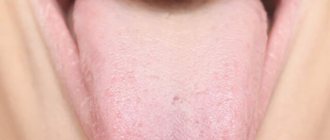
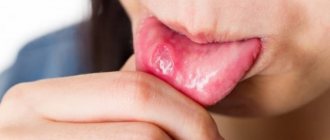
The tongue has several functions in our bodies. There are thousands of taste buds on its surface, thanks to which we recognize the taste and aroma of food. But above all, it is a strong muscle with which we can speak and swallow. A healthy tongue is pink, almost smooth and elastic, and touching it should not cause pain. But if something is wrong in the body, the appearance of this muscle also changes.
What can you tell by the appearance of your tongue?
In traditional medicine, the phrase: “Show your tongue!” is usually said by a therapist and an otolaryngologist who want to examine a patient’s throat. But in Chinese traditional medicine, for more than a millennium, doctors have been diagnosing a person’s health condition by his tongue. But for maximum accuracy of diagnosis, it is recommended to examine the muscle in the morning, in good lighting, and preferably before eating and brushing your teeth.
It is interesting that even before examining the pattern on the surface of the organ, experts even pay attention to how the patient opens his mouth.
Content:
- What can you tell by the appearance of your tongue?
- Surface structure
- Color
- Plaque and possible diseases
- If your tongue hurts or burns
- What does tongue size tell you?
- What about your taste buds?
- Effect of medications on the appearance of the tongue
For example, if a person does this timidly and shows only part of his tongue, as if embarrassed, to Chinese healers this fact indicates a lack of vitality. If the patient sticks out his tongue, tilting its tip to one side, this can be perceived as a signal that there are problems on that side of the body.
According to Eastern medicine, any changes in individual parts of the organ are not an accident. The Chinese even developed a map of the relationship between individual parts of the tongue and internal organs. So, according to this theory, the language is usually divided into 5 functional zones.
Tip
This part is a “mirror” of the state of organs such as the heart and small intestine. In addition, redness on the tip of the tongue or bright spots on it may indicate anxiety or stress.
Piece by tip
By studying the state of this zone, we can draw a conclusion about the normal functioning of the respiratory and immune systems. Changes in this area may indicate bronchitis, tuberculosis, pneumonia or emphysema.
Center
The middle part of the tongue informs about the functioning of the digestive system, in particular the stomach, pancreas and spleen. Redness or yellow spots in this area indicate gastrointestinal diseases. Any changes in the central part may also be a sign of problems with stool: diarrhea or constipation.
Right and left side
These areas reflect the condition of the liver. If the sides of the tongue are swollen, this may be a signal of hepatitis or fatty liver disease. Sometimes such changes appear in people with diabetes or flatulence. Dark spots around the edges sometimes appear in the presence of cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Back (back)
Any changes in this area may indicate renal failure, bladder dysfunction, dysfunction of the gonads, or disruptions in the endocrine system. In particular, a yellow coating on the back may indicate an infectious disease of the bladder, other changes may indicate urethritis or kidney disease.
Treatment of plaque on the tongue
Protein deposits that appear on the tongue make it possible to promptly identify the pathological process and begin treatment. Plaque is not a diagnostic tool, but helps facilitate diagnosis. When examining the oral cavity, the doctor pays attention to the location, color and consistency of the formed layer, therefore he builds a plan for the examination and further treatment measures taking into account these factors.
The treatment plan depends on the nature of the plaque and the factors that triggered its development. Physiological deposits do not require medical intervention, since they are not concomitant signs of certain pathologies. The condition can be controlled by preventive measures, which include careful oral hygiene and the exclusion of coloring products.
Types of therapeutic measures
Treatment of pathological plaque depends on the etiology and pathogenesis of the provoking disease. There are several types of treatment for protein deposits formed on the tongue due to diseases:
- Antibacterial therapy
. If plaque is of bacterial origin or diseases that provoke its appearance, a course of antibiotics or antimicrobial drugs is prescribed. - Dietary food
. For diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, hepatobiliary tract and urinary system, therapeutic nutrition must be included in the therapeutic plan. Diets minimize the harmful effects of certain food groups and promote rapid recovery of the body.
Depending on the nature and characteristics of the disease, symptomatic treatment is carried out. Therapeutic measures are aimed at stopping the underlying disease and restoring normal functional activity of organs.
