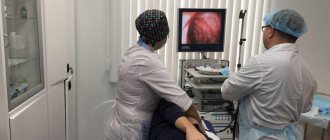
In modern medicine, various methods of examining the gastrointestinal tract are used. The most common is the endoscopic direction. Gastroscopy allows the doctor to visually examine the esophagus, intestines and stomach in real time, as well as take tissue samples for laboratory tests. However, this method is not painless. Patients often complain that their throat hurts both after FGDS and during the procedure.
Carrying out FGDS
The FGDS procedure lasts no more than ten minutes. If a biopsy is needed, it will take a little longer.
The patient is placed on his left side, after which the oral cavity and larynx are treated with a local anesthetic to reduce sensitivity.
A mouthpiece is placed in the mouth, through which the endoscopist inserts a tube with a probe. The doctor moves it deeper with gentle movements, examining the inner walls of the duodenum and stomach. If an ulcer or tumor is found, he will take a tissue sample for a biopsy. He will also remove detected polyps if necessary.
FGDS is a safe procedure, but in some cases it causes pain. Most often this occurs with ulcers or cancerous tumors. In these cases, the patient is recommended to undergo diagnostics under anesthesia.
A few more effective tips
Sometimes the cause of a sore throat is bile in the stomach, which enters the pharyngeal mucosa and causes pain. Cleaning the stomach of bile secretions and mucus will help prevent this condition. In addition, for eight hours before the procedure at the medical center in Krasnogorsk, you will be advised to refrain from taking food and medications, and a few hours before - from liquids. You are not allowed to smoke 3 hours before the examination.
If after the procedure you still have a sore throat, do not rush to panic: most likely the unpleasant sensations will disappear on their own in 2-3 days. Rinse it with warm water with iodine and a pinch of salt, try to talk less and buy softening lozenges. If you are not allergic to honey, you can also suck it between meals and before bed. If the unpleasant sensations do not go away, but rather intensify, which is extremely rare, do not hesitate to seek help from a doctor!
What to do if your throat or stomach hurts after FGDS
Painful sensations in the stomach after gastroscopy in the absence of ulcers and tumors disappear on the second day. For severe pain, it is enough to take painkillers.
Sore throat occurs due to mechanical damage to the walls of the larynx by the endoscope. In this case, it is recommended to talk less and gargle with solutions of furatsilin and miramistin. Rinsing with saline solutions is also allowed.
Painful sensations will be alleviated by taking sea buckthorn oil (2-3 times a day, a teaspoon). Combined with the healing effects of honey, this will help speed up your recovery.
Sprays are also successfully used, effective for sore throats and easy to use. They have a complex effect - healing, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial.
Our clinic employs experienced endoscopists who can conduct an FGDS examination painlessly and without complications.
How to eliminate unpleasant sensations
To reduce discomfort and unpleasant sensations, the doctor may suggest the use of anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and regenerating agents. It is recommended to gargle and use sprays with an anesthetic effect. General scheme of medications to reduce discomfort:
- Inhalipt to provide analgesic effect
- gargling with Chlorophyllipt to reduce the severity of inflammation and accelerate the regeneration of damaged mucous membranes
- gargling with Miramistin to reduce inflammatory reactions
- Furacilin for rinsing to reduce pain and speed up the healing of microcracks and wounds
- Soda-salt rinse every few hours
- Chamomile decoction for gargling
The drugs described are not intended for self-medication; prior consultation with a doctor is required.
Historical excursion
The founder of gastroscopy is Kussmual, who in 1868 first used this method of examining the gastric mucosa in practice. After a while, the scientist Schindler introduced the world to the concept of a “bending gastroscope”, equipped with advanced optics. Over time, such a device only improved. 1957 was marked by the release of the first gastroscope with a controlled bend, which made all-round panoramic viewing possible. And finally, at the beginning of the 20th century, a device was released that projected the resulting image through small bundles of glass fibers. This device is called a “fibrogastroscope”.
A modern gastroscope is a device designed to examine the mucous membranes of the digestive organs. The device is made in the form of a flexible and long tube, the end of which is equipped with a video camera and lighting. During the diagnostic process, a tube is inserted into the organ through the oral cavity. In relatively recent times, a biopsy gastroscope has been developed, which allows for multiple targeted biopsies. This model is distinguished by high quality, information content, and also a lower degree of pain.
Causes of pain
The main cause of pain after gastroscopy is the appearance of microtraumas of the mucous membrane resulting from inaccurate insertion of the gastroscope into the esophagus. A similar phenomenon is observed both when the doctor acts rudely and when the patient behaves inappropriately during the procedure. To carry out FGDS with the least amount of trauma, the patient is required to unquestioningly obey the doctor’s instructions and remain as immobile as possible (position changes are made on command), especially during insertion of the probe.
The thickness of the tube of a modern gastroscope is 5.2 mm
Injuries can be caused by:
- sudden movements of the patient;
- independent withdrawal of the probe;
- strong vomiting;
- conscious refusal to perform the swallowing movement (advancing the gastroscope is least traumatic at the moment of swallowing);
- spasm of the larynx.
