According to historical sources, in the 3rd century BC, Roman generals recommended that their soldiers drink wine to prevent dysentery. And during cholera epidemics in the 19th century, it was believed that brandy could prevent infection. In 2011, an article by Scottish scientists was published in the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine Janet S. Guthrie and Darrell O. Ho-Yenwho tested this theory.
Questions and answers Is there alcohol that does not cause a hangover?
Researchers found that Vibrio cholerae was completely killed in 20% gin after an hour, in 18.75% gin after 6 hours, and in 15% gin after 26 hours. It turned out that red wine copes with bacteria even faster: in 6.25% wine they were gone after 30 minutes. However, the authors of the study emphasize that most of the cholera pathogens die in the acidic environment of the stomach, and with alcohol abuse, the acidity of the stomach decreases. Therefore, those who suffer from alcoholism are at risk of getting sick with fewer bacteria than non-drinkers.
Food poisoning
Food intoxication is caused by poor-quality foods contaminated with pathogens that release toxins. They cause disorders of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), manifested as follows:
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea;
- intestinal colic;
- headache and muscle pain;
- fatigue, lack of appetite;
- increase in body temperature.
Toxins affect the walls of the stomach and intestines, causing irritation and inflammation. Vomiting and diarrhea are a natural protective reaction of the body that helps accelerate the elimination of pathogenic agents and toxic products of their vital activity.
You should not drink alcohol while eating low-quality food.
It aggravates the process: it has an irritating effect, thereby provoking repeated vomiting and diarrhea, and also causes increased urination. This increases dehydration, which leads to metabolic disorders. The higher the percentage of fluid loss, the more serious disorders can occur. Attempts to treat alcohol poisoning lead to a worsening of the condition, since it itself is a toxin for humans.
To make you feel better
, you need to perform gastric lavage: give a few glasses of water to drink and induce vomiting by pressing on the root of the tongue. The procedure is carried out until the water becomes clear. Subsequently, it is recommended to use enterosorbent (activated carbon, Polysorb, etc.) according to the instructions attached to it.
On the first day, you should drink only large quantities of water to prevent or eliminate dehydration. Then you can gradually introduce broths, decoctions, soups, etc. that are nutritious but do not irritate the gastric mucosa. Until complete recovery, any spicy, salty, smoked food, carbonated and alcohol-containing drinks are prohibited.
Clinical symptoms
When away from home, it is important to be able to recognize the first signs of traveler's diarrhea, as this condition, like any digestive disorder, can lead to dehydration and associated serious health consequences. Travelers' diarrhea is accompanied by a set of clinical signs:
- body temperature up to 38 degrees and above;
- chills;
- general weakness and malaise;
- body aches;
- partial or complete loss of appetite;
- nausea and vomiting;
- abdominal discomfort and increased gas formation in the intestines;
- frequent urge to have bowel movements, loose stools.
The clinical picture of travelers' diarrhea is characterized by an acute onset. Depending on the cause, the stool may be watery without any features or contain fragments of undigested food. In severe cases, stool may contain impurities of mucus, blood or pus. Severe diarrhea and frequent vomiting create favorable conditions for the development of dehydration (dehydration) of the body. The development of dehydration is signaled by symptoms such as thirst, hoarseness, dry skin of the mucous membranes, decreased elasticity of the skin, convulsions, and a decrease in the daily volume of urine. In children, the clinical picture is dominated by general weakness, drowsiness, convulsions, silent crying, and refusal to eat and drink.
Alcohol intoxication
This condition occurs as a result of one-time consumption of large amounts of ethanol or prolonged drinking. It itself is a toxin, and when it enters the liver, breakdown products are formed, which further worsen the state of health. Every system in the body is affected, but the brain, liver, cardiovascular system and gastrointestinal tract are most affected.
Alcohol intoxication is a manifestation of the third stage of intoxication, when toxins affect organs and systems, disrupting their proper functioning. Symptoms depend on the amount drunk. The main features include:
- redness of the skin in the face and neck;
- confusion of speech, decreased or increased activity;
- nausea, vomiting, frequent and loose stools, increased urination;
- impairment of motor activity;
- loss of consciousness;
- decrease in breathing rate, heart rate, decrease in blood pressure.
