Indications for the test
In modern clinical practice, a specialized doctor can prescribe one of two types of tests for the specific enzyme described above, detected in the urn and blood. In the first case, it is called an analysis for diastase, in the second - for amylase in the alpha-base modification. Most often, a diastase test is prescribed for suspected:
- Various chronic infections;
- Having diabetes mellitus type 1 or 2;
- The presence of pathologies of the pancreas;
- Traumatic injuries to internal organs in the gastrointestinal tract;
- Regular disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract;
- Local lesions of the ear and salivary glands.
It should be understood that a specialized specialist can prescribe an analysis for diastasis in other situations, when there is a suspicion that the identified disease has provoked the development of complications and secondary dysfunction of the pancreas.
What is diastasis?
A component of the digestive process is called alpha-amylase or diastase. Its synthesis involves not only the pancreas, but also the gland that secretes saliva, as well as the woman’s ovaries and the mucous membrane of the small intestine.
Like other components of digestion, diastase enters the stomach, where it is “divided” into components. Having completed its tasks in the digestive tract, it diffuses into the blood channels, is absorbed by the kidneys and is excreted naturally in the urine.
The primary factor to investigate diastasis is sudden abdominal pain. It is used to determine the level of alpha-amylase (AA) and make further decisions about treatment tactics.
How to properly take a urine test for diastasis?
Before submitting biomaterial for analysis, the patient is recommended to undergo combined preparatory measures. These include the following necessary actions:
- Correction of diet. All fatty types of meat and fish, difficult-to-digest vegetables, cereals (including legumes), exotic fruits (especially shelf-stable ones that grow in tropical countries), as well as all spicy and very salty foods, a large number of seasonings, including including salt and pepper. Dishes are prepared by steaming, boiling or baking, after which they are consumed in small portions about 6 times a day warm (calculating 2500 kilocalories per day for an adult man). It is advisable to adhere to a special diet plan for at least two days before the start of urine testing. In addition, it is not recommended to drink alcohol, regardless of its type, for at least 48 hours before the start of laboratory diagnostics;
- Refusal to use the drug. During the period of preparation for laboratory analysis, at least 48 hours in advance, you must stop using any drugs that may interfere with urinary function (or in any way affect it, including induction), as well as the functioning of systems that affect the vital parameters of the body. If for some reason this is impossible to do, then you should report the problem to a specialized specialist who is referring the patient for a diastase test, indicating the name of the active substance of the drug, its dosage, frequency of administration and other characteristics;
- Limiting activity. The day before the procedure, it is advisable to eliminate physical and emotional stress, get a good night's sleep (at least 8 hours) and get up in the morning in a good mood.
Specific gravity of urine (g/l)
In a healthy person, it can fluctuate over a fairly wide range throughout the day, which is associated with periodic food intake and loss of fluid through sweat and exhaled air.
| Children under 1 month | 1002-1020 |
| Children 2 – 12 months | 1002-1030 |
| Children 1 year - 6 years | 1002-1030 |
| Children 7 - 14 years old | 1001-1040 |
| Children 15 - 18 years old | 1001-1030 |
| Men | 1010-1025 |
| Women | 1010-1025 |
Interpretation
The specific gravity of urine depends on the amount of substances dissolved in it: urea, uric acid, creatinine, salts.
- A decrease in the specific gravity of urine (hyposthenuria) to 1005-1010 g/l indicates a decrease in the concentrating ability of the kidneys, an increase in the amount of urine excreted, and drinking plenty of fluids.
- An increase in the specific gravity of urine (hypersthenuria) of more than 1030 g/l is observed with a decrease in the amount of urine excreted, in patients with acute glomerulonephritis, systemic diseases, and cardiovascular failure; it may be associated with the appearance or increase of edema, large loss of fluid (vomiting, diarrhea ), toxicosis of pregnant women.
How to collect biomaterial for research?
