Manifestations of neurotic encopresis, definition of encopresis
Neurotic encopresis manifests itself in the involuntary release of a small amount of feces in the absence of lesions of the spinal cord, as well as anomalies and other diseases of the lower intestine or anal sphincter. Nocturnal enuresis is 10 times less common. It is detected 5–10 times more often in boys than in girls. Often the causes of neurotic encopresis in children are prolonged emotional deprivation, too strict demands on the child, conflicts in the family, disagreements between mother and child. Perinatal encephalopathy and hypoxic brain damage are contributing factors in the development of encopresis.
The main symptoms of encopresis : a violation of the skill of neatness in the form of the appearance of a small amount of bowel movements in the absence of the urge to defecate. It is often accompanied by low mood, irritability, tearfulness, and neurotic enuresis.
General information
Stool in children is a pathological condition that manifests itself as involuntary defecation at the age of more than 4 years. In medical terminology, stool smearing is also called encopresis or fecal incontinence. The prevalence of this pathology among children, according to various sources, is 0.3-8%, and is more common in boys. Encopresis is characterized by a protracted or recurrent course, the reason for which is the parents’ failure to seek medical help in a timely manner, so this disease remains a pressing problem in modern pediatrics.
Stool stool in children, the causes of which are the absence or loss of the ability to control the excretion of feces or deliberate defecation in inappropriate places, may be a separate pathology or be a symptom of a mental and/or behavioral disorder in the child.
A child stains his panties with feces - what to do?
A child who previously had neat habits periodically during the day experiences a small amount of excrement on his underwear (the child stains his underpants with feces). More often, parents complain that the child only “slightly soils his pants”; in rare cases, copious bowel movements are detected (the child soils his panties). Usually the child does not feel the urge to defecate, at first does not notice the presence of bowel movements and only after some time does he feel an unpleasant odor. In most cases, children are painfully aware of their shortcomings, are ashamed of it, and try to hide soiled underwear from their parents. A peculiar personality reaction to encopresis may be the child’s excessive desire for cleanliness and neatness. The frequency of fecal incontinence may vary. The disorder is often persistent. In most cases, encopresis is combined with low mood, irritability, and tearfulness.
How to help your child solve a sensitive problem
If a child does not go to the toilet regularly for a psychological reason, you will have complex work with the participation of a gastroenterologist, a psychologist, establishing a diet and moderate physical activity.
Develop independence in the child. As we have already said, children with increased neuroticism are characterized by increased dependence on close people and manipulative interaction. You will have to work on developing independence skills. With minimal parental participation, the child must learn to do the simplest household chores: go to bed, clean up his room, provide all possible help around the house.
With minimal parental participation, the child must learn to do the simplest household chores: go to bed, clean up his room, provide all possible help around the house.
Increasing the level of independence activates the vegetative centers. In this way, the child will learn to take responsibility when faced with certain events, and will become more self-confident and calmer.
Engage in moderate physical activity. Physical activity is useful not only for good peristalsis, but also for the body’s correct response to the release of adrenaline. Sports clubs and sections, exercises in the morning, firstly, stabilize hormonal levels, and secondly, they teach our body to cope with increased hormone levels. Adrenaline is released during sports activities, and the body gradually learns to react to it without violent neurotic reactions.
Work on your diet. A set of products and dishes for a child should be selected together with a gastroenterologist. Fast food and products that can cause allergies can cause problems with the gastrointestinal tract. The increased load on the digestive system causes a somatic symptom - then the reflexes trigger the psychological component.
How to protect your child from eating disorders
React to the problem calmly. If relatives react to the situation too brightly, constantly asking why the child is suffering so much, this can increase neuroticism.
Bowel movement
Bowel emptying is carried out by the recto-anal zone. The urge to defecate appears when the pressure in the rectum reaches 40 mmHg. Sensitive receptors that perceive the filling of the rectum with feces are located in the ampulla of the rectum, in the area of the anal crypts and morganian ridges. The main function of the rectum is the accumulation, retention, and evacuation of feces. Holding provides control over the evacuation of intestinal contents and is carried out by the internal and external sphincters of the rectum and the levator ani muscle. In this case, the internal sphincter is passive and ensures closure of the walls of the anal canal. Active closure is carried out by the external sphincter.
Rectal function
The function of the obturator apparatus is regulated by the ganglion of the rectal wall and the inferior hypogastric plexus, the spinal center at the level of 2–4 sacral vertebrae, and the cerebral cortex.