Further drinking of alcohol during ethanol poisoning is prohibited, as it leads to a worsening of the condition. Gastric lavage should be performed immediately. If the victim is unconscious, you need to lay him on his side to avoid choking on vomit and call an ambulance.
Hangover
is a syndrome that occurs as a result of severe intoxication.
A common myth is that the best cure for it is to drink alcohol again
. Attempts to improve your well-being in this way can only destroy the enzymatic system and lead to alcoholism. If you have a hangover, you need to consume large amounts of water, tea, lighten your diet, eliminate caffeine and exercise. The body needs to fully recover.
Intestinal upset after alcohol: how to avoid?
In order not to think about the question of how to restore the intestines after alcohol, it is better to take the necessary measures in advance. To eliminate unpleasant symptoms, it makes sense to give up fatty foods both on the day of drinking alcohol and the day before. The same applies to:
- Spicy foods,
- Heavy foods rich in proteins - meat, sausage, legumes,
- Gribov.
Even if you drink alcohol, the intestinal microflora will suffer the least in this case, and you will not suffer from a hangover in the morning. You can also take an intestinal cleanser or a mild laxative, or do an enema half a day before you drink alcohol - this will help even if you were eating heavy food before.
Alcohol in case of methanol poisoning
Despite the negative properties of ethanol, it can save a person's life. Alcohol for methyl alcohol poisoning is a first aid remedy. It acts as an antidote that can prevent irreversible changes in the body.
Methanol
– technical liquid, highly toxic substance. Under no circumstances should it be ingested. It is used in the production of solvents and household chemicals. Use in the liquor industry is prohibited.
There is a risk of poisoning for those who drink ethanol substitutes or buy an unlicensed product. Methyl alcohol cannot be distinguished from ethyl alcohol just by looking at them. They are identical in taste, color and smell. If you have doubts about the quality of the product, you can conduct several experiments with the drink:
- Set it on fire.
The flame color of ethanol is blue, and that of methanol is green. - Dip the hot copper wire into the glass.
In the first case, nothing will change, in the second, a pungent odor of formaldehyde will appear. - Throw raw potatoes into it.
Ethanol will not change color. If it is a poisonous liquid, it will turn pink.
When poison enters the body, it begins to be broken down by a liver enzyme responsible for the metabolism of alcohols. As a result, formic acid and formaldehyde are formed. These organic compounds inhibit the functions of vital organs.
Signs that poison has been drunk:
- weakness, chills, dizziness;
- abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea;
- the appearance of blood impurities in the vomit;
- photophobia, “fog” before the eyes, decreased vision, blindness;
- loss of consciousness, coma.
How do antibiotics affect the body?
It is not without reason that drugs in this group are taken only as prescribed by a doctor. The principle of their action is to destroy or suppress the growth of bacteria, all of them (both beneficial and harmful).
They attack:
• Cellular synthesis apparatus. This prevents bacteria from building protective peptide walls.
• DNA gyrase. This prevents the replication of genetic information and inhibits the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
• Protein biosynthesis apparatus (ribosomes) - without it, bacteria die.
Modern pharmacology is trying to make antibiotics more selective. But their use leads to an imbalance of microflora. Beneficial bacteria, which form a kind of shield in the intestines, also suffer. Therefore, only a specialist can compare the effect of treatment with possible losses. Also, a number of antibacterial drugs have the property of hepatotoxicity. They damage liver cells, causing cholestasis (impaired bile flow) or necrosis (tissue death).
First aid when taking methanol
The person next to the victim must:
- Call an ambulance.
- Perform gastric lavage.
- Give vodka (100–150 ml) or any other alcohol-containing drink.
When the antidote enters the bloodstream, the liver enzyme responsible for the transformation switches to it, since its sensitivity to ethyl alcohol is much higher. Thanks to this, methyl does not decompose and is excreted from the body unchanged.
When drinking a toxic substance, going to a medical facility is mandatory, since alcohol is only an antidote, and the victim requires full-fledged therapy in a hospital setting
. First aid should be provided promptly, because taking a small dose can lead to death within an hour.