In modern clinical practice, two main methods of collecting biomaterial for research are used:
- Collection of the morning single portion. 10-12 hours before the start of urine collection for laboratory testing, it is necessary to exclude spicy and salty foods, alcohol, medications and other diet elements described above from the diet. When you get up in the morning, you need to wash the external genitalia as thoroughly as possible with ordinary clean warm water, without using any disinfectants (soap, shampoos, gels, etc.) so that the components of the substance do not accidentally get into the collected biological liquid material. During the act of morning urination, the first dose of urine, dispensed over several seconds, is skipped (like the last, 2-3 seconds before the completion of the entire process), while the middle dose is collected in a pre-prepared sterile container. In the latter case, it can be a classic container for collecting liquid biomaterials, which can be purchased at any modern domestic pharmacy. Urine collection should be stopped a few seconds before the end of urination, so that the last batch of liquid does not get into the sample! Be sure to take this nuance into account when collecting urine;
- Daily portion. In this case, the first morning portion of urine is completely drained, and for all subsequent small bowel movements, the liquid is collected in a vessel of sufficient volume (usually a thoroughly washed three-liter bottle), which is covered with a tight lid and stored in the refrigerator throughout the first day. The next morning, before sending the urine for analysis, the biomaterial is mixed in a bottle, after which 30 milliliters of liquid are poured into a sterile container and a note is made on it about the actual collected volume of daily urine. This is done in order not to transport the entire vessel as a whole, since it is quite voluminous and heavy.
Available urine for diastasis is delivered to the laboratory within 2 hours after the end of the procedure. In some cases, provided that it is stored in proper temperature conditions (5-7 degrees above zero, refrigerator), this period increases up to 4-5 hours.
Chemical examination of urine
Currently, chemical testing of urine is carried out on automatic analyzers using the dry chemistry method.
Chemical testing includes determination in urine:
- squirrel
- glucose
- ketone bodies
Protein in urine, normal protein in urine
Normal urine contains a very small amount of protein (less than 0.002 g/l), which is not detected by qualitative samples, so it is considered that there is no protein in the urine. The appearance of protein in the urine is called proteinuria.
| Children under 1 month | absent |
| Children 2 – 12 months | absent |
| Children 1 year - 6 years | absent |
| Children 7 - 14 years old | absent |
| Children 15 - 18 years old | absent |
| Men | < 0,1 |
| Women | < 0,1 |
Interpretation
Physiological proteinuria includes cases of temporary appearance of protein in the urine that are not associated with diseases. Such proteinuria is possible in healthy people after eating a large amount of protein-rich food, after severe physical stress, emotional experiences, and epileptic seizures.
Functional proteinuria associated with hemodynamic stress can occur in children with fever, emotional stress, congestive heart failure or hypertension, or after cooling.
Pathological proteinuria is divided into renal (prerenal) and extrarenal (postrenal):
- Extrarenal proteinuria is caused by an admixture of protein secreted by the urinary tract and genitals; they are observed in cystitis, pyelitis, prostatitis, urethritis, vulvovaginitis. Such proteinuria rarely exceeds 1 g/l (except for cases of severe pyuria - detection of a large number of leukocytes in the urine).
- Renal proteinuria is most often associated with acute and chronic glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis, nephropathy in pregnancy, febrile conditions, severe chronic heart failure, renal amyloidosis, lipoid nephrosis, renal tuberculosis, hemorrhagic fevers, hemorrhagic vasculitis, hypertension.
False-positive results when using test strips can be caused by severe hematuria, increased density (more than 1.025) and pH (above 8.0) of urine.
Determination of glucose (sugar). Normal level of glucose in urine.
Also, urine normally contains traces of glucose not exceeding 0.02%, which, like protein, is not detected by ordinary qualitative tests.
| Children under 1 month | absent |
| Children 2 – 12 months | absent |
| Children 1 year - 6 years | absent |
| Children 7 - 14 years old | absent |
| Children 15 - 18 years old | absent |
| Men | 0 – 1,6 |
| Women | 0 – 1,6 |
Interpretation
The appearance of glucose in the urine (glucosuria) can be physiological and pathological.
- Physiological glucosuria is observed when eating large amounts of carbohydrates (alimentary glucosuria), after emotional stress (emotional glucosuria), after taking certain medications (caffeine, glucocorticoids), and in case of poisoning with morphine, chloroform, phosphorus.
- Pathological glucosuria can be of pancreatic origin (diabetes mellitus), thyroid (hyperthyroidism), pituitary (Ishchenko-Cushing syndrome), hepatic (bronze diabetes). To correctly assess glucosuria, it is necessary to determine the amount of sugar in daily urine, which is especially important in patients with diabetes.
