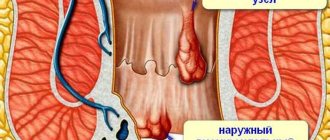
The anus is the opening through which feces leave the rectum. In the anus, there is an orifice (the opening itself) and an anal canal - a small area that is located below the rectum. Malignant tumors in this area are rare.
- Causes and risk factors for anal cancer
- Classification of anal cancer
- Stages of anal cancer
- Symptoms
- Diagnostic methods
- Anal cancer treatment
- Radiation therapy for anal cancer
- Chemotherapy
- Survival prognosis
Causes and risk factors for anal cancer
Like any malignant tumor, anal cancer occurs due to the fact that mutations occur in cells, due to which they become “immortal”, multiply uncontrollably, acquire the ability to grow into surrounding tissues (invasive growth), migrate throughout the body and give rise to secondary foci in different organs. The exact causes of these mutations are unknown.
There are some risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing anal cancer:
- One of the main risk factors is human papillomavirus infection. Human papillomavirus (HPV) is found in many anal cancers.
- Age. The main contingent of patients are people over 50 years of age.
- Anal sex. Chronic irritation and inflammation can lead to changes in the mucous membrane. In addition, there is a risk of HPV transmission through unprotected anal intercourse.
- Smoking. A bad habit increases the risk of many types of cancer, not just in the lungs.
- Complicated anamnesis. Anal cancer is more likely to develop in women who have been treated for cervical cancer.
- Decreased immunity due to taking immunosuppressants, HIV infection.
Key measures to prevent anal cancer include safe sex, HPV vaccination, and quitting smoking.
Classification of anal cancer
Depending on the structure of the tumor tissue under a microscope, the following types of anal cancer are distinguished:
- Squamous cell carcinomas (squamous cell carcinoma) are the most common, occurring in about 9 out of 10 cases. They can develop from cells of the mucous membrane of the mouth and anal canal. Sometimes squamous cell carcinoma occurs on the skin in the anal area.
- Adenocarcinomas originate from glandular cells at the top of the anal canal.
- Paget's disease is a type of adenocarcinoma that develops from sweat gland cells in the skin in the anal area.
- Basal cell carcinoma (basal cell carcinoma) is a malignant skin tumor. It can occur in the anal area, but this is an unusual location for her. Most often, such tumors are located where the skin is constantly exposed to sunlight.
- Melanoma is not a cancer; it is a malignant tumor that develops from pigment cells that produce melanin. Sometimes it is found in the anal area - on the skin or mucous membrane.
In some cases, squamous cell carcinoma of the anus develops against the background of a precancerous condition - anal intraepithelial neoplasia. Due to human papillomavirus infection, cells lose their normal features and begin to multiply too quickly.
Stages of anal cancer
The earliest stage is “cancer in situ.” The tumor has just begun to grow and is located in the upper layer of the mucous membrane or skin. It does not grow into the wall of the anal canal, does not spread to the lymph nodes, and there are no distant metastases. “Cancer in situ” is easily treated, but it is not always possible to diagnose it on time. The tumor further progresses:
- Stage I. The neoplasm is less than 2 cm in diameter.
- Stage II. The tumor diameter is 2–5 (substage IIA) or more than 5 cm (substage IIB).
- Stage III. Cancer cells have spread to the lymph nodes that are located near the rectum, or the tumor has grown into neighboring organs: the vagina, prostate gland, urethra, bladder.
- Stage IV. Anal cancer with metastases.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Prevention of colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer rarely affects people who lead a healthy lifestyle, eat a balanced diet, and do not smoke. Some foods are very important, for example, mushrooms, garlic, onions. They contain substances that have anti-cancer effects. Any plant food stimulates the proper functioning of the intestines, which means it is a means of preventing this terrible disease.
A positive effect of folic acid on delaying the formation of cancer cells has been revealed.
Folic acid in its synthetic form is practically of no benefit. But in its natural form it is absorbed very well. You can get it by eating green vegetables. The resistance of dietary fiber to enzymes makes legumes and beans very good for reducing the time toxic substances come into contact with the body.
Therefore, it is advisable to use these products, as well as brown rice and dried fruits, to improve bowel function. It is very important to engage in cancer prevention and undergo screenings on time. These measures allow you not only to notice a terrible disease in a timely manner, but also to avoid many less complex gastrointestinal diseases.
Symptoms
Anal cancer can go on for a long time without any symptoms. When symptoms appear, many patients believe that it is hemorrhoids, do not go to doctors, and are treated with traditional methods. I am concerned about bleeding from the rectum, itching, and there is a “lump” in the anus that is in the way. The stool becomes pencil thin because the tumor partially blocks the intestinal lumen. Most often, these manifestations actually indicate hemorrhoids or another benign process. But there is always a risk of a malignant tumor, so you need to visit a doctor as soon as possible and get checked.
Causes of hemorrhoids
Anyone can get hemorrhoids, and the risk tends to increase with age.
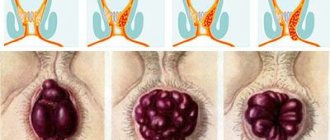
Hemorrhoids can be internal, which means the damaged vein is inside the rectum, or external, which means it is outside the rectum - often at the entrance. Internal hemorrhoids are usually painless, but external hemorrhoids can be painful.
