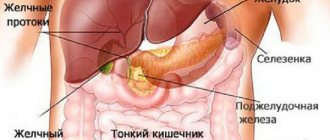
Abdominal pain on the left after eating appears with the development of a pathological process in the organs of the digestive tract. Most people prefer to cope with this symptom on their own and eliminate the pain with the help of antacids or enzyme medications.
But medications have only a temporary effect and do not affect the course of the disease, so the disease progresses, becomes chronic and causes various kinds of complications. To avoid the development of the disease, it is necessary to undergo an examination that can determine why pain appears in the left hypochondrium after eating.
Based on the location of the pain, its nature and time of onset, one can assume which organ of the abdominal cavity has ceased to cope with its function. If pain is felt after eating, this indicates a violation of the digestive or evacuation function of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT).
Pain immediately after eating indicates the presence of an inflammatory or degenerative process in the tissues of the stomach, duodenum or pancreas. In addition to pain, other symptoms occur in diseases of the digestive tract, but they are rarely specific, so laboratory and instrumental testing is required to make a diagnosis.
The sooner the cause of pain is determined, the greater the chance of avoiding the disease becoming chronic and the lower the risk of complications. And yet, if the clinical picture is characteristic of a disease, then knowledge of the features of its non-drug treatment will help to avoid attacks of pain and provide functional rest for the inflamed organ.
Gastritis
Pain in the left side after eating is felt due to inflammation of the gastric mucosa. The parietal cells of the stomach secrete hydrochloric acid, which promotes the activation of propepsinogens and gastrin, the denaturation and swelling of proteins, the curdling of milk, in addition, it has bactericidal properties.
To protect the mucous tissue, a special secretion (mucin) is secreted, which prevents the contact of hydrochloric acid with the cells and thereby prevents self-digestion. Under the influence of bile acids, medications, propionic or butyric acid, alcohol or an excessively high concentration of hydrochloric acid, the process of autolysis begins.
Violation of the protective function of mucus and increased synthesis of hydrochloric acid contributes to the development of Helicobacter pylori. The bacterium synthesizes substances that destroy mucin, urelase (an enzyme that breaks down urea with the release of ammonia) and endotoxins. Ammonia neutralizes the effect of hydrochloric acid and provides an optimal local environment for the existence of bacteria.
At the same time, the substance has an irritating effect on the stomach tissue, which causes inflammation and then cell death. The microorganism colonizes the stomach and duodenum, causing ulcers, gastritis, duodenitis, stomach cancer and, apparently, lymphoma.
Acute gastritis manifests itself violently, but clinical manifestations subside within 3–4 days
As studies show, Helicabacter is present in the vast majority of people examined, but it does not always cause the development of gastritis. The following factors contribute to its activation;
- improper diet, which is dominated by fatty and sweet foods;
- binge eating;
- eating is irregular (fasting);
- consumption of spicy foods, hot drinks, alcohol.
During the inflammatory process in the gastric mucosa, the following symptoms appear:
- acute spasmodic pain in the left hypochondrium in front or in the umbilical region;
- nausea and vomiting;
- belching;
- lack of appetite.
To make a diagnosis, the gastroenterologist prescribes fibrogastroscopy, ultrasound examination and laboratory analysis of blood and urine. The gastric mucosa is hyperemic, edematous, cellular infiltration, significant changes in the epithelium and increased regeneration are noticeable on biopsy.
In severe cases, gastric lavage is prescribed. Patients are advised to refrain from eating food for 1–2 days, then a diet is indicated (table No. 5). It is recommended to consume liquid cereals, juices, and pureed meat. It is forbidden to eat hot, spicy, rough, too hot or cold food, as this irritates the gastric mucosa.
If you ignore the signs of acute gastritis, the disease becomes chronic, in which inflammatory-dystrophic processes are observed, accompanied by changes in tissue structure and the progression of death of the glandular epithelium, as well as deterioration of secretory, protective, and motor functions.