Ketone bodies in urine
Ketone bodies (acetone, acetoacetic acid, (B-hydroxybutyric acid)) can sometimes be detected in the urine of a healthy person with a very small intake of carbohydrates and a large amount of fats and proteins.
| Children under 1 month | none |
| Children 2 – 12 months | none |
| Children 1 year - 6 years | none |
| Children 7 - 14 years old | none |
| Children 15 - 18 years old | none |
| Men | none |
| Women | none |
Interpretation
Ketone bodies appear in the urine during fasting, alcohol intoxication, diabetes mellitus, in children with vomiting and diarrhea, neuro-arthritic diathesis, as well as during severe infectious processes accompanied by a prolonged increase in temperature.
Preparing for analysis
From a technical point of view, the procedure for preparing for the study itself does not require any specific skills. However, to increase the objectivity and reliability of the results, doctors insist on compliance with the necessary conditions.
These simple rules include:
- The study of the enzyme is carried out after a twelve-hour break in food intake.
- Drinking any alcoholic beverages is unacceptable within 24 hours before urine collection.
- To ensure a stylish container for collecting biological material, it is advisable to wash it with baking soda, rinse thoroughly, pour boiling water over it or hold it over steam.
- Follow the rules for urine collection established in this laboratory. For some types of laboratory testing, the biological sample is delivered warm within two hours.
The reliability of the study may be affected by the patient's medication intake. The patient is obliged to warn about this in advance.
These include:
- Antibiotics from the tetracycline group: Doxycycline, Metacycline, Glycocycline, Morphocycline, Oletetrin, Olemorphocycline.
- Dosage forms that contain adrenaline: Brilocaine-adrenaline, Brilocaine-adrenaline forte, Xylocaine adrenaline, Xyloroland with adrenaline, Lidocaine-adrenaline.
- Analgesics with narcotic components: Buprenorphine, Lixir, Pentazocine, Butorphanol, Tramal, Delarin, Naloxone.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Salasat, Diflunisal, Diflofenac, Ketorolac, Sulindac, Indomethacin.
- Preparations using gold: Crizanol, Tauredon 50, Sodium aurothiomalate, Aurothioglucose.
Doctors include subjective factors that can distort the diagnostic picture of the study:
- Pregnancy at an early stage. In women, this circumstance can significantly affect the result of the examination. Therefore, the patient should warn the medical staff about this.
- Asthmatic attacks.
- Colds and diseases aggravated by various infections, with obvious symptoms - cough.
Knowing how to collect urine for diastase, you can be completely confident in the authenticity of the results obtained. To do this, remember the following recommendations:
- Do not drink alcoholic beverages for 24 hours before the test.
- When taking medications, ask your doctor if you can continue treatment or if it is better to stop it for a while. The fact is that some groups of drugs, as mentioned earlier, can significantly influence the results of studies.
- To collect urine, you must use either a sterilized glass jar or a special container, which can be purchased at almost every pharmacy.
- Before you start collecting urine, talk to your doctor. You may have to give your urine directly at the clinic.
Based on what urine diastasis is and what effect its level has on the functioning of all organs and systems in the human body, we can draw a clear conclusion: if you monitor your health and regularly undergo medical examinations just for prevention, you will not miss the moment development of severe pathology.
Decoding the analysis results
As mentioned above, diastase detected in urine is actually amylase, a corresponding important enzyme unit of the digestive apparatus, secreted by several localizations in the body. Its relative norms do not depend on the patient’s gender, but are directly related to the patient’s age.
The norm of diastase in urine in adults and children:
- Children under 1 year of age. Up to 10 units of the element per liter of urine;
- Children under 16 years of age. From 10 to 60 units of the element per liter of urine;
- Adults. From 10 to 124 units of element per liter of biomaterial.
It should be understood that the absence of the obtained result of the actual analysis for diastasis within the specified framework does not always indicate the presence of pathology or disease.
External circumstances, individual characteristics of the body and other circumstances can slightly or even moderately change the level of enzyme in the urine.
Urine color
The color of urine normally ranges from light yellow to deep yellow and is due to the pigments it contains (urochrome A, urochrome B, uroethrin, uroresin, etc.).