In case of insufficient effectiveness of drug therapy, surgical operations are required. Surgical intervention in the presence of tumors, perforated ulcers, staghorn stones and other complex pathologies is aimed at quickly relieving symptoms. As a result of successful treatment, the condition of the mucous membrane of the tongue returns to normal.
Surface structure
If cracks have formed on the surface of the tongue, this usually indicates dehydration and excessive blood thickening, which, in turn, increases the risk of stroke or thrombosis. Also, a dry surface with numerous small cracks is one of the symptoms of diabetes. But depending on their location, cracks can indicate different diseases. For example, one deep one in the middle of the tongue can be a symptom of an upset digestive system and high acidity in the stomach.
A spotted or raised tongue may indicate that a person has fungal infections, vitamin deficiency or allergies.
Sometimes such changes appear in people with vitiligo or psoriasis. But if a curved line is clearly visible on the surface, then the musculoskeletal system should be checked; this may be a signal of a spinal disease.
Color
A healthy person's tongue should be slightly pink. Any changes in color can be regarded as a signal of health problems.
Crimson or violet-tinged
The tongue may acquire this color due to an excessive increase in body temperature caused by inflammation or an infectious disease. Blueness of the tongue often indicates hypoxia (impaired blood supply), and a purple tint sometimes appears after eating too spicy foods.
Scarlet
In people who have a poor diet or are obese, the middle part of the tongue may be bright red. Similar symptoms appear with gallbladder diseases or blood stagnation. If redness is visible on the tip of the tongue, this may be a sign of chronic stress, cardiac disorders, or insomnia and neuroses. If the tip of the tongue is bright red and slightly swollen, there is reason to believe that the person is suffering from coronary heart disease. Additionally, red spots on the surface may be a sign of B vitamin deficiency.
If the tongue is not just bright red, but also completely smooth, this indicates liver disease, toxin poisoning, as well as a lack of vitamin B12 and iron, since this mineral is necessary for the formation of papillae on its surface. By the way, this type of tongue can be seen in vegetarians. But if a person eats a more or less balanced diet, but his body still lacks vitamins, perhaps the reason is an autoimmune disease, due to which nutrients are not absorbed. And this can also be suspected by the unnaturally red and smooth tongue. In some cases, a smooth, very red surface may be the result of a burn or overuse of hot spices. Red spots on an unnaturally pale surface are a signal of disturbances in the respiratory system. A scarlet and grainy tongue most often indicates scarlet fever.
Very pale, almost white
Such an anomaly may indicate several serious diseases. The tongue turns pale at very low body temperatures, due to anemia, a weakened heart, or when the immune system is impaired.
Black
A very dark, almost black tongue always indicates kidney dysfunction. In addition, it does not matter in which particular zone the dark spots appeared, although most often in such cases the base of the tongue turns black.
White spots on the mucous membrane
Sometimes painless white spots may form on the tongue (bottom or along the edges). Medically they are known as leukoplakia. They are formed as a result of excessive cell growth. Smokers often have such spots. And in this case, this is a very alarming signal. Leukoplakia is called a precancerous condition. Between 5 and 17% of people with these spots eventually develop cancer. However, if you quit smoking in time, the spots will disappear. If such spots appear in non-smokers, then perhaps their cause is banal rubbing of the tongue by the teeth. But if leukoplakia does not go away, you should consult a dentist to solve the problem.
Prevention of tongue diseases
To reduce the risk of diseases of the tongue itself and other organs, you need to monitor your diet, daily routine, and have less contact with infectious patients. Caring for the tongue itself should be no less thorough than caring for your teeth.
Accumulating plaque, especially in sick people, is a place for mass reproduction of bacteria and fungi. If it is not removed in time, it will become a source of infectious pathogens that can penetrate any part of the body.
When cleaning the oral cavity, it is useful to use toothbrushes with a ribbed back surface to clean the tongue from plaque, or special spoons and scrapers. But they must be used carefully so as not to damage the taste buds and mucous membrane. After cleaning, it is advisable to use pharmaceutical rinsing solutions or prepare homemade herbal decoctions.
Plaque and possible diseases
During normal functioning of the body, the human tongue is covered with a thin, loose layer of whitish plaque. If it changes color or thickness, this is already an alarming signal.
White
A dense white coating can appear as a result of hypothermia or a slowdown in metabolism (this often happens in the fall). If the plaque is uniform, but very thick, this indicates the presence of a bacterial infection in the body, and if it forms lumps, this is a signal of a fungal disease.
