One of the treatment options for obstruction of the stomach and esophagus is the placement of a gastrostomy tube. Thanks to this intervention, an artificial passage is created through the anterior abdominal wall, which allows the patient to eat normally and the doctor to carry out various diagnostic procedures. The operation can be performed for both benign and malignant diseases.
Varieties of the method
There are temporary and permanent ways to apply a gastrostomy. In the first case, a rubber catheter with a diameter of no more than 1 cm is installed in the stomach, through which liquid or semi-liquid food is introduced. This method is relatively simple, but is accompanied by physical and psychological discomfort for the patient, which is associated with the constant presence of the tube in the lumen of the stomach.
Each method has its own advantages, disadvantages and features, so the choice is always made individually.
When is a gastrostomy tube removed?
The timing of the gastrostomy removal can be very varied. In some cases, 1 or 2 months is enough for this, and sometimes it takes up to six months. It all depends on the patient’s health condition and the speed of restoration of the functions of chewing, swallowing and patency of the digestive tract.
The timing of gastrostomy removal in each case is determined by the specialists of our clinic on an individual basis. In some cases, removing the gastrostomy as early as possible can lead to a speedy recovery and avoid a number of surgical complications. If the patient is unable to get to the clinic on his own, it is possible to call a gastroenterologist at home.
The surgeons of our clinic have extensive practical experience in working with gastrostomies and have extensive theoretical knowledge, and regularly improve their professional qualifications. The staff of our clinic will provide the patient with care and sensitive attention.
Indications for gastrostomy placement
The method is used in a wide variety of clinical situations. Among the most common indications for surgery are:
- Tumor processes in the esophagus and cardia of the stomach that cannot be cured by radical surgery due to massive local spread.
- Cicatricial strictures of the esophagus after injuries and burns (for the purpose of maintaining enteral nutrition and bougienage).
- Diseases of the central nervous system, tumor processes of the head and neck, strokes, which led to the development of oropharyngeal dysphagia.
- Complete obstruction of the esophagus in newborns (atresia) is one of the stages of preparation for plastic surgery.
- Broncho-esophageal and tracheo-esophageal fistulas.
In addition to indications, the method also has contraindications, which are determined individually for each patient.
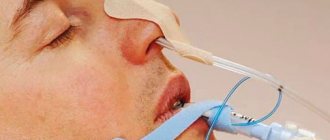
How is a nasogastric tube placed?
This manipulation is performed by the attending physician or a doctor in the endoscopy department when there is a need for endoscopic control. The probe, under local anesthesia, is inserted through the nasal passage into the pharynx and slowly moves into the stomach, while the patient helps the doctor by making swallowing movements. When setting, there is no need to resist, as this brings even more discomfort.
Endoscopic gastrostomy
In modern surgery, endoscopic gastrostomy is used to apply gastrostomy; it is performed as follows:
- Local anesthesia, if necessary, sedation of the patient.
- The surgical approach is performed in the epigastric region to the left of the white line of the abdomen. To perform the operation, a transillumination effect on the skin of the anterior abdominal wall in the area of gastric puncture is necessary. The skin is cut 1 - 2 mm longer than the diameter of the gastrostomy tube.
- Puncture of the stomach with a needle - trocar. The stylet is removed and a guidewire is inserted into the stomach.
- Capturing the conductor with an endoscopic loop, which is previously inserted into the lumen of the stomach through the instrumental channel of the gastroscope.
- Removing the conductor through the mouth.
- Attaching a gastrostomy tube to the guide and inserting it into the lumen of the stomach, then onto the anterior abdominal wall.
- Control examination of the stomach using an endoscope.
- Suturing the wound.
Rehabilitation of the patient can begin within 24 hours after surgery.
Under no circumstances should you:
- Apply bandages, plasters, and napkins over the stoma. They can cause bedsores or granulations;
- Use a bandage or cotton wool for wiping: irritation may occur due to lint and fibers left on the skin;
- Use talc and hydrogen peroxide: they can cause irritation and allergic reactions;
- Use any ointments without special indications.