Causes of chronic gastritis:
- infection with Helicobacter, herpes virus, cytomegalovirus, fungal flora;
- antibodies to parietal cells are synthesized by the body;
- reflux of duodenal contents (in particular, bile acids and isolecithin have a negative effect);
- addiction to rough, spicy, hot food, as well as lack of a meal schedule;
- smoking, excessive drinking;
- drug therapy (prednisolone, salicylates, digitalis preparations);
- chronic pathologies (oral cavity, tuberculosis, cholecystitis);
- pathology of endocrine organs (Addison's disease, hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus);
- metabolic deterioration (iron deficiency, obesity, gout);
- diseases in which oxygen transport is impaired (pulmonary and heart failure).
At the initial stage of the disease, functional disturbances in the secretion and motility of the organ occur, which leads to organic changes.
With exacerbation of chronic gastritis, the following symptoms appear: gastric dyspepsia (distension in the stomach after eating, heaviness, belching, regurgitation, vomiting, heartburn, nausea, unpleasant taste in the mouth, loss of appetite), mild pain, intestinal dyspepsia (change in consistency and frequency of stool, flatulence), asthenoneurotic syndrome (mood swings, irritability, fatigue, sleep disturbance).
Treatment depends on the phase of the disease (remission, exacerbation), causes, stomach acidity
Patients are advised to reduce the load on the organ and exclude foods that can cause thermal or mechanical irritation (adhere to diet table No. 2), eat small portions, but often. If secretory insufficiency is detected, the doctor prescribes drugs that improve nutrition of the gastric mucosa and microcirculation (B vitamins, Solcoseryl, Methyluracil).
If gastritis is associated with Helicobacter, antibacterial drugs and gastroprotectors are prescribed (De-nol, Metronidazole, Amoxicillin, Venter, Alsukral, Andapsin).
If secretion worsens, drugs are prescribed that increase the production of hydrochloric acid (tincture of dandelion roots, wormwood herb), and if hydrochloric acid is absent, then they resort to replacing it (tablets Acedin-Pepsin, Abomin, Betacid).
If a lot of acid is synthesized, then motor function is restored with anticholinergics (Atropine sulfate, Gastrocepin, Metacin, Platiphylline). When erosion occurs, H-2 receptor blockers (Omez, Cimetidine, Famotidine, Ranitidine) are prescribed, which suppress secretory function.
You can avoid exacerbation of chronic gastritis only by adhering to a balanced diet, following a meal schedule (to prevent the feeling of hunger or overeating), and also by giving up alcoholic beverages and smoking. It is necessary to carry out sanitation of chronic infectious foci.
What kind of pain is there?
Information about the location of unpleasant sensations gives the doctor an almost exact picture of what exactly is happening to the patient at the moment.
- Constant pain with a clear localization is called peritoneal. It is considered a symptom of exacerbation of inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract or kidneys, and is felt more strongly during breathing and when walking.
- If the patient complains of discomfort in the front, then this is a direct indication of injury to the spleen or stomach.
- When an unpleasant feeling shifts to the center of the abdomen, then gallbladder disorders can be suspected.
- When a patient talks about the localization of pain in the back, then in most cases, this is an indicator of damage to the left renal pelvis or developing pyelonephritis.
- Such pain may appear during examination if a person suffers from osteochondrosis in the thoracic region.
- The pain may be described as stabbing. This is one of the main symptoms of acute pancreatitis. The discomfort may be relieved slightly if the person sits or leans forward.
Doctors also highlight visceral pain, which can develop with intestinal colic, excessive accumulation of gases, and also with sprained muscles and ligaments. Another mechanism of occurrence is referred pain. Develops as a result of disruption of the functioning of organs not located in the abdomen. As a rule, it is localized there during myocardial infarction, as well as inflammatory changes in the tissues of the lungs: pneumonia and pleurisy.
