Psychotherapist
Krashkina
Irina Ivanovna
31 years of experience
Psychotherapist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, member of the Russian Professional Psychotherapeutic League
Make an appointment
Therapists are most often approached with complaints that are characteristic of disorders of the digestive system. Everyone should know what the symptoms of dyspepsia are in an adult. Diagnosis requires a serious differential approach, since this group includes all nonspecific signs of symptom complexes of the gastrointestinal tract. Treatment of dyspepsia directly depends on the causes of the disease, and in most cases this is a deficiency of digestive enzymes or poor nutrition.
Symptoms and signs of dyspepsia
Dyspepsia syndrome is a digestive disorder and symptoms that are characteristic of various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and their borderline phases.
When digestion is disturbed, symptoms appear that are united by a common name - gastric dyspepsia, this includes:
- problems with swallowing;
- nausea and vomiting attacks;
- belching;
- pain in the stomach;
- heartburn;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- bloating;
- constipation, diarrhea.
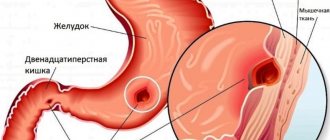
Dyspepsia of the stomach and intestines causes pain in the epigastric region. They can be either quite intense or in the form of mild discomfort. There is a feeling of rapid satiety and fullness, and as a result, nausea, belching, and heartburn. Another alarming sign is loss of appetite, quickly and sharply. After this, the person begins to lose weight for no reason. Intestinal dyspepsia is accompanied by rumbling in the stomach, flatulence, diarrhea or constipation.
Disruption of the process of digesting food in the intestines may indicate pathologies such as dysbiosis, diverticulitis, enzymopathy, enteritis, colitis, tumors in the intestines, irritable bowel syndrome, pancreatic diseases, and metabolic pathologies. Also, intestinal dyspepsia may indicate that an infection is developing in it (dysentery, cholera, intestinal tuberculosis, salmonellosis, etc.).
There are 2 main groups of dyspeptic disorders - functional dyspepsia and organic. In the first case, only disturbances in the functioning of the organ are detected, that is, functional lesions, while in the second they are exclusively organic in nature. In the latter case, the symptoms will be more pronounced, and the disorders will continue for a long time.
Are you experiencing symptoms of dyspepsia?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Constipation in a child, children
Constipation is a long-term (more than 48 hours) delay in bowel movement, accompanied by difficulty in defecation, as well as a small amount (less than 100 g per day) or increased hardness of feces, and a feeling of incomplete bowel movement. Constipation can be organic and functional. The most common causes of constipation are:
1) nutritional defects, malnutrition, monotonous milk nutrition, lack of products in the diet of older children that provide a significant amount of food waste; 2) anatomical defects in the development of the intestine, malformations of the anorectal zone; 3) atonic intestinal conditions; 4) reflex constipation with cracks and abrasions of the anus and rectum.
If children do not have stool for several days from birth, one should think about congenital anomalies of intestinal development. In older children, constipation is observed with hypothyroidism, colitis, dolichocolon, megacolon. Mechanical obstacles and medications (atropine-like, catecholamines) lead to constipation.
Among functional constipation, spastic or hypokinetic constipation is most common. As a result of the absorption of rotting products from the intestines during chronic constipation, children’s well-being is disrupted: increased fatigue, headaches appear, appetite decreases, and sleep deteriorates.
Conditioned reflex constipation appears in a child as a result of a change in the usual lifestyle: with the start of attending kindergarten, school, when the usual time of defecation shifts.
In the occurrence of psychogenic constipation, factors such as prolonged and frequent stressful situations in the family, school, excessive emotional and mental stress with simultaneous physical inactivity are important.
Causes
There are several forms depending on the reasons that cause the development of the syndrome:
- simple dyspepsia. It is also called nutritional. Caused by nutritional problems. In turn, there is fatty (soapy), fermentative and putrefactive dyspepsia. In the latter case, it develops if the food is dominated by protein products or stale meat is used. Fermentation develops from excessive consumption of carbohydrates (bread, cabbage, legumes, sugar) and drinks that cause fermentation (beer and kvass). Fatty dyspepsia develops with excessive consumption of fatty foods, especially pork and lamb;
- dyspepsia associated with a deficiency of secreted enzymes for digesting food in the intestines and stomach. In turn, it can be gastrogenic (lack of enzymes in the stomach), pancreatogenic (deficiency of pancreatic substances), enterogenic (lack of intestinal juices), hepatogenic (insufficient secretion of bile from the liver);
- dyspepsia, which is associated with problems with the absorption of food in the intestines with malabsorption syndrome. As a result, nutritional components do not flow from the intestines into the blood;
- dyspepsia, which is associated with intestinal infections. In this case, it could be either dysentery or salmonellosis.