Important! Very often, severe pain appears when diagnosis is carried out using old equipment, the thickness of the gastroscope in which is much greater than in modern models.
One of the common complications caused by microdamage to the mucosa is inflammation. This is due to the fact that microcracks become a kind of gateway for infection that accompanies diseases of the ENT organs. In this case, in addition to pain, the following symptoms may be observed:
- hyperemia of the pharynx;
- swelling of the throat;
- burning sensation;
- soreness.
The origin of pain may be neurological in nature. A similar diagnosis is made if the pain is extremely intense and durable, but when conducting a detailed additional examination, for example, using a barium X-ray, no pathological changes are detected in the upper gastrointestinal tract.
In this case, pain may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- difficulty swallowing;
- spasm of the esophagus, even when eating liquid or pureed food;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- temperature increase.
When perforation of the gastrointestinal mucosa by endoscopic equipment, any of the above symptoms may be present, accompanied by bloody discharge during expectoration (if the trachea is damaged) or during vomiting (if the esophagus or stomach is damaged).
The endoscope is inserted into the stomach through a plastic mouthpiece
Consequences of FGDS. What are the possible complications?
Gastroscopy is a diagnostic procedure used to examine the esophagus, stomach and duodenum. The procedure is carried out inside the abdominal cavity, which makes it possible to examine the mucous membranes of the digestive organs. Gastroscopy is a fairly general concept that includes different types that differ in the location of the examination. Thus, the most well-known way to diagnose pathologies associated with the digestive system is FGDS or fibrogastroduodenoscopy. This method allows you to simultaneously examine the stomach and duodenum. Despite the high information content and safety of the procedure, there is a possibility of complications occurring after FGD. However, first things first.
Gastroscopy and colds
Is it possible to perform an FGDS procedure when the throat hurts? Having a cold that has already started is not a direct contraindication; you just need to take some precautions. Immediately before the manipulation itself, it is necessary to treat the mucous membrane of the throat and pharynx with a local anesthetic - this will reduce pain. Also, drip a vasoconstrictor into the nose to reduce a runny nose and improve nasal breathing.
After the procedure, patients are also recommended local antiseptics (spray, rinse), including antibiotic therapy to prevent bacterial infection.
Proper preparation for research
To some extent, it is unlikely that patients will be able to influence the skills of a specialist or the quality of the equipment used. However, they have the power to avoid severe pain and other complications on their part. Compliance with all the doctor’s instructions will help compensate for those unpleasant sensations when your throat hurts after an FGDS. And they simply cannot be avoided during the procedure.
The rules themselves are not that difficult to follow:
- For a day or two you should refrain from eating “heavy” meals. Fatty meats, smoked meats, anything spicy, as well as carbonated (alcoholic) drinks, including strong coffee, are strictly prohibited!
- During this period of time, mild heat treatment should be used - steaming, boiling, baking. The dishes themselves should be crushed and taken in small portions.
- The last meal should be no later than 10 hours before the procedure.
- Upon completion of the diagnosis, a temporary corrective diet should be continued for several more days.
And if a doctor needs to prescribe an FGDS procedure for a patient, then he should explain to the patient the features of its implementation and familiarize him with the rules for preparing for it. If any questions arise regarding this diagnostic method, they should be asked to the specialist immediately.
General information about gastroscopy
The high efficiency of fibrogastroduodenoscopy, or FGDS, is achieved thanks to the method of conducting such diagnostics. Special medical equipment is used - a gastroscope (fibrogastroscope). This is a flexible tube at the end of which there is a chamber with a light source. While controlling the probe, the doctor is able to examine areas of the stomach, which in turn makes it possible to detect changes that cannot be detected by x-ray.
Can my throat hurt after FGDS? The sizes of modern gastroscopes are becoming smaller, which is due to understandable reasons - to avoid severe discomfort. Large varieties are becoming a thing of the past, and they are being replaced by video endoscopes of smaller diameter. The distal end (remote part of the device) of the latest models is equipped with a camera, which during the study transmits an image to the monitor.
The quality of the resulting image is of high resolution, which makes it possible to accurately diagnose the disease. In addition, the difference between modern devices is that with their help you can not only examine the mucous membrane in detail, but also take a scraping for subsequent research.
Indications and contraindications
Indications for gastroscopic examination are the following factors:
- painful sensations localized in the area of the substrate, which are directly related to food consumption;
- frequent manifestations of heartburn;
- vomiting, in which blood is found in the vomit;
- frequent belching, accompanied by a sour taste;
- frequent attacks of nausea, subsequently turning into a gag reflex with food consumed the day before;
- regularly appearing feelings of heaviness and fullness in the stomach.
Sometimes this diagnostic method becomes impossible to use. Then we are talking about the following contraindications:
- severe respiratory failure;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- serious forms of mental disorders;
- strokes.