Doctors at the Onco.Rehab integrative oncology clinic have gained extensive experience in successful surgical interventions and recovery after them. We not only treat, but also ensure that our patients feel the taste of a full-blooded life.
Preparation for surgery and postoperative period
No specific preparation is required before applying a gastrostomy. If the patient has electrolyte imbalances that have developed due to the lack of adequate enteral nutrition, then they are first corrected. In addition, before the operation it is necessary to undergo laboratory and instrumental examination, which includes:
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Biochemical blood test.
- Fibroesophagogastroscopy.
- Electrocardiography.
- X-ray of the chest organs, etc.
A week before surgery, you should stop taking medications that affect blood clotting. One day before the installation of a gastrostomy tube, food intake is prohibited, and water is prohibited 6 hours before the intervention.
On the first day after surgery, the gastrostomy tube remains open and its end is immersed in the receiver vessel. Then begin gradual feeding through a tube, starting with nutritional mixtures of 100 - 150 ml every 2 - 3 hours. By the end of the first week after the intervention, they begin to eat 400-500 ml of liquid or semi-liquid food 4-5 times a day. If the operation was performed against the background of a serious condition of the patient, then nutritional mixtures are administered drip-wise on the first day, with short breaks to monitor gastric emptying. Gradually, such patients are transferred to standard fractional feeding.
Feeding through a gastrostomy tube. To help parents
In this case, any nutrition must pass through a gastrostomy tube.
You need to open the gastrostomy tube and insert a syringe into it. If it's a Janet syringe, you insert it into the wide part of the gastrostomy tube.
Syringe Janet
For medications or liquids, a Luer-type syringe is used, but the volume of the syringe must be at least 10 ml, otherwise the gastrostomy tube can be damaged.
Syringe Luer
If the food being inserted into the syringe has a thick consistency, then a syringe with a wide spout and a wide opening on the gastrostomy tube is used.
Before starting feeding, you need to place the baby horizontally. Before you start feeding, you need to open the tube itself and check how much food is left in the stomach after the last feeding. And, if there is air, then let it out. If everything is done correctly, then the tube will contain either clear, yellowish gastric juice, or nothing at all if the child has digested everything.
Then you need to rinse the gastrostomy tube itself with 10 milliliters of water, draw puree or mixture into a syringe and very slowly introduce it into the gastrostomy tube so that the child with SMA has time to digest it. The minimum feeding time is 15-20 minutes, otherwise reflux or belching may occur after eating. If necessary, you can administer food within 40 minutes, but in this case it is better to use special syringe pumps or pumps.
Important Any administration through a gastrostomy tube should be painless for the child and not cause any discomfort.
After feeding, you need to fill the syringe with boiled water at body temperature (36-37 degrees) - you should always check that the water is not hot and not very cold. After this, air is released from the syringe, it is inserted into the gastrostomy tube, and flushing with the required volume of liquid begins.
The volume of fluid depends on the age of the child. If he is less than a year old, then 10-12 milliliters will be enough; if the child is large and he tolerates a sufficient volume of fluid, then up to 40 milliliters can be administered after feeding.
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA): what is it? SMA is a rare genetic disease that requires the participation of palliative care specialists. What degrees of SMA are there, how each is characterized, what equipment patients need - read the article by the SMA Families Foundation
Neurological problems
Flushing is necessary in order, firstly, to clean the tube itself, and secondly, to prevent a food plug from forming inside, on the side of the stomach: then the device will always be passable and will not become clogged. You also need to rinse slowly. After this, the gastrostomy tube is closed and wiped with a clean cloth moistened with boiled water.
We talked in detail about caring for a gastrostomy tube in the video instructions.
If the device has an extension set, the feeding procedure changes slightly. First you need to fill the tube itself with water so that there is no air in it and air does not enter the stomach. The water-filled tube is then inserted into the gastrostomy tube. Then food is introduced very slowly (over 20 minutes). After finishing feeding, you need to snap everything back together, disconnect the syringe and close the gastrostomy tube. Then the extension tube is washed with a small amount of water (10-20 milliliters). After this, you can close the tube and disconnect it, and the gastrostomy itself can be closed.