Reference values:
| Children | Various shades of yellow |
| Men | Various shades of yellow |
| Women | Various shades of yellow |
Interpretation
The intensity of the color of urine depends on the amount of urine excreted and its specific gravity. Rich yellow urine is usually concentrated, excreted in small quantities and has a high specific gravity. Very light urine is slightly concentrated, has a low specific gravity and is excreted in large quantities.
Discoloration may be the result of a pathological process in the urinary system, the effects of dietary components, or medications taken.
What is diastasis?
The enzyme alpha-amylase or diastase is produced by the pancreas, takes an active part in the functioning of the digestive organs and is involved in food processing. Amylase is part of pancreatic juice.
The process of carbohydrate breakdown occurs in the duodenum. Diastasis is within standard limits in the healthy body of any person.
If the main organ of the endocrine system does not have pathologies, then the concentration of amylase is at a constant level. Changes in diastase saturation indicate disorders in the body.
An increased degree of amylase is a consequence of pathology of the endocrine and digestive organs.
To measure the content of this enzyme, a coefficient per liter of blood is used.
The enzyme content index changes during different life periods. And the patient’s age is of great importance for the diagnostic result.
The standard values for the diastase enzyme in the male body and the standard levels for the enzyme in the female body are the same. The female body is resistant to pancreatic disorders.
Table of normative indicators of amylase in the blood during different life periods:
In women, while carrying a child, the diastase index does not change and corresponds to the coefficient that was before pregnancy. An increase or decrease in the enzyme indicates that there may be pathologies in the digestive organs.
There is also a fluctuation in amylase, which is temporary and occurs after the operation. The density of the enzyme in the blood can change after constant overeating.
The indicator in children should be within the corridor of up to 40 units/l. If the numbers reach an index of 100 units/l, then we can confidently talk about pathology in the body.
Amylase is one of several enzymes that are produced in the pancreas and are part of pancreatic juice.
Synonyms Russian
Urine diastasis, urine amylase.
English synonyms
Urine Amy, Urine Alpha-amylase, Urine AML, Urine diastase, Urine amylase.
Research method
Kinetic colorimetric method.
Units
Units/day (unit per day).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Daily urine.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Do not drink alcohol for 24 hours before the test, and do not drink diuretics for 2 days.
- Eliminate spicy, salty foods and foods that change the color of urine (for example, beets, carrots) from the diet 12 hours before the test.
- Avoid physical and emotional stress during the collection of daily urine (during the day).
General information about the study
Amylase is one of several enzymes that are produced in the pancreas and are part of pancreatic juice. Lipase breaks down fats, proteases break down proteins, and amylase breaks down carbohydrates. From the pancreas, pancreatic juice containing amylase passes through the pancreatic duct into the duodenum, where it helps digest food. The amylase molecule is so small that it can pass through the kidney barrier and then be excreted in the urine.
Normally, only a small amount of amylase circulates in the bloodstream (due to the renewal of salivary and pancreatic cells) and enters the urine. When damage to the pancreas occurs, as in pancreatitis, or if the pancreatic duct is blocked by a stone or tumor, amylase begins to enter the bloodstream in large quantities and then into the urine.
This enzyme is also secreted by the salivary glands, the ducts of which open into the oral cavity. Therefore, its activity in urine may increase with pathology of the salivary glands.
Small amounts of amylase are produced in the ovaries, intestines, bronchi and skeletal muscles.
What is the research used for?
- For the diagnosis of acute or chronic pancreatitis, as well as for identifying other diseases involving the pancreas in the pathological process. As a rule, urine amylase activity corresponds to blood amylase activity, but rises and falls with a delay of 6-10 hours in comparison. After acute pancreatitis, urine amylase activity may remain elevated for up to 7-10 days, in contrast to blood amylase, which usually returns to normal after 2-4 days.
- To monitor treatment for cancer affecting the pancreas.
- To determine the efficiency of the kidneys (compare the activity of amylase in the blood and urine).
When is the study scheduled?
- For symptoms of pancreatic pathology: intense pain in the abdomen and back (“girdling pain”),
- temperature rise,
- loss of appetite,
- vomiting.
What do the results mean?
Reference values: 1 - 408 U/day.