- intoxication. It manifests itself due to poisoning in various diseases, including influenza, acute surgical pathologies, and also when consuming poisons.
All of these factors can contribute to the onset of the disease. Symptoms and treatment of dyspepsia of the stomach and intestines directly depend on the causes.
Preventing indigestion
The normal functioning of the digestive system requires compliance with the following rules:
- healthy eating to prevent indigestion
(refusal of strict diets, balanced composition of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, consumption of vegetables and fruits in sufficient quantities, exclusion of fast food, etc.); - getting rid of bad habits
(frequent drinking of alcohol, eating dry food, eating on the go, overeating at night, not having breakfast); - developing an adequate response to stress
(indigestion is often associated with negative emotions and nervous tension).
Measures to prevent dyspepsia also include proper rest, healthy sleep, and sufficient physical activity.
You can get tested for a tendency to gastrointestinal diseases, including indigestion, at the Medical Genetics Center.
Risk factors
These include:
- frequent and severe stress, emotional tension. In this case, the pathology will have a neurotic origin;
- some medication use. This applies to antibiotics, hormonal or antitumor and other agents;
- poor nutrition. Most often this concerns overeating;
- intoxication. In this case, there may be either a disease of viral or bacterial origin, or household poisoning;
- excessive release of hydrochloric acid;
- problems with gastrointestinal motility.
These are the main factors that contribute to the occurrence of dyspepsia.
Why you should contact our clinic
You should not try to save on your health and go to dubious cheap clinics with old equipment and unprofessional doctors - this often leads to irreversible consequences.
If you want to undergo a preventive examination, or suspicious symptoms appear, make an appointment at our clinic without further hesitation. Thanks to the work of highly qualified specialists, first-class equipment and a modern approach to treatment methods, you will not regret your choice.
Complications
Gastric dyspepsia occurs in diseases such as esophagitis, GERD, cancer, stenosis or ulcer of the esophagus, cancer or the presence of benign tumors, periesophagitis, scleroderma, diverticulum. Also, the presence of dyspepsia of the stomach and intestines may indicate diseases of the muscles, central and peripheral nervous systems, pathologies of internal organs, for example, narrowing of the esophagus can be caused by cysts and tumors that oppress it from the outside. This also applies to aortic aneurysm, vascular anomalies, and thyroid hyperplasia.
Complications of dyspepsia are most often associated with the underlying illness that causes the appearance of this syndrome. The patient may suddenly lose weight and lose appetite for a long time. One of the severe consequences is Mallory-Weiss syndrome. In this case, the mucous layers of the lower part of the esophagus, where it passes into the stomach, rupture. Because of this, gastric bleeding begins. It can be quite intense and even lead to death. Most often, the occurrence of Mallory-Weiss syndrome is associated with repeated bouts of vomiting.
When to see a doctor
For treatment of stomach or intestinal dyspepsia, you should contact a gastroenterologist. Don't delay going to the doctor. Particular attention should be paid to such symptoms as abdominal pain at night, sudden weight loss for no reason, nausea, vomiting, frequent belching, and heartburn attacks. Diagnostics can be carried out at JSC "Medicine" (clinic of Academician Roitberg), which is located in the center of Moscow.
Polyfecalia in children
In children, the amount of feces exceeds 2% of food eaten and liquid drunk. It should be taken into account that the amount of feces increases with age. The amount of excrement in children of the 1st year of life is relatively greater than in older children and adults.
Polyfecalia is characteristic primarily of malabsorption syndrome. Polyfecality and stool disorders in chronic pancreatitis are caused by a violation of the topography of cavity and membrane digestion due to enzymatic deficiency.
Hungry stools resemble dyspeptic stools, but are usually thicker, darker, and may contain an admixture of mucus.
With simple dyspepsia, the stool is liquid, contains an admixture of greens (due to the rapid transit of biliverdin impurities through the intestines) and white lumps (a large amount of calcium soaps), a sour odor, and often foamy (fermentative dyspepsia).
Diagnosis of dyspepsia
Before starting treatment for dyspepsia, it is necessary to undergo an examination, which includes not only a description of complaints, an external examination, but also the following:
- laboratory tests - general and biochemical blood tests, examination of stool for the presence of blood, coprogram;
- instrumental studies - a test for gastric acid secretion, esophagogastroduodenoscopy, examination of gastric materials for the presence of Helicobacter pylori, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, colonoscopy, radiography, computed tomography, esophageal and antroduodenal manometry.