A thick layer of white plaque also occurs with chronic gastritis with high acidity or enterocolitis. With gastritis with low acidity, the plaque is not as thick and drier. It is also interesting that by the thick white coating on the tongue you can recognize those with a sweet tooth and lovers of dairy products.
Grey
Gray plaque is a sign of infectious diseases accompanied by fever. Also, a grayish coating may indicate diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or liver. In particular, the tongue may acquire a grayish tint during an exacerbation of peptic ulcer disease. If a gray coating appears in the company of small blisters on the tongue, the person may be suffering from herpes. A grayish coating can also signal that the body lacks iron.
Brown
Most often, a tongue with a dense brown coating can be seen in smokers. The same symptom indicates disturbances in the respiratory system, which can lead to hypoxia. Also, brown plaque is a signal of digestive problems.
Yellow
If such a plaque appears in a person in the summer, this may indicate overheating of the body. The surface of the tongue also turns yellow after drinking coffee or certain spices. In more serious cases, the appearance of yellow plaque indicates a gastric ulcer, malfunction of the pancreas or liver.
Greenish
Plaque with a green tint is a very alarming signal. As a rule, it warns of serious liver diseases, including the development of cancer.
Map of diseases of internal organs by language
Scientists believe that the tip of the tongue is connected to the heart, the central part - to the stomach and pancreas, the back part - to the kidneys, the right lobe of the tongue - to the spleen and right lung, the left - to the liver and left lung. If strong changes occur in any area, it means there are problems with one or another organ.
This map will help you identify tongue disease by color and location.
Redness:
- at the base - impaired renal function;
- in the middle - diseases of the colon;
- at the tip - problems with the cardiovascular system;
- front part - weak lungs, breathing problems;
- the central part is stomach diseases.
Small cracks located throughout the entire area of the mucosa appear with intestinal diseases.
Changes in the fold in the middle of the organ:
- transformation of shape - problems with the spinal column;
- deviation of the fold to the right - back pain;
- deviation to the left – displacement of the cervical vertebrae;
Trembling in the tongue may indicate severe stress or a disorder of the nervous system.
When diagnosing diseases by the color of the tongue, additional symptoms should be taken into account, since the same shade of the tongue characterizes both problems that do not require serious intervention and diseases that require immediate hospitalization.
If your tongue hurts or burns
In many cases, painful sensations in the tongue appear as a result of not following a balanced diet. In particular, pain can occur due to a lack of iron, vitamins B6, B3 (PP) and B12.
A burning sensation on the surface of the muscle may indicate that the stomach is producing too few digestive juices, so this symptom usually indicates a malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract.
Sometimes, if the tongue looks no different, but there is a burning sensation, this may indicate a hormonal imbalance. By the way, women experience this symptom almost 7 times more often than men. In addition, the burning sensation may be the result of an allergy to the wrong toothpaste.
What does a healthy tongue look like?
First, let's remind parents what a healthy tongue looks like. The following signs indicate the state of normality:
- the size is not increased;
- humidity is moderate;
- the color of the tongue is pale pink, without spots or grooves;
- sensitivity is normal, papillae are not enlarged;
- allow for a light coating that is easy to clean;
- There is no bad breath.
If, upon examination of the child, the condition of his tongue corresponds to the signs described above, there is no reason to worry and see a doctor.
What does tongue size tell you?
If we carry out diagnostics based on the appearance of the tongue, then experts also advise paying attention to its size. If it is excessively large and swollen (touches the corners of the mouth), you should check for problems with the heart, thyroid gland, spleen, kidneys.
The tongue increases in size with anemia, allergies, or if for some other reason the whole body swells in a person, as well as in people who are overly nervous. Swollen veins under the tip of the muscle may indicate heart failure.
If the tongue is smaller than normal size, then it is quite possible that the body is suffering from a deficiency of vitamins and minerals, and this may also be a symptom of a very weakened immune system.
What about your taste buds?
On the surface of the tongue there are thousands of small pimples - these are papillae. All of them can be divided into 6 groups, each of which plays its own role, including the ability to distinguish four basic tastes: sweet, salty, bitter and sour.
Interestingly, over time, taste buds “wear out,” but if a person is healthy, they are replaced by new “pimples.” At a young age, this process occurs quite quickly, and after 45 years, as a rule, it slows down.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Therefore, with age, a person ceases to distinguish tastes and aromas so keenly. But sometimes the inability to taste food is not just due to age. Loss of sensitivity in taste buds may be a symptom of a bacterial infection in the digestive tract or indicate problems with the pancreas.