Reasons for increased amylase activity in urine
- Acute pancreatitis. In this disease, amylase activity can exceed the upper reference value by 6-10 times. Typically, its activity in urine increases 6-8 hours after damage to the pancreas and can remain at a high level for up to 2 weeks. However, in some patients with acute pancreatitis, amylase may increase slightly or even remain normal. In general, its activity does not reflect the severity of damage to the pancreas in this disease.
- Chronic pancreatitis. With it, the activity of urine amylase is initially moderately increased, but then it can decrease and return to normal as the damage to the pancreas worsens.
- Trauma to the pancreas.
- Pancreas cancer.
- Blockage (stone, scar) of the pancreatic duct.
- Acute appendicitis, peritonitis.
- Perforation (perforation) of a stomach ulcer.
- Decompensation of diabetes mellitus – diabetic ketoacidosis.
- Impaired drainage in the salivary glands or salivary ducts, such as with mumps (mumps).
- Surgery on the abdominal organs.
- Acute cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Aborted tubal pregnancy.
- Ruptured aortic aneurysm.
Reasons for decreased amylase activity in urine
- Pancreatic insufficiency, when its function decreases.
- Chronic renal failure.
- Severe hepatitis.
- Cystic fibrosis (cystic fibrosis) of the pancreas is a severe hereditary disease associated with damage to the exocrine glands (lungs, gastrointestinal tract).
- Removal of the pancreas.
- Macroamylasemia is a rare benign condition where amylase binds to large proteins in the serum and therefore cannot pass through the glomeruli.
What can influence the result?
- Urine amylase activity is increased in pregnant women.
- Captopril, corticosteroids, oral contraceptives, furosemide, ibuprofen, and narcotic analgesics can increase amylase activity.
Causes of increased levels of diastase
An increase in the level of diastase in urine is possible for the following pathological reasons:
- Pancreatitis in the acute stage. Most often, the level of diastase jumps sharply, up to 10 times;
- Chronic pancreatitis. The enzyme concentration increases quite smoothly, sometimes decreasing below normal by up to 1.5 times;
- Benign and malignant neoplasms. They are almost always formed in the pancreas. As a rule, these are cysts and cancerous tumors;
- Mumps. It is a common “children’s” infectious disease (although adults can also suffer from it, albeit in more severe forms in the absence of full systemic immunity and antibodies to the pathogen formed at an early age), in which the salivary and ear glands become actively inflamed. In some cases, further development of the pathology can lead to various complications, including meningitis;
- Diabetes. The amylase level increases quite quickly, but linearly, regardless of the type of metabolic disorder in the form of diabetes. The pathological condition is often accompanied by ketoacidosis and secondary complications;
- Peritonitis. Acute, life-threatening pathology of inflammation of internal organs is always accompanied by a significant increase in the concentration of amylase in the urine, and with lightning speed.
Factors exceeding the norm
Sometimes the diastase indicator goes beyond the normal range, which indicates the development of pathology:
- Pancreatitis. As a result of a violation of the secretory function of the pancreas, the quantitative and qualitative composition of gastric juice is destabilized, because of this there is an excess of the enzyme in the blood cells.
- A malignant formation in an organ that provokes an increased content of the enzyme.
- Movement of stones through the bile ducts due to cholelithiasis.
- Violation of the normal functionality of the renal structures (normally, diastase is excreted through the kidneys; in pathology, accumulation of the enzyme in the blood is observed).
- The inflammatory process in the peritoneal area significantly affects the amount of amylase, which accumulates in large quantities in the pancreas.
- The breakdown of carbohydrates in diabetes mellitus.
- When the parotid salivary gland becomes inflamed, it causes an increase in the level of diastase.
The results of diagnosing urine for diastasis may show serious pathology of the pancreas. Its timely identification will help to take measures to restore the normal functioning of the organ and prevent the unpleasant consequences of the problem. Seeking qualified help will allow the patient to lead a normal life, periodically undergoing the necessary diagnostic examinations.
Anatoly Shishigin
Reading time: 3 minutes
A A
Diastase, also known as lipase or amylase, are the main enzymes of the digestive system. Amylase promotes the natural breakdown of carbohydrates, and lipase carries out the same process with fats. Both amylase and lipase are produced by the pancreas. For this reason, urine analysis studies using these indicators help to identify deviations in the functioning of this organ. If diastasis in the urine is increased, the causes should be sought through additional studies of the whole organism, in particular the pancreas.
