Physiological causes of rumbling
The rumbling in the stomach can be very strong if it is associated with a feeling of hunger. Some people experience painful sensations, and with pathologies of the stomach and pancreas, this pain becomes almost unbearable and goes away as soon as you eat a little. Seething is also possible as a result of other deviations:
- Overeating - the noise becomes loud due to the long and intense process of digesting food. If a person has not eaten for a long time and then eats too much food, the sounds become louder and additional discomfort appears.
- Abuse of sugar and fatty foods - when eating sweets, fermentation processes are activated, and fatty foods have a bad effect on overall digestion.
- Emotional stress - the body of some people reacts with strong rumbling to shocks, experiences and stress.
- Carbonated drinks, beer and other alcohol - this liquid can cause intense rumbling and even pain, and also lead to the development of gastritis and other gastrointestinal diseases.
- A sudden change of position, a long stay in the wrong position - many have noticed that sleeping in an uncomfortable position sometimes leads to pain in the intestines. In addition to pain, rumbling may also appear.
The symptoms themselves in these conditions are not dangerous to the body. However, alcohol, soda, and constant overeating over time lead to the development of dangerous diseases: gastritis, dysbacteriosis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis and even intestinal obstruction.
Constant rumbling and flatulence
Constant rumbling often occurs due to the consumption of harmful, stale or low-quality food containing palm oil, preservatives, and chemical additives. Acidic and fatty foods can also provoke unpleasant symptoms.
The situation gets worse if a person consumes a lot of simple carbohydrates. Similar symptoms appear in those who chew food poorly, eat in a hurry or on the run. Most often, people who eat fast food and talk while eating suffer from constant rumbling. The accumulation of gases increases if a person suffers from chronic constipation.
Seething can be triggered by eating certain foods that are quite healthy, but not consumed correctly:
- watermelon seeds;
- seeds from other fruits, berries and vegetables;
- other foreign objects that our body is not able to digest.
Constantly gurgling under the diaphragm on the left is not only due to poor quality nutrition. Dysbacteriosis and the proliferation of pathogenic flora are dangerous causes of unpleasant symptoms. These disorders can be provoked by taking antibiotics and other drugs.
Answer:
Greetings! I cannot advise on treatment. This is done by a gastroenterologist. My specialty is endoscopist, a doctor who conducts endoscopic examinations. He sees changes in the mucous membrane inside organs and can interpret them. The endoscopist must also know the morphology, i.e. biopsy results. These doctors do not have the right to provide treatment, especially remotely. Therefore, I can only analyze the gastroscopy protocol and the biopsy result.
According to the presented gastroscopy protocol, the doctor did not describe any visual data for Barrett’s esophagus. A thickened fold was recorded, but its dimensions, mucosal pattern and vascular pattern on the surface were not indicated. It is also necessary to know at what distance from the incisors the cardia, proximal folds of the stomach and the dentate line itself are located. This information is not included in the protocol. At the time of examination, there is bile reflux in the lumen of the stomach, which may cause irritation and inflammation of this thickened fold. According to the results of the biopsy, there is an adenomatous structure, which is not a sign of Barrett's esophagus. The hallmark of Barrett's esophagus today is the presence of columnar epithelium (which includes the adenomatous structure) and intestinal metaplasia (cells characteristic of the intestine) in the esophagus at a distance above 1 cm from the dentate line. You do not have clear indications of where the process is located (above 1 cm or below the dentate line, the material was generally taken) and there is no intestinal metaplasia as a result of histology. I conclude that there is not enough data for Barrett's esophagus.
Regarding colonoscopy. If clinicians cannot cope with your diarrhea, then performing a colonoscopy is obvious! But - with a mandatory examination of the terminal ileum and performing a biopsy from its mucosa, at least 5 pieces.
print version
Rumbling in the left side
The stomach and large intestine are located on the left, so seething indicates increased peristalsis in these sections. The symptom appears if the food bolus moves through the gastrointestinal tract too quickly. Indicates such movement and diarrhea, the cause of which may be:
- infectious gastroenteritis and chemical irritation of the digestive system;
- severe stress, allergies or other emotions;
- irritable bowel syndrome.
With IBS, the clinical picture is extensive, but there are no problems with the digestive organs.
