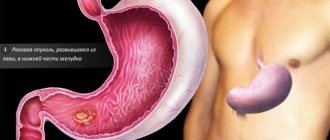
What is gastric neurosis? This is a gastric disease that is now becoming more common. It can appear in absolutely each of us. But it is more often observed, nevertheless, in young people against the background of mental and physical stress, some other neurosis, alcohol and nicotine abuse, with diseases of the intestines, stomach, and other organs.
In addition, this disease can be caused by:
• stressful situations;
• emotional stress;
• malnutrition;
• mental overstrain;
• general intoxication.
It leads to disruption of the stomach and general functional disorders, often associated with exhaustion of the nervous system.
Treatment of constant heaviness in the stomach and preventive measures
Heaviness in the stomach is an unpleasant sensation that occurs both due to poor nutrition and due to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
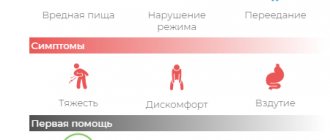
Quite often, the main cause of heaviness in the stomach after eating is the ingestion of a large amount of food, which is difficult for the stomach to “cope” with. There is only one solution in this case - consultation with a specialist. There is no point in self-medicating here. Uncontrolled use of pharmaceuticals can only worsen the situation. Reasons for feeling heaviness in the stomach:
- unhealthy diet (quick snacks, fast food, fatty and spicy foods);
- eating a large amount of food at one time;
- overeating (usually before bedtime);
- improper diet (eating once or twice a day);
- eating dishes consisting of foods that take a long time to digest or that are incompatible with each other;
- eating under stress;
- the presence of gastrointestinal diseases (gastritis, pancreatitis, peptic ulcer and cholelithiasis).
As for the feeling of heaviness in the stomach during pregnancy, the reasons are somewhat different. Read about them further.
2. Reasons
The range of reasons for foreign objects entering the stomach is also very wide. Most often, foreign bodies (buttons, pins, fruit pits, beans, small toys, coins, etc.) are swallowed by small children during play, out of pranks, or simply by accident. As for adults, accidental ingestion is typical for workers whose profession involves constant contact with small parts or fasteners, provoking the bad habit of holding these parts in their teeth (needles, screws, insulating material, etc.). Sometimes there are cases of swallowing too large pieces of food (for example, a piece of meat with a large bone inside), which usually results from hasty “eating on the run.” Separate, and quite extensive, categories of victims are formed by mentally ill people who, in a psychotic state or for delusional reasons, can sometimes swallow a large number of different objects, or manage to swallow surprisingly large objects; persons in a state of alcoholic intoxication (in whom foreign bodies enter the stomach “on a dare”, out of drunken recklessness or without any clear motive at all); elderly and senile people, especially with senile or vascular dementia, parkinsonian syndrome, atrophic pathology of the central nervous system; patients with epilepsy; people who lost consciousness, were shocked by sudden news or fell into a semi-fainting state while eating or putting on dentures; suicides, swallowing nails, glass fragments, etc. for suicidal purposes.
In all of these cases, the foreign body penetrates the esophagus and stomach in the most expected way: through the pharynx. However, there are also situations when a foreign or, rather, an object inaccessible to enzymatic decomposition is formed in the body itself - such as, for example, gallstones in gallstone disease (penetrating into the stomach through a cholecystogastric fistula) or gastric bezoar stones, which can reach significant and even gigantic sizes.
Finally, traumatic penetration of foreign bodies into the stomach from the outside is relatively rare (in peacetime) - with open thoracic or abdominal trauma, explosions, road accidents, industrial accidents, as well as during surgical operations (the notorious “forgotten scalpel inside”, packing material and so on.).
Visit our Gastroenterology page
Symptoms of heaviness in the stomach after eating
Heaviness in the stomach, with the complete exclusion of gastrointestinal diseases, can occur only in two cases: improper diet and low-quality products.
If a person consumes a large amount of food at a time and eats one or two times a day, then this feeling will occur quite often. The explanation here is simple - it is difficult for the body to cope with such food portions and it begins to work in increased mode. In this case, the food is not digested properly, which will ultimately lead to the occurrence of one or another gastric disease.