When pressure in the rectum increases, impulses go to the cerebral cortex, from there through the spinal center they return to the external sphincter and levator muscle, giving a signal to contract the external sphincter and levator muscle. This ensures fecal retention.
Maintaining feces in the early stages of accumulation is a passive process. At the late stage, storage becomes active and retention is regulated by the cerebral cortex. Defecation normally occurs under conscious control.
In young children, neuro-reflex connections have not yet been established. The mechanism of their formation is developed gradually depending on the environment and the characteristics of the body. The skill of bowel movement begins to develop in the first months and is reinforced as a conditioned reflex for the time of day, sounds, and light stimuli. Conditioned reflex connections to the act of defecation are established from the second year. When creating conditioned reflexes to the act of defecation, they need to be regulated. It is necessary to inculcate the habit of daily morning bowel movement, as well as the habit of washing your face, brushing your teeth, and washing your hands before eating.
Classification
Depending on the time of occurrence, there are:
- Primary encopresis. Occurs when the skill of controlling bowel movements did not previously exist, that is, from birth the child does not have a conditioned reflex.
- Secondary encopresis. It is formed when the skill of normal regulation of bowel movements was previously present, but it has been lost.
Based on severity, fecal incontinence is classified into:
- I degree. Only gas incontinence is observed.
- II degree. Characterized by incontinence of gases and liquid feces.
- III degree. The child is unable to hold solid feces.
Based on the causes of occurrence, they are distinguished:
- Organic encopresis. It is observed against the background of various pathologies and diseases of the organs involved in the regulation and implementation of bowel movements.
- Functional encopresis. Occurs when it is not possible to identify the pathomorphological cause of the development of this condition.
Depending on the frequency of manifestation, encopresis occurs:
- frequent (1-3 times a day);
- moderate (up to several times a week);
- rare (appears several times a month);
- episodic (occurs no more than once a month).
Calomasia in children, the causes of which are functional disorders, is divided into:
- Non-retentional (true). It is not associated with fecal retention and is characterized by disruption of the cerebral cortex, resulting in involuntary bowel movement. Rarely seen.
- Retention (false). Characterized by fecal retention, observed in children who suffer from constipation and suppress the urge to defecate. It is a common form of this pathology.
- Mixed. Appears against the background of false smearing, as a secondary pathology.
Calomania
By 2–3 years of age, defecation in healthy children is conscious, volitional, and controlled. Children are clean and tidy. However, the parents of some children begin to notice that the child, who was previously clean, gets his panties dirty and dirty. The child develops stools . This greatly alarms some parents; others consider dirty panties to be a manifestation of the inability to properly perform hygiene skills after defecation; the child is often punished. This circumstance leads to untimely consultation with a doctor. Encopresis occurs when one of the chains of an already formed conditioned reflex arc breaks down.
True encopresis
The basis of fecal incontinence in true encopresis is inhibition of the defecation center in the cerebral cortex. The center's control over the perception of the urge to defecate and the opening of the anal sphincters is disrupted. True encopresis is observed much less frequently than false (paradoxical) encopresis, in only 5% of cases.
One of the reasons for true encopresis is stressful situations, the presence of constantly depressing impressions on the psyche in kindergarten, family, and school. Sometimes the parents of these children are divorced and pay little attention to raising the child. In children with true encopresis, astheno-neurotic syndrome is often detected. They had a history of hypoxia during intrauterine development (umbilical cord entanglement, gestosis, toxicosis, maternal anemia, birth trauma, threatened miscarriage); children were often born through cesarean section.
What does the patient need?
First, the patient needs help in relieving himself. It is necessary to provide the patient with a medical bed or disposable diapers. The container must be clean, so after each trip to the toilet the device is treated with antiseptics. Also, after physiological functions, it is necessary to carry out hygiene procedures to prevent the development of infection. Care for patients with fecal incontinence includes treatment of the primary disease. The doctor prescribes medications that normalize the functions of the gastrointestinal tract. The optimal diet is selected.
False encopresis
False encopresis (false - paradoxical - fecal incontinence) occurs when the rectum is overfilled with feces in children suffering from constipation. One of the causes of false encopresis is the systematic suppression of the reflex to void due to an unfavorable environment. The child deliberately suppresses the urge to defecate due to the fact that he cannot adapt to a public toilet (visiting a kindergarten, school). Most often, these children have an unstable emotional sphere.