You can undergo diagnostics at JSC "Medicine" (clinic of Academician Roitberg), which is located in the central district of Moscow, near the Tverskaya, Novoslobodskaya, Belorusskaya, Chekhovskaya metro stations. If you have a disease, you may need to consult not only a gastroenterologist, but also other specialists: a psychiatrist, neurologist, cardiologist, endocrinologist.
How is the disease treated?
Our doctors say that in order for the treatment of dyspepsia to be as effective as possible, it must be comprehensive. In addition to taking medications, it is necessary to normalize your lifestyle, diet and diet.
Treatment of stomach disease depends on its type:
- Treatment of functional dyspepsia involves eliminating salty, spicy and fatty foods from the diet. Therapy is also carried out with antacids, inhibitors, and sedatives.
- Fermentative dyspepsia is treated by eliminating carbohydrate foods from the diet. Therapy also consists of taking adsorbent substances and enzyme preparations.
- Treatment of putrefactive dyspepsia involves prohibiting the consumption of protein foods. Sorbents, probiotics, and in some cases antibiotics are prescribed.
For these types of diseases, it is not recommended to consume foods containing large amounts of fiber. Sometimes sorbents that are effective in eliminating the syndrome can be prescribed. If severe pain is present, then antispasmodics can be taken.
Treatment
To treat dyspepsia, drug therapy is necessary. Separately, you need to get rid of diarrhea or constipation, and for this purpose special means are prescribed. Other drugs are also prescribed to treat dyspepsia and alleviate the patient’s condition:
- painkillers (antispasmodics);
- drugs that reduce the level of acidity in the stomach;
- enzyme agents to improve digestion processes.
Treatment must be comprehensive and systemic. It is necessary to treat the disease that caused dyspepsia, that is, gastritis, duodenitis, GERD, cholecystitis, gastric or intestinal ulcers, pancreatic diseases.
How is the disease diagnosed?
To determine the disease, our doctors use complex measures. Consultations are provided with a gastroenterologist, an infectious disease specialist and a therapist.
Diagnosis of dyspepsia depends on the symptoms present. The syndrome is determined using:
- ultrasound examination to diagnose pancreatitis and cholelithiasis.
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy, with the help of which it is determined whether a person suffers from reflux esophagitis, peptic ulcer, stomach tumors, intestinal pathologies;
- electrogastroenterography, which reveals gastric motility disorders;
- esophagomanometry, with the help of which a specialist is able to determine how the esophagus contracts and coordinate its peristalsis with the functioning of the lower and upper sphincters;
- 24-hour pH measurements exclude the presence of gastroesophageal reflux disease.
After the diagnosis of dyspepsia is completed and the diagnosis has been confirmed, the doctor prescribes treatment.
Myths and dangerous misconceptions in the treatment of dyspepsia
Main misconceptions:
- nausea, heaviness and bloating will go away on their own. They are temporary, so you don't have to go to the hospital;
- antispasmodics or enzyme agents remove heaviness in the stomach and discomfort in the intestines;
- If you eat something sour or spicy, the discomfort will disappear.
All of the above opinions are completely wrong. You should not rely on myths that were previously believed. If alarming symptoms appear, you should consult a specialist.
Fecal incontinence in a child, children
Fecal incontinence (encopresis) is a functional disorder of defecation in which there is a dysfunction of the rectum and external or internal sphincters of the anus, manifested by involuntary defecation.
Clinically, fecal incontinence, regardless of the cause, manifests itself in the same way: a dry and clean child begins to involuntarily lose more or less amount of feces. These phenomena can occur acutely, develop quickly and end in recovery within a short time, or develop slowly and progress steadily.
Literature
- E. A. Lyalyukova, V. N. Drozdov. “Unspecified dyspepsia”: differential diagnosis, tactics for patient management at the outpatient stage. Attending doctor. No. 8, 2022.
- E. I. Vovk. Functional and organic dyspepsia: “crossover” of diagnostic and treatment strategies in general practice. Attending physician. No. 9, 2012.
- Instructions for use of the drug IMODIUM® Express
- Register of medicines in Russia. Active ingredients. Loperamide. https://www.rlsnet.ru/mnn_index_id_637.htm.
- A study by Ameri et al. "A multicenter, double-blind study: a comparison of the effectiveness of loperamide in acute diarrhea with two popular antidiarrheal agents and placebo," 1975.