What should you not do when feeding through a gastrostomy tube?
You cannot use inhomogeneous (heterogeneous) formulas for feeding through a gastrostomy tube. Sometimes parents try to grind something in a blender - meat, potatoes, vegetables - and feed the child. But if it is an inhomogeneous mixture that does not have the desired consistency, it may clog the tube and you will have to change it. If there is a balloon tube, then replacing it is quite simple, but the bumper tube will have to be changed in the hospital under anesthesia.
Important: Do not fill the balloon with various liquids that contain salts, medications, or fill it with air, because the balloon will deflate too quickly. You should use boiled or distilled purified water that is practically free of impurities and foreign matter.
How to give medicine through a gastrostomy tube?
If a child needs to be given medicine, it should be in liquid form. There are special preparations intended for administration through a gastrostomy tube - solutions, syrups, suspensions. If this form is not available, you need to crush the tablet and insert it through the tube, while you must be sure that this mixture of tablet and water will not clog the tube.
By the way, you can read about how parents can get medicine for their child for free by following the link. The legal adviser of the Vera Foundation, Anna Povalikhina, tells the story.
There are medications that are contained in a capsule in the form of granules; these granules can settle on the wall of the tube and clog it. Such medicines cannot be used. If you do use them and a blockage occurs, then you should try to rinse the tube with boiled water, but under no circumstances should you pick out the granules or try to break through the resulting blockage with some sharp object.
The article was prepared on the basis of a video by a pediatrician, Ph.D. Natalya Nikolaevna Savva, chief physician of the children's hospice “House with a Lighthouse,” “Feeding through a gastrostomy tube. To help parents."
The full version can be found here.
Nutrition and care of the gastrostomy tube
In order to reduce the risk of complications and maintain the normal functioning of the gastrostomy tube, the following rules should be followed:
- Always flush the catheter after each meal, as well as in the morning and evening. To do this you need to use warm boiled water.
- Release gases using a Janet syringe before each feeding.
- After each meal, you need to clean the skin around the stoma and then dry it with a napkin. It is also recommended to regularly treat the skin with an antiseptic solution.
- The fixing disk of the gastrostomy should be located at a distance of several millimeters from the surface of the skin. When the weight changes, it needs to be tightened or loosened.
The nutritional mixture for feeding is injected into a rubber tube using a Janet syringe. Food is introduced slowly, 100-150 ml every 5 minutes. Special nutritional mixtures can be administered by drip.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Care
Stoma care is complex and involves caring for the oral cavity, tube, and skin in the stoma area.
Oral cavity.
Don't forget to brush your teeth regularly in the morning and evening.
If your mouth is dry:
- Dissolve the ice;
- Use the drug “Artificial saliva” purchased at the pharmacy;
- Treat the oral cavity with glycerin on cotton swabs.
A tube.
Handle the pipe only after thoroughly washing your hands.
After the wound has healed (this takes 5-7 days), the tube must be turned at least twice a day for 1 month. This is important for the stoma to form correctly.
Be sure to rinse the tube using boiled water. This is done before and after eating. A syringe can be used to inject water. The water is introduced slowly, do not press too hard.
If food comes through a tube, it also needs to be flushed every six hours.
Skin covering.
In the mornings and evenings, the skin in the stoma area should be washed with a soapy solution of warm water or an alcohol-free skin antiseptic.
After washing the skin, wipe it dry using sterile non-woven wipes.
How will you feel?
Slight pain in the nasal cavity, pharynx and vomiting are possible, but not all patients experience this. It is important to listen to your doctor's commands and breathe properly through your mouth. Almost all patients tolerate both this manipulation and treatment with an installed probe satisfactorily. Don't worry, nasal breathing will continue. Sometimes it takes 2-3 days to get used to the probe. In extreme cases, the doctor may prescribe painkillers, antiemetics and antispasmodics. At first, you need to listen to yourself and understand what position you should be in in order to reduce discomfort in this area. The main thing is to remain calm and remember that this is a necessary and temporary measure. According to many patients, their fears about inserting a probe were greatly exaggerated.