Hemorrhoids occur when a vein in the rectum becomes irritated and inflamed. It increases in size, causing the intestines to rub against it. This may cause pain.
Hemorrhoids occur naturally. Some risk factors include:
- pregnancy, overweight or obesity, as this puts more pressure on the rectum
- constipation or low fiber diet
- straining during bowel movements
- sedentary lifestyle
Diagnostic methods
If anal cancer is suspected, the doctor conducts an examination, a digital examination, and then an endoscopic examination: anoscopy or sigmoidoscopy. If a pathological formation is detected on the mucous membrane, the doctor will perform a biopsy: remove a fragment of suspicious tissue and send it to the laboratory for histological and cytological examination.
To assess the stage of cancer, additional diagnostic methods are used: ultrasound, MRI, CT, PET scan, chest x-ray (to look for metastases in the lungs). Is it possible to detect anal cancer at an early stage? There are screening studies, but they are recommended only for people at high risk:
- with precancerous changes in the anus;
- in homosexuals;
- for anal warts (HPV);
- in women who have had cancer of the vulva, cervix;
- in HIV-infected people and after organ transplantation.
Digital examination of the rectum and cytological analysis help to detect a malignant tumor in the early stages. Sometimes a tumor is discovered by chance when the patient was initially treated for hemorrhoids. Anal cancer rarely metastasizes, and most often it can be successfully treated.
Anal cancer treatment
If there is a small tumor near the edge of the anus that does not grow into the surrounding tissue, local resection can be performed. Only the tumor and a small area of healthy tissue around it are removed. At the same time, the integrity of the sphincter (muscle sphincter) and the ability to defecate are preserved. Previously, abdominal resection was often performed for anal cancer. Through two incisions - on the abdomen and in the anus - the rectum was completely removed, sometimes along with nearby lymph nodes. To pass stool, a colostomy was performed: an opening was made from the colon onto the skin.
Currently, for anal cancer, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are usually used. These treatments have been proven to work as well as surgery.
Differences in disease symptoms
How to distinguish cancer from hemorrhoids? If you have the disease, additional symptoms may include abdominal cramps, unexplained weight loss, fatigue and nausea. If you are experiencing any of these problems, contact your colorectal surgeons immediately to get a diagnosis and begin working on a treatment plan. If the disease metastasizes or spreads to other parts of the body, symptoms may vary.
Symptoms may not be noticeable until the disease progresses. Signs and symptoms (if they occur) that do not occur with hemorrhoids may include:
changes in frequency of bowel movements;
bloating or pain;
unexplained or persistent nausea or vomiting;
unexplained weight loss;
changes in stool;
constipation;
Research shows that the average duration of colon cancer symptoms (from onset to diagnosis) is 14 weeks.
Signs and symptoms of internal, external and thrombosed hemorrhoids progressing to cancer may include:
painless bleeding;
pain that increases with swelling of external or ruptured hemorrhoids;
anal itching.
Causes also include adenomatous polyps, genetic abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease (ulcerative colitis, obesity, smoking.
Radiation therapy for anal cancer
Typically, radiation therapy sessions are carried out 5 days a week, the course of treatment lasts about five weeks. It is important to correctly direct the radiation to the tumor area so that it minimally affects healthy tissue. Before starting radiation, careful planning is carried out, MRI, PET/CT helps with this. Currently, modern techniques such as 3D conformal radiation therapy and intensively modulated radiation therapy are used.
If the tumor responds poorly to radiation therapy, treatment is supplemented with brachytherapy - a miniature radiation source is placed inside or near the tumor. This helps deliver a larger dose without the risk of damaging healthy tissue. The main indications for radiation therapy for anal cancer:
- As a primary treatment, in combination with chemotherapy.
- Tumor recurrence in the lymph nodes after treatment.
- After surgery to prevent the risk of relapse.
- As part of palliative treatment for cancer with metastases.
Survival prognosis
Anal cancer has a fairly high five-year survival rate. If treatment is started at the first stage, 71-77% of patients remain alive within 5 years, at the second stage - 59-67%, at the third - 35-58%. Metastases are rarely detected, but if they are present, the prognosis worsens sharply. This type of cancer is difficult to treat. The five-year survival rate for such patients is 7–15%.
| More information about treatment at Euroonco: | |
| Proctologist-oncologist | RUB 5,100 |
| Chemotherapy appointment | RUB 6,900 |
| Emergency oncology care | from 12,100 rub. |
| Palliative care in Moscow | from 44,300 rubles per day |
| Radiologist consultation | RUB 11,500 |
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Forecast
Surgery offers a chance to defeat the disease
There are many examples where a person survived after treatment for colorectal cancer and spent many more years with his loved ones. The key to determining survival rate is the stage at which the disease is detected and treated.
Everything is individual, so there are no exact numbers, but there are approximate statistics.
According to available data, if the disease is started to be treated at the first stage, then 70–80% of patients will remain alive for another 5 years. When intervention in the development of the disease begins only at the second stage, only 60% can expect to live 5 years.
In the third stage, only 30% of people will remain alive for 5 years. A detected disease at stage 4 guarantees survival only in exceptional cases, no more than 10%.