Heartburn and bloating are symptoms that also indicate low-quality products. Quite often, clinical manifestations are accompanied by pain in the right hypochondrium. In both cases, there is only one way out - to review the diet and adjust the diet.
Belching and nausea after eating
Nausea, belching and stomach pain can be symptoms of diseases such as cholecystitis, gastritis or pancreatitis. In addition, a person may experience pain in the right side and sometimes vomiting. Many gastrointestinal diseases have similar symptoms, which only a specialist can understand. Therefore, you should not take risks; entrust the treatment of constant heaviness in the stomach to a doctor, who, after the necessary research, will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
On our website https://www.dobrobut.com/ you can familiarize yourself with the list of services provided and the qualifications of specialists.
Heaviness in the stomach after the holidays
Fatty and spicy foods, an abundance of fried foods, alcohol - all this stimulates the secretion of acid, which is part of the gastric juice. It is this that causes irritation of the mucous membrane, and as a result, heaviness in the stomach. If there are motor skills disorders, then heartburn will also be added to the unpleasant sensations. So how to get rid of heaviness in the stomach and what can be done at home?
Experts recommend having a fasting day and allowing the gastrointestinal tract to “catch its breath.” There is no point in going hungry. Treat your digestive system with oatmeal, vegetable salad, or light broth with crackers. Recommended drinks include compotes, fruit drinks and herbal teas without sugar.
4.Treatment
According to existing statistics, 85-95% of cases of a foreign body in the stomach are resolved naturally: the object is excreted during bowel movements. However, in some cases, when there is a threat of perforation of the walls of the stomach or intestines, constant monitoring of the migration of the object along the digestive tract is necessary.
If there is a foreign object in the esophagus, emergency endoscopic intervention is indicated due to the high risk of developing life-threatening complications. A foreign body in the stomach, as can be seen from the above, does not always create such indications, however, if there is reason to believe that the endoscope will quickly and safely eliminate the threat, special replaceable manipulators are used, and with a probability of over 95% the problem is eliminated.
Finally, in the most severe and complicated cases, the only choice is emergency surgery; if possible, it is performed by laparoscopic access, but often it is necessary to undergo open abdominal surgery, which is sometimes technically very complex, labor-intensive, risky and requires the highest qualifications from all members of the complex surgical team.
Feeling of heaviness in the stomach during pregnancy
Almost all women carrying a baby complain about this symptom. So why does a pregnant woman feel heaviness in her stomach? The first reason is the growing fetus, which puts a little pressure on the stomach, thereby causing an unpleasant symptom. Secondly, there is toxicosis in the early stages and intra-abdominal pressure in the later stages. It is these two factors that contribute to the appearance of such an unpleasant sensation. In addition, heaviness can also occur with the accumulation of gases in the intestines. If such symptoms occur, you should consult a specialist who will advise what to do if there is severe heaviness in the stomach.
Therapeutic measures
Therapy is prescribed by a doctor after a comprehensive examination of the patient and is carried out under his strict supervision. During the treatment process, the specialist can make adjustments, taking into account the condition and individual characteristics of the patient. General recommendations in this matter are as follows: avoiding fatty and spicy foods, normalizing your diet and limiting alcoholic and carbonated drinks. You should eat fractionally and in small portions. Fast food and quick snacks on the go are not recommended. You should also pay attention to the psychological state. If you have difficulty breathing due to heaviness in your stomach, seek help from a specialist and under no circumstances self-medicate!
1.General information
A foreign body in the stomach is a situation that is periodically encountered first by emergency doctors, then, as a rule, by radiologists, and then, if the problem does not resolve spontaneously, by gastroenterological surgeons.
Such situations can vary in degree of difficulty: from anecdotal (“Save me, doctor, I swallowed a button!”) to very serious and life-threatening (when, for example, there is a suspicion or certainty that a child has swallowed something sharp, or when a foreign body contains highly toxic compounds, or in principle cannot be evacuated naturally).