Basic information
Fecal incontinence (encopresis) is characterized by a violation of conscious emptying of the rectum. The patient does not control the functioning of the sphincter, which is why defecation occurs at any time when the intestines are full. Encopresis is often accompanied by urinary incontinence, since control of all physiological processes is ensured by the nervous system. This condition reduces the patient's quality of life. The patient may be deprived of the ability to self-care due to a forced position or brain pathology. Outside help is required.
Older men and women suffer from encopresis due to age-related changes and chronic diseases. Typically, this complication appears at the age of 65-80 years. Care for patients with fecal incontinence can be easily organized at home if relatives are able to regularly monitor the patient and carry out hygiene procedures. In some cases, care is complicated by the general condition of the patient. Contacting a boarding house for the elderly helps solve the problem associated with immobility or dementia of the patient. This institution employs doctors, caregivers and nurses. Comfortable living conditions are provided.
Fear of defecation
Fear of defecation occurs with fissure, cryptitis, papillitis. Suppressing the urge to defecate leads to stool retention and rectal overflow. Its overstretching reduces the sensitivity of the receptors, which reduces the urge reflex. Feces are spontaneously released through the anus. In these cases, encopresis is preceded by constipation of psychological origin (psychogenic). One of the causes of false encopresis is intestinal infections suffered in infancy, which lead to degenerative changes in the intramural ganglia of the intestine. The latter are in an immature state at the time of birth and mature after birth.
Due to functional and later organic changes in the nerve cells of the rectal wall, the threshold of excitability of mechanoreceptors decreases. In such children, the sensitivity and reflex relationship of the rectum with its sphincter apparatus decreases. The rectum becomes full and the sphincter opens until the urge to defecate occurs. In this case, the cause of fecal incontinence is not dysfunction, but a decrease in the sensitivity of the rectal wall to increased pressure in it.
Symptoms of true encopresis
True encopresis ( fecal incontinence ) occurs against the background of regular, independent bowel movements. The main symptom is stool anointing. Spotting occurs during physical or mental stress, and often for no apparent reason. The majority of the disease develops gradually, slowly progressing. In rare cases, it occurs quickly and ends in a short time. The clinical picture and course depend on the cause, the degree of change in the neuropsychic sphere, and the duration of the disease. Over time, the volitional act of defecation decreases and then disappears altogether. The child constantly has dirty underwear (underpants), the perineum is covered in feces, skin irritation in the perianal area (near the anus, anus) is often observed, and there is an unpleasant odor (stinks). On digital examination, the rectum is of normal size, the sphincter tone is reduced. Sometimes encopresis is combined with enuresis.
What to look for if your child has a fear of going to the toilet
Other symptoms of neurosis. Parents may not pay attention, but if a child has difficulty going to the toilet due to a neurotic condition, he will also have other manifestations: increased anxiety, emotional lability, instability of sleep, reduced resistance to stress, moodiness, tearfulness (while crying often turns into hysterics) , low independence, tendency to protest. Such children are very dependent on loved ones, try to involve them in all their activities, and do not like to be left alone. Other somatic complaints may also be observed.
Relationship with stress and life changes. Think about what events could have caused this problem? Did your child go to kindergarten or school for the first time? Any changes in home life? What stresses did the child encounter before the disease manifested? What stressors are still present?
How to help your child cope with stress
A problem with bowel movements may be a somatized manifestation of depression or subdepression, and may be associated with the difficulty of adaptation and anxiety. Sometimes an increase in symptoms can be observed in the fall and spring - a classic time for exacerbation of all psychosomatic disorders, when the incoordination of the autonomic centers is especially pronounced.
Such children are very dependent on loved ones, try to involve them in all their activities, and do not like to be left alone.
The child refuses certain foods. Such children are often very selective in their diet. They have a persistent craving for certain foods and a persistent rejection of others - those that are more difficult to digest. They instinctively refuse foods that may cause them discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract. This is also an indicator of the immaturity of the system.
Heredity. The hereditary factor matters. If one of the parents or close relatives experienced similar or other psychosomatic symptoms, if one of them has a reactive nervous system, decreased resistance to stress, or nervousness, this may partially explain the child’s symptoms.
