- canned food;
- seasonings;
- millet;
- sausages;
- carbonated drinks;
- berries;
- mushrooms;
- seafood.
Mostly prohibited foods include foods that cause flatulence.
Diet principles
There are general principles of diet for dysbiosis. But you need to keep in mind that it may be accompanied by diarrhea or constipation.
For diarrhea
If the pathology is accompanied by diarrhea, then it is recommended to give the stomach and intestines rest for 2-3 days. You can use compotes, decoctions, broths, jelly. Decoctions of oak bark, bergenia root, and bird cherry fruit normalize stool. Sugar should not be added to drinks. Further, the diet should be based on pureed food at room temperature. Otherwise, you need to follow the general recommendations.
For constipation
Fiber is needed to normalize intestinal function. The diet includes fresh vegetables and fruits, not only stewed and baked, but also raw. Under the influence of digestive juices, fiber swells in the intestines and ensures the proper formation of feces. It also activates the growth of beneficial microorganisms. It is recommended to drink plenty of fluids.
Useful products for improving peristalsis are bran, prunes, applesauce, rhubarb compote. Otherwise, you need to adhere to general principles.
General recommendations
The general rules for constructing a therapeutic diet for correcting microflora are as follows:
If you want to restore the bacterial balance of the intestines and improve your overall health, start with proper nutrition. It is recommended to eat food 5-6 times a day in small portions, chewing it thoroughly.- If there is an individual intolerance to any product, it is excluded from the diet.
- It is necessary to minimize the amount of refined foods in the diet.
- Mandatory components in the diet are fermented milk products and fiber.
- You need to maintain a balance of proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
- The body must receive enough arginine and glutamine. Their sources are fish, chicken, beef, nuts, pumpkin seeds, wheat flour, peas, spinach, parsley.
- It is recommended to lean on mucous fresh food, which should be mild and unsalted.
- Food needs to be boiled or steamed. Frying is not allowed.
- When bloating occurs, fresh foods need to be thermally processed.
- It is important to drink enough water.
- Nutrition should be complete, but you should not overeat, since with dysbacteriosis the body absorbs and digests food more slowly.
Therapy methods
The main method of treatment is diet. It creates a diet for every day, including foods that have a beneficial effect on the performance of the digestive tract. They should not cause fermentation or gas formation.
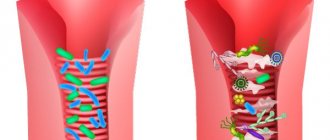
The main beneficial microorganisms in the digestive tract are bifidobacteria. A large volume is observed in fermented milk products, so they are included in the daily diet.
Antibiotics are required for patients who have an intestinal infection. But the technique is prescribed only in the most severe cases, when it is impossible to cope with diet. The following medications that affect the intestines are recommended:
- Alpha Normix;
- Enterofuril;
- Enterol.
Therapy lasts 7-10 days; shorter intervals are prohibited, since microorganisms may develop resistance to the active substance. In addition to antibiotics, sorbents are prescribed that remove bacteria, fungi, viruses, and their intoxication products. The following types of sorbents are used:
- Enterosgel;
- Polysorb;
- Smecta.
To normalize the composition of the intestinal microflora, it is necessary to take medications that normalize the composition of the intestinal microflora. They contain different types of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, which colonize in the affected intestines. The following combination is recommended:
- probiotics
- contain beneficial microorganisms; - prebiotics
- stimulate the production of intestinal microflora; - synbiotics
- contain both of these groups.
In order for the therapy to really help, they additionally use techniques that improve the functioning of the immune system.
Diet for pregnant and lactating women with microflora disorders
For intestinal dysbiosis in pregnant and lactating women, diet is the safest treatment measure. To normalize metabolic processes and the functioning of the digestive tract, it is recommended to eat 5-6 times a day in small portions.
The diet is based on porridge, lean meat and fish, which are steamed, stewed or boiled. Vegetables, fruits and herbs are also useful. They can be consumed fresh or cooked - this should be decided by the doctor. Fruits are acceptable in the form of fruit drinks, compotes, and purees.