Table. Nature of pain by group.
| Group | Description |
| Visceral | This group includes pain associated with pathological changes in gastrointestinal motility. The pain is dull and can be jerky or cramping. They radiate to both the shoulder and thigh area. Most often occur with intestinal spasms. The cause may also be stretching of muscle fibers. With acute flatulence, the pain is cramping in nature, and with intestinal colic it radiates to all nearby organs. |
| Peritoneal | They arise due to irritation of peritoneal receptors, which occur as a result of ruptures of organs and the release of their contents into the surrounding tissue. They are distinguished by the severity of their manifestations, cutting, clearly localized, lasting constantly, intensifying with activity and stress. More often they are encircling. May occur when a gastric ulcer perforates. They intensify with any load, movement, even with breathing, from inhalation and exhalation. |
| Spastic | They are generated by a spasm of smooth muscles. They occur with pathologies of internal organs of any nature - from colic to poisoning. They appear suddenly and just as suddenly go out. They can radiate to the shoulder blade and lower back, as well as to the legs. |
| Reflected | The cause of these pains is inflammatory changes. They can be different in duration and in character too - from aching and pulling, to pain and colic. They are “reflected” from organs located quite far from the left hypochondrium. They can occur with a heart attack, pleurisy, left-sided pulmonary inflammation and other diseases. |
| Psychogenic | This type of pain is not at all associated with diseases of any internal organs. Neurotic pain that cannot be diagnosed. But the patient is not pretending, but may actually experience acute pain, especially when in a depressive state or in the stage of a mental disorder. |
For example, with cardiomyopathy, pain is felt after exercise, with pneumonia - during coughing, with stomach and intestinal infections, pain is associated with meals, intensifying after eating, and with stomach cancer it is constant.
Peptic ulcer
If you ignore gastritis, then over time ulcers will appear in the gastric mucosa, perforation of which can threaten the patient’s life. Peptic ulcer is a recurrent chronic pathology, prone to development, affecting the stomach and duodenum. The disease is characterized by deterioration of endocrine and neurohumoral regulation, motor, secretory and protective functions of the affected organ.
Peptic ulcer disease develops as a result of:
- genetic predisposition and heredity (antitrypsin is not sufficiently active, there is an HLA-B5 antigen, blood group 1, increased production of hydrochloric acid);
- diseases of the stomach and intestines (duodenitis, functional disorders, gastritis);
- smoking, alcohol abuse;
- improper diet;
- taking medications that inhibit the protective properties of the mucous membrane (Butadione, Aspirin, Indomethacin);
- chronic stress.
With a stomach ulcer, pain appears in the upper abdomen, which can radiate behind the sternum, to the left shoulder, so sometimes they are confused with angina pain. If the ulcer has developed near the lesser curvature of the stomach, pain appears 15–60 minutes after eating.
Lesions of the antrum cause night, “hungry” or so-called late pain, which is felt 2-3 hours after eating. An ulcer formed in the pyloric part causes intense pain that does not depend on food intake. Pain in the left hypochondrium after eating appears if there is an ulcer in the sphincter area, fundus or body of the stomach.
How does a stomach ulcer hurt?
In addition to pain, belching of air or food, nausea, vomiting (with pyloric ulceration), regurgitation, flatulence, and constipation are also characteristic.
With a peptic ulcer, bleeding, perforation into the abdominal cavity, or malignancy (cells degenerate into cancer) may occur.
Treatment involves following a gentle diet (table No. 2), giving up bad habits, and includes drug therapy. Excessive production of pepsin and hydrochloric acid is suppressed with the help of Atropine, Platiphylline, Metacin, Ranitidine, Omez. Helps normalize the evacuation function Motilium, Cerucal.
Bismuth-based preparations (De-nol) will protect the gastric mucosa. To destroy Helicobacter, you need to take an antibiotic. Venter, Methyluracil, Solcoseryl will speed up the process of cell regeneration. If your stomach begins to hurt severely, while the muscles are tense and gases do not pass away, then it is likely that this is a perforation of the ulcer. This condition requires urgent surgical intervention.