Causes of pain in the intestines on the right and left lower abdomen
Experts identify several reasons that could cause pain in the intestines on the left and right side of the lower abdomen.
- Problems of the small intestine.
If the patient feels severe pain in the lower right abdomen, then these symptoms indicate problems with the small intestine. They can be caused by metabolic disorders, microflora, poor diet, long-term use of medications, and alcohol. Pain may indicate the development of dangerous diseases - enteritis, cancer, celiac disease, dyskinesia, ischemia, dysbacteriosis, the appearance of neoplasms, ulcers, polyps, cracks.
- Overeating food.
If a few minutes after eating any food a person begins to belch, acute pain in the intestines in the lower abdomen, these symptoms indicate a weakness of the digestive process. Stomach pain and gastrointestinal disorders are associated with low acidity. The human body does not have enough gastric juice. As a result, the body does not properly digest food, which over time begins to ferment and cause pain.
- Severe stress.
Cutting pain in the lower abdomen may be associated with problems of the nervous system. Nervous tension causes the body to produce nonspecific ulcerative colitis. The pain goes away after a few days. If a person does not feel improvement, the disease enters the chronic stage.
- Pain in the intestines on the right and left lower abdomen in women is associated with the genital tract.
During menstruation, blood flow into the pelvis increases, so this process is accompanied by pain.
- This can provoke stagnation in girls who are prone to developing varicose veins.
Pain in the intestines can appear with decreased vascular tone and observed weakness of connective tissue. The patient begins to experience painful sensations, pain during bowel movements, an increase in the size of hemorrhoids, and gastrointestinal disorders.
- Diverticulitis.
The disease is accompanied by painful sensations in the intestines in the lower abdomen. Diverticulitis occurs due to inflammation in areas of protrusion of the colon. Painful sensations occur when feces and food stagnate in these areas.
- The appearance of neoplasms.
The appearance of tumors in the human body is accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen on the left and right. The pain syndrome increases with changes in the size of the tumor.
- Irritable bowel syndrome.
Irritable bowel syndrome is characterized by severe acute pain in the lower abdomen, and the patient has no appetite. This disease is accompanied by gastrointestinal disorders, diarrhea and constipation, diarrhea, and flatulence. Sometimes the patient notices weakness, an increase in the size of the abdomen, bloating and discomfort in the intestinal area.
- Problems with the genitourinary system
Stitching pains in the lower abdomen on the left and right indicate problems with the kidneys and bladder. The patient should visit a urologist and get tested.
- Pregnancy.
In pregnant women, the size of the uterus increases. This process can affect the appearance of pain in the intestines in the lower abdomen. The enlarged uterus puts pressure on the intestinal walls, which can be accompanied by severe cutting pain, nausea, vomiting and flatulence.
- Pancreatitis.
The next cause, which is characterized by pain in the intestines in the lower abdomen and nausea, is pancreatitis. With pancreatitis, the patient experiences severe cutting pain in the upper abdomen. In some cases, the size of the abdomen increases. Gastrointestinal disorders, including constipation, accompany pancreatitis.
- Duodenal ulcer.
With a duodenal ulcer, the patient is bothered by severe sharp pain in the intestines in the lower abdomen. They are accompanied by vomiting and upset.
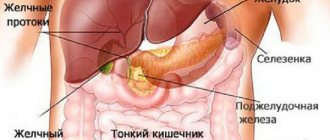
Bubbling in the right side
The intestines are partially located on the right, as well as the gallbladder and liver. If it boils in the right hypochondrium, this indicates problems in the small intestine, as well as dysbiosis in the large intestine. Among the symptoms that confirm the presence of pathology:
- chronic constipation or diarrhea;
- constant soreness and bloating;
- Urge to go to the toilet immediately after eating.
Rumbling can be caused by reflux gastritis. A chronic ulcer can also cause bubbling in the right area, but much less frequently. Because of the liver, seething cannot appear, unless the pathology is associated with impaired outflow of bile.
Why does my left side hurt under my ribs?
Pain in the left side is characteristic of diseases of the abdominal organs. Sometimes there are cases when the cause of pain can be pathologies of the lungs, heart and neuralgia. To identify the exact cause, instrumental diagnostics are used using ultrasound, x-rays and radio wave studies. Depending on the cause of the pain in the left side, appropriate treatment is prescribed. Below, we will talk in detail about the most common pathologies that cause pain. But you should understand that self-diagnosis and self-medication will most likely only worsen the condition, so you should contact a qualified specialist for help as soon as possible.