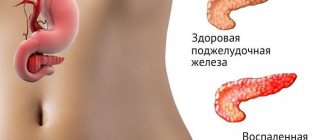
At the top of the peritoneal cavity is the pancreas, next to the stomach and intestinal region. It is connected to the intestine by a canal in its initial part, this zone is called the duodenum, and, in fact, is part of it, a continuation directed towards the liver from the left side to the right. The canal connecting the duodenum and pancreas carries enzymes from the pancreas to other organs.
What does the pancreas do?
The main functions of the pancreas are:
- synthesis of enzymes and enzymes that improve the process of food digestion. Fermentation reduces proteins, carbohydrates and fats in size, which facilitates their rapid absorption into the blood in the intestinal cavity. The purpose of enzymes is to accelerate metabolism;
- synthesis of hormones regulating metabolism. When moving with the bloodstream, hormones transmit signals from the brain to the organs, regulating the response depending on the purpose of the vital system.
Digestive enzymes are produced by acinar cells, which also produce gastric juice. Such conditions are essential for enzymes to function properly. There are three types among all the enzymes produced by the pancreas. Protease, which digests proteins, diastase, which breaks down carbohydrates into simple sugar, and lipase, which is responsible for the digestion of fats into fatty acids.
Protease is also often called thymoripsin and trypsin. With the coordinated work of these enzymes, all incoming fatty acids, simple sugars and other substances are easily absorbed in the small intestine.
Enzymes, the synthesis of which occurs in the pancreas, are under the control of the endocrine and nervous systems of the body. When food is ingested, electrical signals are sent through the nervous system to the pancreas. The acinar cells are activated, and enzymes begin to be released into the gastric juice, which passes through the duodenum through small passages.
Why are low levels of amylase found in urine?
The main pathological reasons for a decrease in the level of diastase compared to relative norms may include the following problems:
- Various forms of hepatitis , both infectious and non-infectious in nature;
- Renal failure at any stage (from mild to decompensatory);
- Malignant neoplasms in the pancreas or adjacent systems and organs, most often already metastases;
- Insufficiency of the pancreas, up to the stage of decompensation;
- Other diseases, pathologies, syndromes that directly or indirectly affect the level of enzyme in the urine.
What do deviations in the analysis indicate?
Although the content of this enzyme primarily gives the doctor information about the pancreas, the results of the analysis can partially judge the functioning of the kidneys or bladder. Sometimes there is a need to conduct additional tests to clarify the suspected diagnosis.
Low urine amylase levels
If amylase S levels are low, this indicates:
- liver cirrhosis;
- intoxication of the body for various reasons;
- chronic kidney disease.
High urine amylase levels
If the test reveals too high levels of the amylase P enzyme, this may indicate the following:
Other indicators for pancreatitis: what do they pay attention to?
Urine analysis for inflammation of the pancreas always shows elevated amylase results. In acute stages of the disease, daily monitoring is necessary. To do this, urine is collected from the patient every three hours. If he does not have the urge to urinate, then a catheter is used (especially in men). After receiving test data, treatment is prescribed or adjusted.
They may also refer the patient for duodenal intubation. But this diagnostic method is quite unpleasant and not every person agrees to do it. Another way to monitor the condition of the body is to collect venous blood for testing.
The appearance of urinary discharge during pancreatitis even visually helps to understand that the patient’s pancreas is impaired. They become dark, similar to the color of beer. Sometimes the shade becomes almost black.
Among other indicators, ketones are released in urine due to intoxication of the body. Acetone and hydroxybutyric acid are mainly diagnosed. Leukocytes and erythrocytes are also noted, and protein increases. If the urinary system is simultaneously affected, cellular elements from the renal tubules will be detected.
Treatment of abnormalities
Although the content of this substance in urine mainly provides information about the pancreas, an imbalance of this enzyme can be useful in studying the condition of other human organs and systems. Additional tests may be required to clarify the doctor's conclusions.
If the analysis shows that the amylase content in urine is not normal, you need to consult a doctor. So that he can determine the cause of the existing violations. Based on the diagnosis, the most effective treatment will be proposed.