The use of alcohol in case of poisoning of unknown etiology is prohibited. Alcohol-containing drinks will only do harm: they will increase dehydration and other symptoms. The exception is the use of methyl alcohol, when ethyl alcohol can save a human life.
How do alcoholic drinks affect the body?
The basis of any such drink is ethanol. The difference lies in its content. For example, there is 10 times more of it in vodka than in beer. Drinking alcohol in large quantities has a negative effect on the body. No more than a tenth of the volume of ingested ethanol is excreted in the urine and then, the remaining 90% is broken down and absorbed.
Ethanol harms cell membrane lipids. Their viscosity decreases, and the receptors become insufficiently sensitive to the necessary mediators. To prevent this effect, the stomach tries to neutralize ethanol. To do this, the mucous membrane produces much more mucus than in normal digestive mode. On the one hand, this slows down the absorption of the unwanted substance, on the other hand, it causes irritation of the mucous membrane and inhibits the absorption of nutrients and other drugs.
A complex of pathologies called alcoholic liver disease cannot be excluded. When ethanol is abused, cellular degeneration develops, interfering with the normal functioning of the organ.
Literature:
- On the question of the effect of alcohol on stomach poisoning in healthy people: (Clinical research): Dis. on the steppe Dr. med. Resident Therapist. clinics prof. DI. Koshlakova Evgenia Blumenau / From Therapist. clinics prof. DI. Koshlakova. — St. Petersburg: type. Ettinger, 1890. - 59 p.
- Acute and chronic alcohol intoxication / Strelchuk, Ivan Vasilievich./. - Moscow: Medicine, 1966. - 331 p.
- Methanol: Pathology, clinic and therapy of poisoning: Abstracts for the dissertation. for the job application scientist Doctor of Medicine degree Sciences / Naval Med. acad. - Leningrad, 1948. - 3 p.
Need some advice?
OR CALL A DOCTOR
CALL!
+7
Which antibiotics are best not to combine with alcohol?
Antibacterial drugs form a fairly large pharmacological group. The drugs included in it have varying degrees of activity. Therefore, the use of some together with alcohol is undesirable, while others are not prohibited.
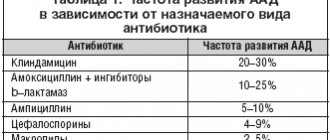
The first include antibiotics that have a high hepatotoxic effect:
• amoxicillin;
• flucloxacillin;
• erythromycin;
• sulfamethoxazole;
• gatifloxacin.
There are different points of view on the interaction of ethanol with tetracyclines. Some believe that with this combination the medicine is neutralized, others believe that it enhances the negative effect on the liver.
Some antibacterial drugs should not be taken with alcohol due to possible side effects. This is especially true for metronidazole.
Consequences of drinking alcohol with antibiotics
If a person does not abuse alcohol, he will not feel any effect on the liver from a single combination of an antibiotic and ethanol. However, reactions may follow from other systems:
• Digestive. Stomach pain is due to irritation of the mucous membrane, and excess mucus secretion can cause diarrhea.
• Nervous. Antibiotics themselves have a detrimental effect on neurons. When interacting with ethanol, which excites the nervous system, convulsions are possible.
• Cardiovascular. Fluoroquinolones increase the risk of impaired blood flow, which increases stress on the heart. And every additional portion of beer or wine (not to mention stronger drinks) multiplies this load.
Allergy sufferers are generally prohibited from mixing any medications with alcohol, as the body's reaction can be unpredictable. Even a doctor cannot always predict the outcome.
Why shouldn't you drink alcohol while taking antibiotics?
We found that the main reasons are the danger to the liver and the possibility of side effects. But patients often ask the question: does the intensity of the drug’s action change under the influence of ethanol?
Overall it is decreasing. While the body resists the absorption of alcohol components, it unconsciously protects itself from medications. The stronger the alcoholic drink, the less likely it is that the medicine will be completely absorbed.
If you combine ethanol with metronidazole, a synergistic effect occurs. However, it concerns not the effect of the drug itself, but its side effects:
• drowsiness;
• concentration disorders;
• heart rhythm disturbances;
• nausea;
• headache.
There are also questions about a possible overdose. There is no need to be afraid of it - there is no alcohol in antibacterial drugs. Such assumptions arise due to inattentive study of the composition of drugs.