Fully or partially limited products
The diet for dysbacteriosis excludes foods that stimulate the secretion of gastric juice - hot seasonings and spices, smoked meats, canned vegetables containing vinegar, any dishes in a marinade. Fatty, rich broths and first courses based on them are prohibited. Mushrooms and seafood, animal and confectionery fats, fatty meats and fish, sausages and various meat delicacies, offal (liver, brains, kidneys), fresh bread from yeast dough and pastries, sour berries and fruits, sauerkraut, legumes, fatty foods are excluded. cream, sour cream and cheese.
Porridges made from coarse cereals (pearl barley, millet, barley) and legumes, which are poorly digested in the gastrointestinal tract and cause bloating, are not recommended. It is not allowed to include jam, dried fruits, honey, sweet yoghurts, condensed and whole milk, whole grain bread with the addition of cereals and seeds, sweets, lemonade, chocolate, and ice cream in the diet. Sugar is allowed in limited quantities (50 g/day).
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| potato | 2,0 | 0,4 | 18,1 | 80 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| turnip | 1,5 | 0,1 | 6,2 | 30 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
Fruits | ||||
| quince | 0,6 | 0,5 | 9,8 | 40 |
Berries | ||||
| blueberry | 1,1 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 44 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
| noodles | 12,0 | 3,7 | 60,1 | 322 |
Bakery products | ||||
| wheat bread | 8,1 | 1,0 | 48,8 | 242 |
Confectionery | ||||
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk | 3,2 | 3,6 | 4,8 | 64 |
| condensed milk | 7,2 | 8,5 | 56,0 | 320 |
| cream 35% (fat) | 2,5 | 35,0 | 3,0 | 337 |
| sour cream 25% (classic) | 2,6 | 25,0 | 2,5 | 248 |
Meat products | ||||
| fatty pork | 11,4 | 49,3 | 0,0 | 489 |
| pork liver | 18,8 | 3,6 | 0,0 | 108 |
| pork tongue | 14,2 | 16,8 | 0,0 | 208 |
| pork kidneys | 13,0 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 80 |
| pork heart | 15,1 | 3,2 | 0,0 | 89 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| beef brains | 9,5 | 9,5 | 0,0 | 124 |
| bacon | 23,0 | 45,0 | 0,0 | 500 |
| ham | 22,6 | 20,9 | 0,0 | 279 |
| beef stew | 14,1 | 17,4 | 0,0 | 214 |
| pork stew | 13,0 | 35,0 | 0,0 | 367 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 16,2 | 44,6 | 0,0 | 466 |
| dry-cured sausage | 24,1 | 38,3 | 1,0 | 455 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| fried fish | 19,5 | 11,7 | 6,2 | 206 |
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| marinated fish | 1,7 | 3,0 | 11,4 | 82 |
| pink salmon | 20,5 | 6,5 | 0,0 | 142 |
| seafood | 15,5 | 1,0 | 0,1 | 85 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| salmon | 21,6 | 6,0 | — | 140 |
| hot smoked mackerel | 22,1 | 23,8 | 4,1 | 317 |
| trout | 19,2 | 2,1 | — | 97 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| beer | 0,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 42 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| cola | 0,0 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 42 |
| instant coffee dry | 15,0 | 3,5 | 0,0 | 94 |
| lemonade | 0,0 | 0,0 | 6,4 | 26 |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
| energy drink | 0,0 | 0,0 | 11,3 | 45 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
What foods go together: general principles and approximate diet
In case of dysbacteriosis, separate nutrition is recommended. It is recommended to eat legumes with cereals, vegetable oils, sour cream, vegetables, and bread. Sour fruits can be safely combined with fermented milk products. The latter can also be combined with vegetables. You can use nuts and dried fruits with fruits and vegetables. Cereals are combined with plant foods, but combining meat and fish with carbohydrates is not recommended.
It is not recommended to mix whole milk and eggs with other products, except perhaps with a light vegetable salad. Fermented milk products go well with fresh herbs.
Sample diet for a week
The diet should be prepared together with a doctor. An approximate menu for intestinal dysbiosis for a week is presented below.
Monday
- Breakfast: banana, 20-30 minutes later - porridge, herbal tea;
- Second breakfast: vegetable salad with added herbs, medium-sized fruit;
- Lunch: boiled chicken with grated cheese and herbs;
- Afternoon snack: fruit;
- Dinner: boiled or steamed fish, egg.