Symptoms of false encopresis
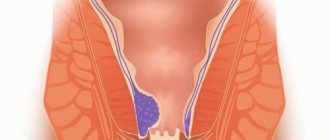
False (paradoxical) encopresis is characterized by chronic constipation (stool retention for more than 32 hours for more than three months). Main symptoms: constipation and stool . Against the background of constipation, spotting may be observed sporadically at first. As constipation progresses, stool formation intensifies. A fairly large amount of feces accumulates in the rectum (rectum), and the pressure in the intestine exceeds the force of the anal sphincter. Large diameter fecal column. Stool comes out like toothpaste from a tube. Parents often complain of foul-smelling diarrhea. This is false diarrhea. In the upper sections, a fermentation process occurs and liquid feces, washing the accumulated solid feces, are involuntarily released through the anus. A digital examination of the rectum reveals an enlarged ampoule tightly filled with hard feces. When palpating the abdomen, an accumulation of feces in the overlying parts of the colon is palpated, which can simulate neoplasms.
Diagnostics
If parents suspect their child has stool, they should contact a pediatrician. To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor will conduct a comprehensive examination and, if necessary, prescribe additional consultations with specialists (neurologist, surgeon, gastroenterologist, psychiatrist).
Children are always assessed with the assistance of parents or other caregivers. The diagnosis of encopresis is made on the basis of a detailed analysis of the medical history, which can be used to obtain significant information about the causes, type and nature of the disease.
During the initial consultation, the pediatrician pays special attention to the period before the onset of colomasia in children. Often at this time there was chronic constipation or diarrhea, combined with fecal retention. An important role is given to clarifying the psychological situation in the family, as well as the course and characteristics of pregnancy and childbirth in the mother.
During a physical examination, the doctor examines the perineal area, describes the structure of the spine, reflexes, and also palpates the abdomen and digitally examines the rectum. The specialist prescribes general clinical blood and urine tests, and bacteriological examination of stool.
To verify the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of calomania, the following instrumental examination methods are used:
- transrectal ultrasound examination (determine the condition and diameter of the rectum, in children with constipation the diameter is more than 25-30 mm);
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space;
- sigmoidoscopy (endoscopic examination method to exclude organic pathology of the rectum: tumors, malformations, polyps);
- magnetic resonance imaging (the most detailed examination technique);
- manometry (a method that allows you to determine the susceptibility of the rectum to various irritants);
- proctography (x-ray examination using barium contrast agent).
Invasive methods are used to diagnose encopresis in children in exceptional situations. Also, in most cases, a neurological and/or psychiatric examination of the child is performed.
Treatment of encopresis in Russia, treatment of neurotic encopresis in Saratov
Sarklinik in Saratov successfully uses innovative comprehensive reflexology methods for the treatment of neurotic encopresis in children, adolescents, and adults (men, women). As a result of therapy, the processes of excitation and inhibition in the central nervous system, the interaction between various regulatory systems in the body are normalized, stagnant inert foci of excitation in the cerebral cortex and subcortical formations are eliminated, and neurotic disorders that arise during the course of the disease are corrected. Unfortunately, treatment of encopresis with folk remedies and folk remedies, psychotherapy, exercises, and traditional medications rarely give positive results.
Sarklinik knows how to treat encopresis in Russia, how to get rid of encopresis in Saratov!
Treatment of encopresis in children (boys, girls, preschoolers, schoolchildren), adolescents (boys, girls) may include various methods: reflexology, acupuncture, microacupuncture, moxibustion, non-traditional methods. The effectiveness of complex treatment of encopresis reaches 81% and depends on the patient’s age, severity of the diagnosis, duration of the disease, the presence or absence of complications, which often arise when encopresis lasts more than 2 years. Functional encopresis is curable with timely and comprehensive treatment! Treatment at Sarklinik (Russia, Saratov) is carried out on an outpatient basis and individually. All methods are safe. Treatment periods are individual. Sarklinik knows how to treat encopresis and how to cure encopresis, how to get rid of fecal incontinence (stool), how to treat fecal incontinence! On the website sarclinic.ru you can read reviews, free online to the doctor. Sarklinik also treats enuresis in children, adolescents and adults.
Reviews about the treatment of encopresis at Sarklinik: , , , .
Interesting questions to the Sarclinic doctor about the treatment of fecal incontinence: , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , ,
Sign up for a consultation. There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Photo: Katin | Dreamstime.com\Dreamstock.ru. The people depicted in the photo are models, do not suffer from the diseases described and/or all similarities are excluded.
Related posts:
Sound, vocal tics in children: treatment, symptoms; adult tics
Minimal brain dysfunction in children, treatment of mmd in children
Cerebral palsy in children, children with cerebral palsy, treatment
Movement disorder syndromes (muscular dystonia, cerebral palsy)
General speech underdevelopment in children, phonemic onset: levels, correction, treatment