- Diseases of the spleen.
The spleen is a hematopoietic organ. Inflammation is characterized by a rapid increase in size of the spleen (splenomegaly), and with injuries there is a high risk of rupture of the organ capsule with heavy bleeding. Diseases of the organ are characterized by bursting, pressing pain in the left hypochondrium, which does not depend on physical activity and food intake. - Intestinal diseases.
Pathology of the small intestine leads to visceral or referred pain in the left side. A tumor of the left colon in the later stages of the disease causes aching pain that intensifies 2-3 hours after eating. The pain syndrome occurs against a background of weakness, weight loss, and aversion to food. - Stomach diseases.
Gastritis and gastric ulcer cause pain in the epigastric region and in the left hypochondrium. In the case of gastritis, the pain is stabbing, drilling, shooting, and intensifies after eating spicy and fatty foods. Characterized by a feeling of heaviness in the stomach, belching rotten or sour, heartburn, nausea. - Diseases of the pancreas.
Inflammation of the pancreas is called pancreatitis. Chronic pancreatitis causes indigestion and periodic pain in the left side. Characterized by diarrhea, greasy stools with lumps of undigested food, and flatulence. Pain of a stabbing, bursting, shooting nature occurs 1-1.5 hours after eating. Often the pain syndrome becomes girdling - spasmodic pain compresses the left and right hypochondrium in a “ring”. - Muscle disease.
Muscle inflammation - myositis can be accompanied by pain in the left side. The pain syndrome is shooting and cramping, intensifies when muscle fibers are stretched while bending in the opposite direction. Dull or burning pain develops when food passes through the esophagus and bends the body after eating. - Intercostal neuralgia.
Inflammation of the intercostal nerves is commonly called intercostal neuralgia. In most clinical cases, the disease develops with herpes zoster. An acute burning pain occurs, which is localized in the left hypochondrium and can spread to the back in the area of the shoulder blades and spine. Discomfort increases when bending towards the affected side. - Disease of the left lung.
Pain in the left side may appear with left-sided lower lobe pneumonia involving the pleura in the pathological process. There is a cutting, stabbing, boring pain in the left hypochondrium, which intensifies at the height of inspiration. Pneumonia is characterized by an increase in temperature up to 40 degrees, shortness of breath, weakness, dry or productive cough, wheezing when listening to breathing. - Heart diseases.
During myocardial infarction, pain occurs in the left half of the chest, between the shoulder blades, and radiates to the arm on the affected side. The atypical course of the disease leads to referred pain in the left hypochondrium. If pain occurs in the left hypochondrium, you should consult a doctor for examination and treatment. Timely consultation with a specialist reduces the risk of disease progression and complications.
Causes of rumbling and frequent diarrhea
Rumbling practically cannot occur in the stomach; most often it is localized in different parts of the intestine. When regular diarrhea occurs, we can safely say that dysbacteriosis develops. Especially if a person is addicted to fast food or is forced to take antibiotics or other potent drugs.
Dysbacteriosis is a disorder of microflora, which can only be restored by a strict diet and taking vitamins, as well as probiotics.
The second common cause is food infection. It often occurs in the summer due to the consumption of unwashed fruits and vegetables, berries, spoiled dairy products, and insufficiently processed meat.
Rumbling during pregnancy
Constant seething develops in women after the 2nd trimester, which is associated with stretching of the uterus and compression of the stomach, intestines and other organs. Seething may also appear as a result of complications of chronic gastrointestinal diseases, so if they are present, it is important to regularly monitor the condition and consult a doctor at the first sign of exacerbation.
Sometimes the seething, even in the first stages, is caused by a change in diet and a desire to eat incompatible foods. Since women during pregnancy tend to experience an increased appetite and eat whatever is at hand, indigestion occurs often. Elevated hormone levels only worsen the situation, causing gas formation.
Diagnostic methods
To detect a condition that can provoke constant seething with additional unpleasant symptoms in the form of belching or flatulence, a full diagnosis is required:
- testing stool for dysbacteriosis, parasites, bacteria;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- examination of the intestines using a probe;
- FGDS for examination of the stomach.