Tuesday
- Breakfast: buckwheat, kefir, tea without sugar;
- Second breakfast: fruit;
- Lunch: steamed fish with vegetables;
- Afternoon snack: fruit;
- Dinner: steamed chicken, fresh vegetable salad.
Wednesday
- Breakfast: rice, kefir;
- Second breakfast: fruit;
- Lunch: salad of boiled beef and vegetables;
- Afternoon snack: dried fruits and milk;
- Dinner: cottage cheese casserole without sugar.
Thursday
- Breakfast: cottage cheese casserole without sugar;
- Second breakfast: sour fruits;
- Lunch: stewed fish with vegetables;
- Afternoon snack: dried fruits;
- Dinner: salad with cheese, tomatoes, herbs and basil.
Friday
- Breakfast: cereal soaked in kefir;
- Second breakfast: citrus fruits;
- Lunch: veal stew with peppers and tomatoes;
- Afternoon snack: seasonal berries;
- Dinner: vegetable salad with Feta cheese;
Saturday
- Breakfast: millet porridge with water without sugar;
- Second breakfast: fruit;
- Lunch: vegetables, fish soup;
- Afternoon snack: nuts;
- Dinner: steamed omelette.
Sunday
It is recommended to make this day a fasting day by choosing one product: apples, kefir, cucumbers, and so on.
Video on the topic: What is dysbiosis? What foods should be consumed if the intestinal microflora is disturbed?
Authorized Products
The basis of the diet for intestinal dysbiosis is pureed porridge made from buckwheat, oatmeal and white rice with the addition of a small amount of butter. It is allowed to consume 150 g of dried white bread or crackers. Soups are prepared with low-fat fish/meat broth, adding pureed meat, cereals, meatballs, egg flakes and some vegetables. Meat products in the diet include lean beef, veal, rabbit or chicken, which are served boiled. Fish is allowed in “white” low-fat varieties, which is steamed or boiled.
The use of various fermented milk products (kefir, fermented baked milk, kumiss, acidophilus milk) is indicated. It is allowed to include astringent foods and dishes in the diet: jelly from blueberries, sloe, rowan, quince, dogwood, persimmon, pear, bird cherry and fruit drinks made from them, as well as raw pureed apples or applesauce. Herbal teas, strong green and black tea, rosehip decoction, infusion of dried dogwood, bird cherry, blueberry, and non-carbonated mineral water are allowed as drinks.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| sauerkraut | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,4 | 19 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
Fruits | ||||
| apricots | 0,9 | 0,1 | 10,8 | 41 |
| watermelon | 0,6 | 0,1 | 5,8 | 25 |
| melon | 0,6 | 0,3 | 7,4 | 33 |
| nectarine | 0,9 | 0,2 | 11,8 | 48 |
| peaches | 0,9 | 0,1 | 11,3 | 46 |
| plums | 0,8 | 0,3 | 9,6 | 42 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| dried figs | 3,1 | 0,8 | 57,9 | 257 |
| dried apricots | 5,2 | 0,3 | 51,0 | 215 |
| dried apricots | 5,0 | 0,4 | 50,6 | 213 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| corn grits | 8,3 | 1,2 | 75,0 | 337 |
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| wheat bran | 15,1 | 3,8 | 53,6 | 296 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Bakery products | ||||
| oatmeal bread | 10,1 | 5,4 | 49,0 | 289 |
| Rye bread | 6,6 | 1,2 | 34,2 | 165 |
| bran bread | 7,5 | 1,3 | 45,2 | 227 |
| doctor's bread | 8,2 | 2,6 | 46,3 | 242 |
| whole grain bread | 10,1 | 2,3 | 57,1 | 295 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jelly | 2,7 | 0,0 | 17,9 | 79 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| milk candies | 2,7 | 4,3 | 82,3 | 364 |
| fondant candies | 2,2 | 4,6 | 83,6 | 369 |
| fruit and berry marmalade | 0,4 | 0,0 | 76,6 | 293 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
| oatmeal cookies | 6,5 | 14,4 | 71,8 | 437 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
| chicory | 1,7 | 0,2 | 4,1 | 21 |
Dairy | ||||
| kefir | 3,4 | 2,0 | 4,7 | 51 |
| sour cream 10% (low-fat) | 3,0 | 10,0 | 2,9 | 115 |
| curdled milk | 2,9 | 2,5 | 4,1 | 53 |
| kumiss | 3,0 | 0,1 | 6,3 | 41 |
| acidophilus | 2,8 | 3,2 | 3,8 | 57 |
| yogurt | 4,3 | 2,0 | 6,2 | 60 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese | 17,2 | 5,0 | 1,8 | 121 |
Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| beef tongue | 13,6 | 12,1 | 0,0 | 163 |
| veal | 19,7 | 1,2 | 0,0 | 90 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| chicken | 16,0 | 14,0 | 0,0 | 190 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| herring | 16,3 | 10,7 | — | 161 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| corn oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| plum juice | 0,8 | 0,0 | 9,6 | 39 |
| tomato juice | 1,1 | 0,2 | 3,8 | 21 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
What can patients with dysbiosis drink?