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Prevention
Paying attention to your health and following the following recommendations will help you avoid the feeling of heaviness in your stomach. So, preventive measures include:
Follow the recommendations and stay healthy.
Related services: Family doctor consultation Videogastroduodenoscopy
Gastroparesis - delayed bowel movements of the stomach
05.11.2021
Chronic retention of gastric - gastroparesis. Symptoms most often include nausea and vomiting, feeling quickly full or even full after eating, upper abdominal and gas . What are the causes of gastroparesis and how to treat it?
Gastroparesis - what is it?
Gastroparesis is a condition in which gastric is delayed and is not caused by any mechanical obstruction. Food accumulates in the stomach and stretches its walls. The most common causes are idiopathic gastroparesis (of unclear origin, possibly related to infection with certain viruses) and diabetic gastroparesis (a neurological complication of chronic diabetes ). Less commonly, it can occur as a result of surgery , Parkinson's disease , systemic scleroderma, certain medications, systemic lupus erythematosus, amyloidosis, paraneoplastic syndromes, and others.
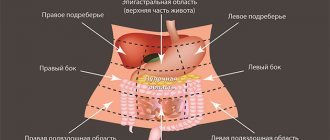
How does the stomach work?
The stomach is not a particularly exotic organ. Located in the upper part of the abdominal cavity and slightly to the left of center, it connects above to the esophagus and below to the duodenum, that is, the first segment of the small intestine. In the stomach , food is crushed, mixed, partially digested and moved on. Under proper conditions, the stomach effectively moves its contents to other parts of the intestine . This process can be disrupted by any obstacles in the area of the pylorus (this is the part of the stomach that connects it to the duodenum), for example, a tumor or disturbances in the autonomic innervation of the stomach .
Gastroparesis - symptoms
Gastroparesis is a delay in gastric . Thus, the symptoms are associated with food residues in the stomach . Most often this leads to nausea and vomiting. Feeling full quickly and feeling full after eating is also typical. This may be accompanied by abdominal , flatulence, or frequent belching . In extreme cases, significant weight loss, malnutrition, and dehydration can occur.
Gastroparesis - diagnosis
Worrying symptoms prompt a specialized examination. An endoscopic examination is performed to exclude mechanical causes of delayed gastric . Laboratory test results are also important.
There are several methods for assessing gastric . Most often, scintigraphy is performed - the patient is given food labeled with a technetium isotope, in order to then assess the speed of movement of the food further. If necessary, other tests such as ultrasound , x-ray , manometry or magnetic resonance imaging are also performed.
If a patient has been treated for diabetes for many years, it is most likely diabetic gastroparesis. However, the symptoms themselves are the same as with gastroparesis of other origins, so a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s condition is important. Interestingly, the degree of distress shown in the study often does not correlate with the severity and persistence of symptoms experienced by the patient.
Gastroparesis - how is it treated?
If gastroparesis is the cause of your symptoms, you can try to relieve your symptoms with a proper diet . First of all, try to eat smaller portions. Eat slowly and chew thoroughly. Avoid high-fat foods (fat also slows stomach under the right conditions), and limit your intake of fiber, alcohol and tobacco. Remember that even in healthy people, liquids and finely ground foods leave the stomach faster than larger food particles. So it might be worth mixing up some dishes.
Sometimes prokinetic drugs (which support intestinal ) taken before meals, such as erythromycin, domperidone or itopride, may be helpful. Pharmacological treatment of nausea and vomiting is based on the use of drugs from different groups, for example, ondansetron or thiethylperazine. They relieve symptoms but do not speed up gastric .
If you suffer from severe gastroparesis , whose symptoms include weight loss and malnutrition, more invasive treatment may be required. Options would include, for example, targeting the pylorus (botulinum toxin injection, special incisions, or balloon expansion) or electrically activating the stomach using a device implanted under the skin. If, on the other hand, you cannot meet your body's needs with regular oral intake, other feeding methods are used, such as enteral (which bypasses the pylorus) or parenteral, that is, intravenous. For diabetic gastroparesis, remember that good diabetes and proper blood .
Published in Gastroentorology Premium Clinic