If doctors are unable to detect the cause of rumbling and seething in the left or right side, additional examination methods are prescribed, including CT or MRI with a contrast agent.
Ways to eliminate rumbling
The easiest way to get rid of annoying symptoms is if their cause is discovered. Other methods give only temporary results. If boiling occurs in response to overeating or eating poorly tolerated food, you can take tablets to remove gases:
- Motilium is used to improve intestinal motility.
- Espumisan is a carminative that removes excess gases.
- "Linex" is a probiotic that normalizes the state of intestinal microflora.
The doctor will select other drugs if they are needed to treat a particular disease.
In the treatment of boiling caused by pathologies of the intestines and stomach, proper nutrition is of particular importance. Only a rational diet can relieve unpleasant symptoms and even completely cure the patient from the disease.
Various gastrointestinal diseases can provoke rumbling in the hypochondrium, but they all require careful attention, correct diagnosis and strict treatment. Without making a diagnosis, you should not treat disorders yourself - this can lead to complications.
What to do if your stomach growls?
To stop the rumbling, they use medicines and folk remedies, and be sure to prescribe a diet.
Eating for stomach turmoil
Prescribing your own diet is not only ineffective but also dangerous, but you can develop good eating habits that will help you avoid stomach discomfort.
Nutrition rules:
- Follow the regime, eat 4-6 times a day, have dinner 2-3 hours before bedtime, do not overeat.
- Eat slowly, chew your food well, and do not be distracted by conversations or other activities while eating.
- Drink at least 8 glasses of water a day, and keep the number of caffeinated drinks to a minimum.
- Avoid eating fatty foods and sweets.
- If you do not have allergies or intolerance to milk sugar, include cottage cheese, natural yogurt, kefir in your daily diet, and choose products of medium fat content.
Products that provoke increased gas formation are all types of legumes, vegetables and cabbage, mushrooms, root vegetables, yeast baked goods, whole milk, avocados, bananas.
Treatment with drugs
Properly selected drug therapy can eliminate abdominal discomfort and the causes of its occurrence.
The stomach makes strange sounds - how to treat:
- probiotics – Acipol, Hilak forte, restore the balance of intestinal microflora in case of dysbacteriosis;
- nitrofurans – Furazolidone, Nifuroxazide, eliminate intestinal infectious pathologies;
- The carminative drug – Espumisan, after taking the tablets the gas bubbles burst, flatulence and rumbling go away, the medicine can be taken during pregnancy, the drug in the form of a suspension is safe for infants;
- enzymes - Creon, Orlix, improve the process of digestion and breakdown of complex substances;
- drugs to improve motor skills - Motilium, Motilak.
The most popular remedy for eliminating rumbling is activated carbon and other enterosorbents. These drugs eliminate all harmful substances in the stomach, but they must be taken separately from other drugs because they absorb everything that is in the stomach and intestines.
How to get rid of the problem using folk remedies?
Alternative medicine eliminates disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract; rumbling and discomfort will bother you much less frequently.
Seething in the stomach - traditional methods of treatment:
- Brew 1 tsp. dry crushed chamomile inflorescences 270 ml of boiling water, leave in a closed container for half an hour, filter. Take 120 ml three times a day after meals. The drink eliminates inflammatory processes, flatulence, bloating, and normalizes peristalsis.
- Pour in 1 tsp. dill seeds 220 ml of boiling water, leave in a sealed container for 2 hours, filter. Drink the entire infusion in small portions throughout the day. This remedy quickly eliminates increased gas formation.
- For severe flatulence, add 1 tsp. chopped parsley root 220 ml of cold water, after 20 minutes heat, but do not bring to a boil, strain. Drink the drink in small portions throughout the day.
- Peppermint tea eliminates nausea, pain and abdominal cramps, and has a mild anti-inflammatory and sedative effect. Pour 220 ml of boiling water over 5-10 fresh or dried leaves, strain after 10 minutes. Drink a drink instead of tea.
- Brew 1 tbsp. l. crushed wormwood 500 ml boiling water, leave for 24 hours, strain. Drink 35-45 ml in the morning before breakfast, you can add a little honey to improve the taste.
To avoid problems with peristalsis, exercise regularly and do exercises to strengthen your muscles. Swimming has a good effect on the functioning of the digestive system.