Pain and its causes
Pain on the left side under the ribs occurs quite often, and many people mistake it for heart problems. Only a doctor can accurately determine what hurts in the left side below the ribs, after a diagnosis. Discomfort in this area can be a harbinger of serious problems with various systems and organs. On the left, below the ribs, there are: vessels, nerve endings, lymph nodes, muscles, spleen, part of the pleura, left kidney, stomach. Pain in this area can be caused by pathologies of these organs, or radiate from some other ailments.
Cardiomyopathy
It is often a consequence of previous tonsillitis, tonsillitis and other infections. With cardiomyopathy in the left side under the ribs, pain is felt constantly, but rather weak. The manifestations of pain intensify during physical activity. At the same time, a rapid, erratic pulse is recorded, and the patient experiences severe fatigue.
Heart diseases
With diseases of the heart and vascular system, and in particular with vegetative-vascular dystonia and angina, pain also occurs in the left hypochondrium region. In the case of dystonia, this is due to a violation of the mechanism for maintaining the tone of blood vessels, and in the case of angina pectoris, heart pain is radiated to this area.
The nature of the pain in these cases can be dull, stabbing, or aching. Patients usually find it difficult to describe such phenomena, because they can be both prolonged and paroxysmal with unclear localization. When conducting research, typical diseases of the organs located in this area of the hypochondrium are not detected and the person is sent for examination to a cardiologist or neurologist.
Respiratory pathologies
The front left hypochondrium hurts with any pathology of the respiratory organs: pneumonia, pleurisy, pneumonia, bronchitis. At the initial clinical stage, the pain is weak and radiates throughout the body - to the chest, back, shoulder and even the right side. But the characteristic signs will be: fever accompanying the pain, a feeling of weakness, pain when exhaling in the back (pneumonia) or when inhaling (pleurisy), cough, sweating, constricted, too frequent and shallow breathing.
Umbilical hernia
With this pathology, the pain is not immediately under the rib in the depths, but in front closer to the waist. The pain is pulling downwards, quite intense, almost constant. They can continue even if the patient is in a supine position, subsiding slightly only when lying on his back.
Gastritis
Here, a pulling subcostal pain is necessarily accompanied by a feeling that the stomach is swelling from the inside, it is bursting. The pain is accompanied by heartburn immediately after eating and belching some time later. There is also a feeling of heaviness in the epigastrium, and there may be a urge to vomit. In this case, a bad odor emanates from the mouth, and the patient may experience an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
Peptic ulcer
A gastric ulcer is manifested by a nagging pain on the left side, which appears and intensifies after eating. Accompanied by heartburn. Often the symptom is belching with a sour taste. The patient loses weight and almost constantly experiences nausea or vomiting after eating.
By the way. A duodenal ulcer is different in that pain in the left hypochondrium occurs with this disease not on a full stomach, but on an empty stomach - on an empty stomach. Then, if the patient eats something, even in small quantities, the pain goes away.
When any type of ulcer is perforated, the pain acquires a cutting, dagger-like character. The patient bends in half, the skin rapidly turns pale, loss of consciousness may occur and vomiting of a substance resembling coffee grounds may occur.
Stomach cancer
With diseases of the heart and vascular system, and in particular with vegetative-vascular dystonia and angina, pain also occurs in the left hypochondrium region. In the case of dystonia, this is due to a violation of the mechanism for maintaining the tone of blood vessels, and in the case of angina pectoris, heart pain is radiated to this area.
The nature of the pain in these cases can be dull, stabbing, or aching. Patients usually find it difficult to describe such phenomena, because they can be both prolonged and paroxysmal with unclear localization. When conducting research, typical diseases of the organs located in this area of the hypochondrium are not detected and the person is sent for examination to a cardiologist or neurologist.
Splenomegaly
In pathological conditions of the spleen, the pain is dull, but pulsating and localized strictly under the left rib. The causes of spleen pathologies can be ruptures and injuries, organ enlargement, and abscess. The pain is accompanied by fever and weakness, enlarged liver, migraine and sweating.