If changes are observed in the intestinal microflora, you also need to carefully monitor your diet. You should drink liquid no later than half an hour before meals and no earlier than 2 hours after it.
All alcoholic drinks and carbonated waters are prohibited. It is recommended to limit kvass and sour jelly. Infusions of chamomile and mint, cranberry juice and jelly, and compote based on dried fruits will be useful. You can also supplement your diet with drinks based on bitter herbs. For diarrhea, compotes made from astringent berries, infusions based on pomegranate peels and oak bark are useful. You need to drink still water, preferably mineral water. For carbonated drinks, you must first eliminate the gases. To do this, leave the bottle open for some time.
Prevention
Specific prevention of dysbacteriosis has not been developed. It is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle and monitor your diet. In the prevention of the disease in children and infants, attention is paid to breastfeeding the baby, at least until he is six months old.
During treatment, it is necessary to monitor the fluid balance in the body.
Supplement to the diet: folk recipes
After consultation with a specialist, the diet can be supplemented with herbal medicinal infusions. It is recommended to combine different plants with each other. Herbal medicine is usually divided into several stages:
- Stage 1 . Plants such as St. John's wort, anise, and coltsfoot are used to help normalize the microflora. Chamomile, blackberry, calamus and other herbs can be used for disinfection.
- Stage 2 . Treatment is aimed at relieving inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, restoring balance in the body and normalizing digestion. Plants such as chamomile, yarrow, marigold, St. John's wort, etc. are used.
- Stage 3 . To eliminate toxins from the body, flax seeds, leaves and roots of elecampane, angelica, and calamus are used.
- Stage 4 . For diarrhea, it is useful to use astringent components that are contained in oak bark, cinquefoil, and bergenia root. Bird cherry fruits, infusions with burnet root and erect cinquefoil also help.
- Stage 5 . Anise, cumin, and fennel can be used to combat constipation. If there is a large amount of feces that injure the anus, you can use a mixture of buckthorn, milkweed, Alexandria leaf and hogweed.
- Stage 6 . Elecampane, marshmallow, angelica, and flax seeds will help protect the mucous membranes of organs from the negative influence of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Stage 7 . The body needs to be saturated with energy and vitality. For this, infusions of rowan, black currant, rose hips, string, and strawberries can be used. Herbs can be combined with milk sugar. Chamomile will help normalize stools and eliminate intestinal spasms; lactose will help restore microflora. Plantain is useful for diarrhea. For flatulence, you can chew fennel seeds. Another proven remedy for problems with microflora is garlic along with fermented milk products.
Diagnostics
After detecting primary signs, contact a gastroenterologist. An infectious disease specialist may be needed if you have a fever, vomiting, or diarrhea. The following types of research are carried out:
- bacteriological culture of stool to identify a pathogenic microorganism and an antibiotic that is sensitive to it;
- PCR test that detects bacteria, viruses, fungi;
- analysis of feces for dysbacteriosis;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
Once the diagnosis is made, a diet must be prescribed. It is compiled by a gastroenterologist together with a nutritionist.