Diaphragmatic hernia
Directly under the ribs on the left, there is a constant discomfort in the form of prolonged dull pain. They radiate to the shoulder area and are often found in the back (shoot through). All this goes away with belching, sometimes accompanied by heartburn. Even with the slightest exertion, the pain can increase significantly. With obesity, pain is much stronger.
Intercostal neuralgia
With this diagnosis, pain can be localized both in front under the ribs and behind, in depth. The pain varies in nature (depending on the nature of the neuralgia). It can be dull and aching or sharp and burning. Piercing pain may occur when exhaling, sudden movements, exertion, at any time of the day or night. A feeling of numbness at the painful point occurs after an attack of pain
Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis occurs with pronounced pain in the left hypochondrium or surrounding the entire body, accompanied by severe nausea. Vomiting does not bring relief, the patient loses appetite and complains of headache. Chronic pancreatitis without exacerbation does not have such a pronounced clinical picture; the symptoms of exacerbation resemble acute pancreatitis.
Cholecystitis
Dull, constant pain in the left hypochondrium. Localization is diffuse, periodically intensifies, and is present in the background. This may be a symptom of chronic cholecystitis. When the pain becomes cutting in nature, the disease takes on an acute form.
Colitis
Accompanied by stool disorders - prolonged diarrhea with a high frequency of bowel movements and tenesmus (false urge to defecate). The pain is paroxysmal in nature.
Pancreatitis
It hurts most often under the left rib due to inflammation of the tail of the pancreas. Due to the disruption of the release of enzymes as a result of blockage, the process of self-digestion begins in the gland, which leads to severe pain. The amount of enzymes increases after eating, and accordingly, pain increases during this period. In acute pancreatitis, the pain gradually intensifies.
Pancreatitis develops as a result of:
- chronic alcoholism;
- autoimmune diseases (immune cells recognize body cells as foreign and attack them);
- parasite penetration;
- metabolic disorders (the walls of blood vessels narrow due to the deposition of lipids on them);
- long-term hormonal therapy;
- exposure to viral infection (mycoplasma, hepatitis, mumps).
Signs of pancreatitis are:
- abdominal pain when palpated and after eating;
- nausea, vomiting;
- foamy stools, there is pain during bowel movements;
- cardiopalmus;
- dyspnea;
- weight loss.
The diagnosis is confirmed by ultrasound examination. In acute pancreatitis, fasting is indicated for 3–5 days to ensure functional rest for the organ. In some cases, intravenous nutrition is prescribed. Then the patient is recommended to adhere to a strict diet (table No. 5 P) for 2–4 months.
Antispasmodics and a cold compress will help relieve pain. For pancreatitis, conservative therapy is prescribed, and in case of blockage of the bile duct with a stone, surgical treatment is prescribed. The patient is prescribed antispasmodics (No-spa, Drotaverine) to relieve pain, diuretics (Furosemide, Diacarb) to remove toxins and relieve swelling of the gland, enzyme inhibitors (Kontrikal, Gordox), antibiotics for purulent infections, vitamins (groups B, C, E , A).
What to do for pain in the left side
In most cases, medical consultation is necessary, in some cases immediate hospitalization is necessary, and only in some painful episodes nothing can be done; it is enough to remove the factor that provokes the pain.
When you don't need to see a doctor
The mildest episodes that do not require medical intervention include:
- sudden physical activity;
- eating disorder;
- binge eating;
- taking alcohol or certain medications (non-steroids and other drugs).
If you overate and drank a lot of alcohol at night, abruptly started a workout without warming up, went for a run too fast, and all this (or one thing) caused pain in the left side below the ribs in front, after eliminating the factor that caused the pain, it will disappear.
When to visit a doctor
But there are a number of cases when the appearance of pain requires consulting a doctor.
- If you feel pain frequently.
- If pain negatively affects your vital activity, it prevents you from living and working fully.
- If there is a decrease in appetite and weight.
- With changes in bowel function.
- When the pain reaches high intensity, especially at night.
- If there is a history of intestinal inflammatory diseases.
- If you are constantly taking aspirin and non-steroids.
- If you are a woman between 20 and 40 years old and suffer from autonomic disorders.
First aid for pain in the lower ribs
Treatment depends on how severe the symptoms are. Patients who are aware of their existing diseases should also know how to eliminate the pain that occurs. Self-medication can distort the symptoms of the disease and complicate its course, which can lead to dire consequences. You need to see a doctor and get examined.
It is strictly forbidden to heat the area where the pain occurs; you can only apply a little cold. You should also not take antispasmodics, because numbing the pain will make it difficult to diagnose the disease. The need to call an ambulance may arise in the following cases:
- Sharp pain that suddenly appeared.
- Dull pain, accompanied by coughing and vomiting blood.
- When the aching sensation does not go away within an hour.
- If the stabbing pain does not subside within 30 minutes, but, on the contrary, may intensify with a change in position.
Table. The intensity of pain development in various diseases.
| Intensity and nature of pain | Cause (disease) |
| They appear instantly, are painful and intense in nature. | Rupture of an aneurysm, movement of gallstones or kidney stones, heart attack, perforation of an ulcer. |
| They appear quickly, within a few minutes, grow, and are permanent. | Intestinal obstruction (complete), vascular thrombosis, exacerbation of pancreatitis. |
| Gradual onset, intensifying over several hours. | Exacerbation of cholecystitis, appendicitis, diverticulitis. |
| Intermittent pain, intermittent, colicky, prolonged. | Obstruction of the small intestine, early stage of exacerbation of pancreatitis. |
Dangerous accompanying symptoms
If acute hypochondrial pain occurs on the front left side, which is accompanied by the following accompanying symptoms, urgent surgical intervention may be required.
- Dizziness, severe weakness, apathetic state.
- Detection of bleeding.
- Arterial hypotension.
- Feverish condition.
- Tachycardia.
- Continuous vomiting.
- Increasing abdominal pain.
- Increasing bloating.
- No passing of gas.
- Overstrain of the abdominal muscles.
- Painful bowel movement.
- Fainting during defecation.
How can exercise therapy help?
When your left back hurts after training or hard physical work, this indicates severe overwork and unpreparedness. It is necessary to reduce the intensity of the exercise to a suitable level. A set of exercises to relieve pain:
- Bring your shoulder blades together and apart;
- Clutching hands behind the back;
- Circular movements of the shoulder blades.
If your lower back hurts, you need to get down on all fours and bend towards the floor without making sudden movements. Next, they round and bend their back, stretching their arms forward. The training is repeated 2-3 times. Protect yourself from overwork and excessive stress, this negatively affects the health of the musculoskeletal system and leads to various diseases of the spine.
Pain under the ribs in the left side occurs in acute and chronic diseases of internal organs, nerves, and muscles. In the projection of the left hypochondrium are the spleen, the left flexure of the colon, the fundus of the stomach, the tail of the pancreas, the left part of the dome of the diaphragm, intercostal nerves, the lower lobe of the left lung and the pleura. The nature of the pain syndrome helps to distinguish one disease from another, prescribe a diagnostic examination and determine treatment tactics.
What to do if it hurts?
Even if you experience pain in the front, quickly passing on the left under the ribs, below, in the navel or in the center, which is accompanied by a burning sensation, vomiting, fever, you need to call an ambulance. As an immediate first step, you can help the person lie down on the bed and open the window and door to increase access to fresh air. It is prohibited to self-administer medications that may complicate the determination of the root cause of the disease. The following doctors can diagnose and prescribe treatment in case of pain under the left rib:
- traumatologist;
- gastroenterologist;
- surgeon;
- neurologist;
- infectious disease specialist;
- cardiologist.